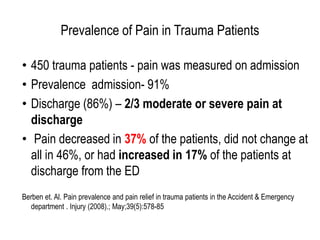
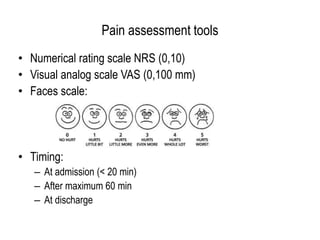
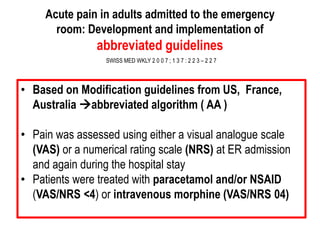
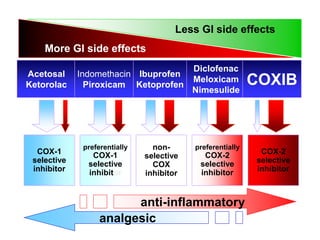
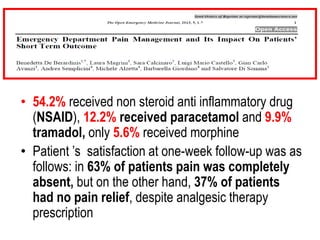
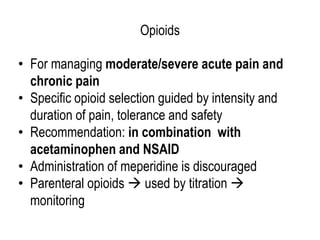
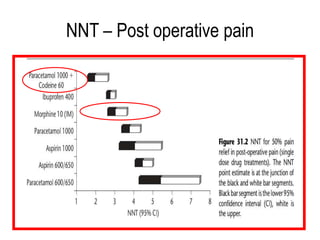
The document details the prevalence and management of acute pain in emergency settings, highlighting that a significant percentage of patients experience moderate to severe pain upon discharge, often without adequate analgesia. Key barriers to effective pain management include underassessment of pain, lack of management guidelines, and concerns regarding opioid use. Recommendations include improved pain assessment protocols, the development of clinical guidelines, and better physician-patient communication to enhance pain management outcomes.