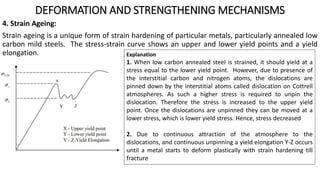
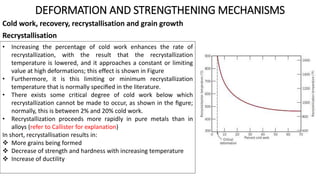
Metallic materials can undergo elastic or plastic deformation when stressed. Plastic deformation is permanent and corresponds to the movement of dislocations on an atomic scale. Several mechanisms can strengthen materials by impeding dislocation movement, such as grain refinement, solid solution strengthening, and strain hardening. Grain refinement strengthens materials by introducing more grain boundaries that act as barriers to dislocation motion. Solid solution strengthening occurs when alloying elements are added, which impose lattice strains and interact with dislocations. Strain hardening makes metals stronger through plastic deformation, which increases dislocation density and hinders their movement.