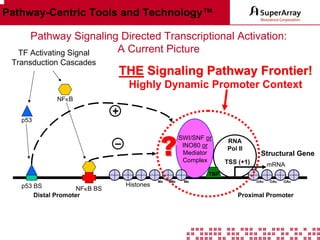
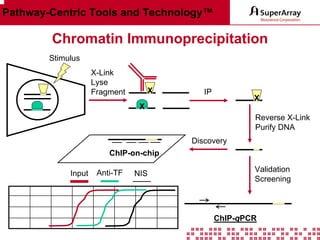
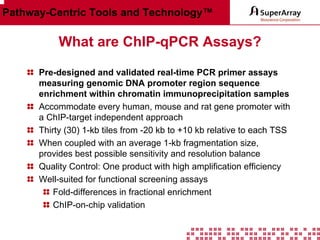
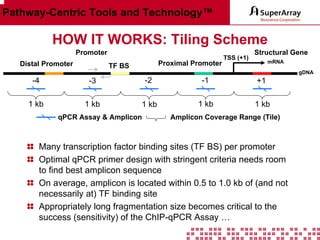
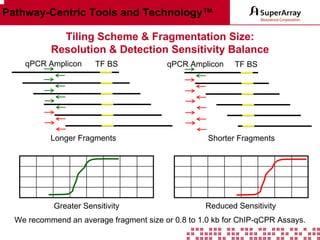
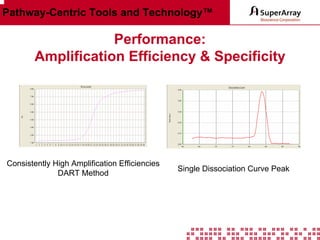
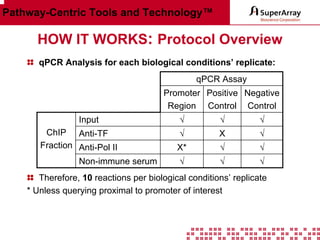
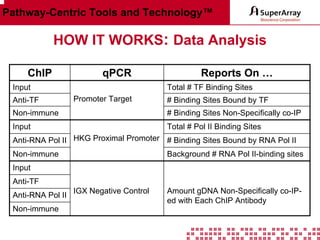
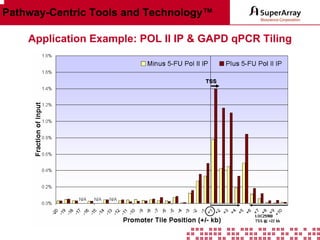
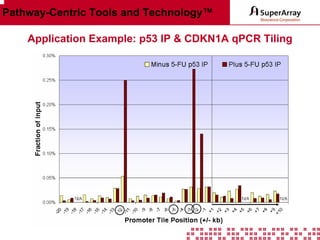
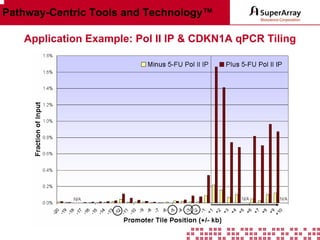
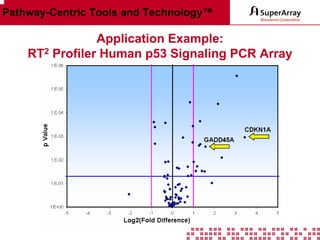
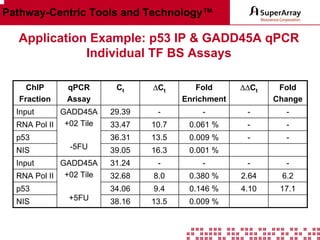
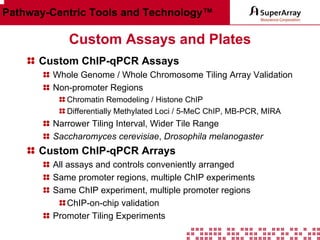
The ChIP-qPCR assays provide pre-designed and validated real-time PCR primer assays that measure genomic DNA enrichment within chromatin immunoprecipitation samples. They save researchers time and money by eliminating the need to design their own assays. The assays provide quick, easy, and quantitative analysis of multiple promoter regions from a single ChIP sample using real-time PCR, addressing challenges of traditional ChIP workflows. The assays offer comprehensive coverage of human, mouse, and rat genomes and can be customized, allowing researchers to expand their ChIP experiments.