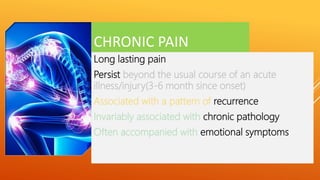
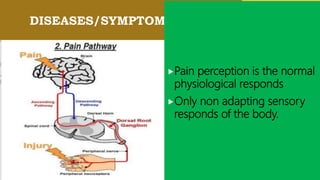
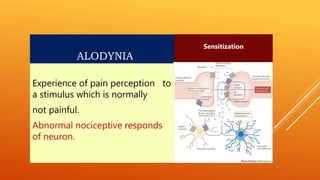
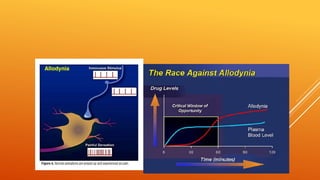
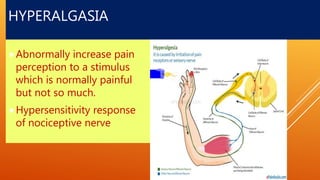
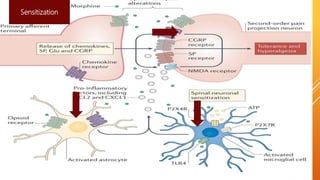
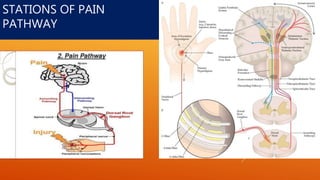
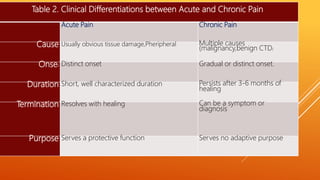
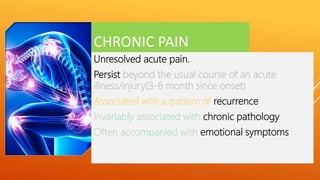
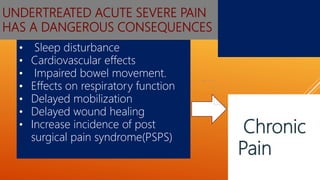
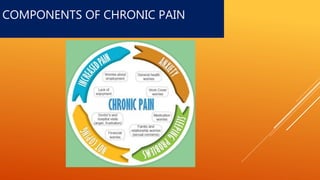
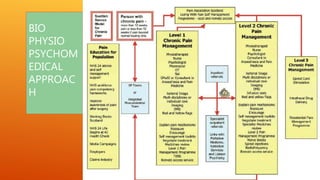
This document discusses chronic pain management strategies and tips. It notes that chronic pain is a major healthcare problem worldwide, accounting for one third of total healthcare costs. Chronic pain is defined as pain that persists beyond 3-6 months from the onset of an illness or injury and is often accompanied by emotional symptoms. Undertreated acute pain can lead to chronic pain through physiological and psychological effects. Effective chronic pain management requires a biopsychosocial approach including treating the underlying medical condition, addressing precipitating psychosocial factors, and using multimodal treatment including medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes.