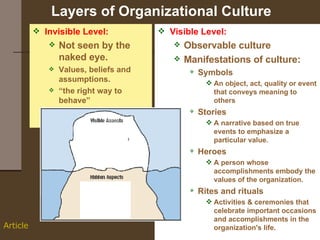
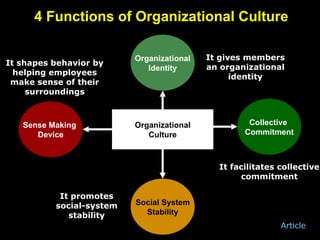
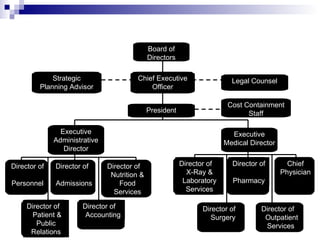
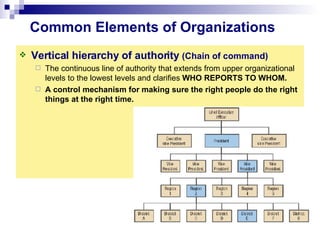
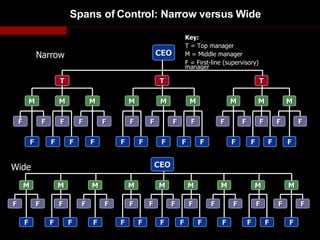
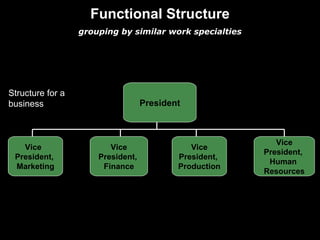
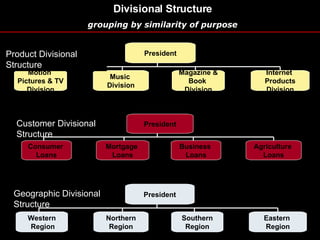
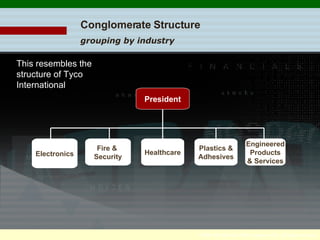
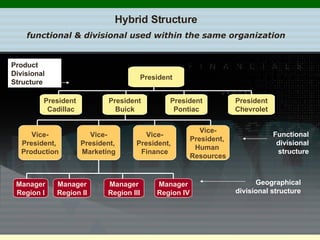
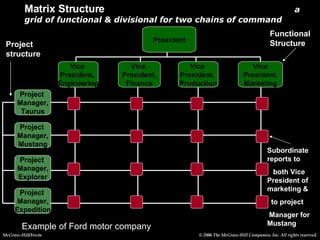
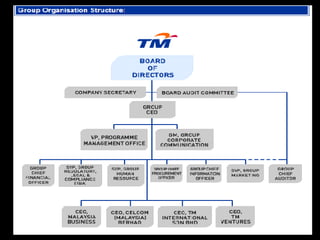
Organizational culture is a system of shared beliefs and values that guides member behavior. It has visible and invisible levels. The visible level includes symbols, stories, heroes, and rituals while the invisible level includes underlying values and assumptions. Organizational culture serves four main functions - sense making, collective commitment, shaping behavior, and promoting stability. Common elements of organizations include a common purpose, coordinated effort through division of labor, a vertical hierarchy of authority, span of control, and centralized or decentralized decision making. There are several types of organizational structures including functional, divisional, matrix, and hybrid structures.