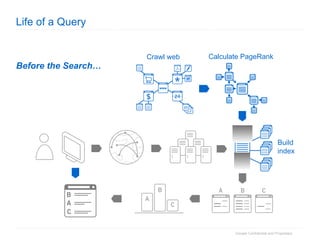
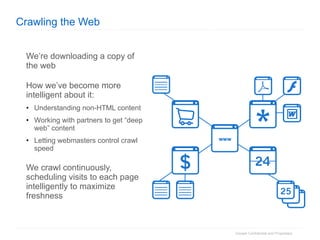
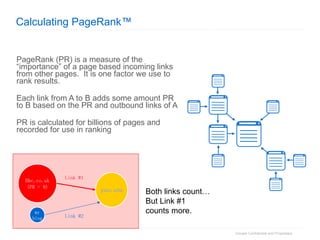
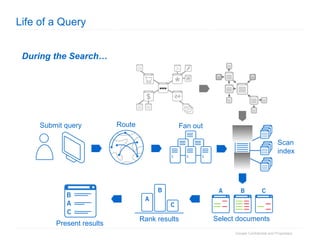
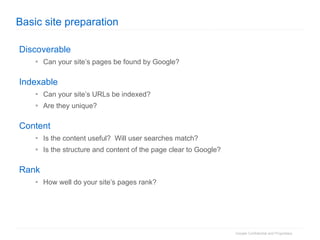
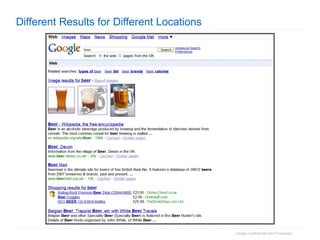
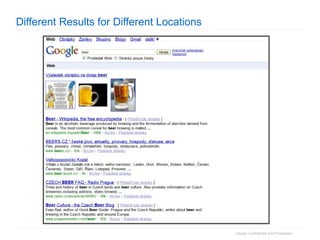
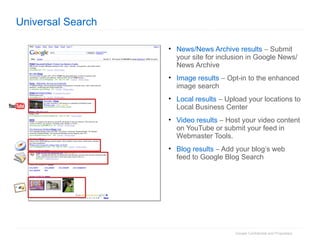
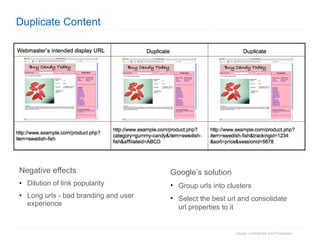
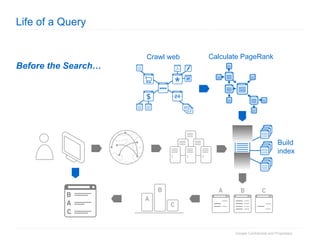
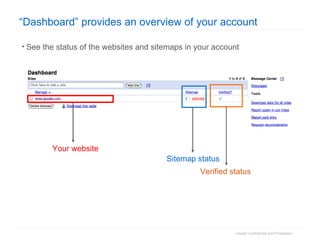
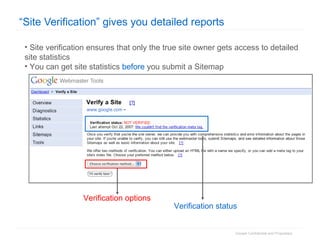
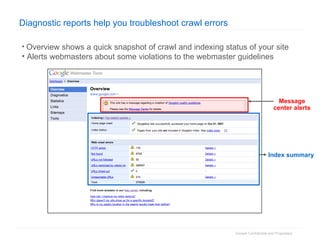
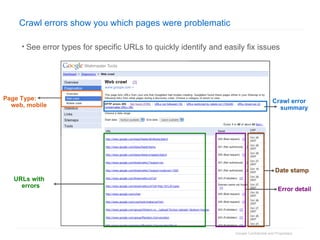
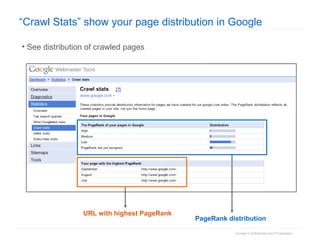
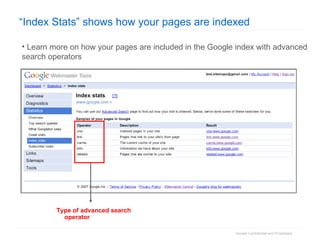
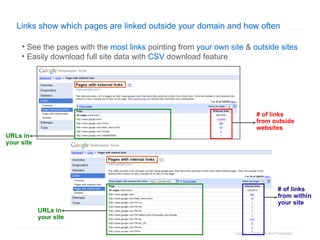
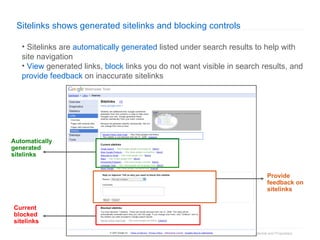
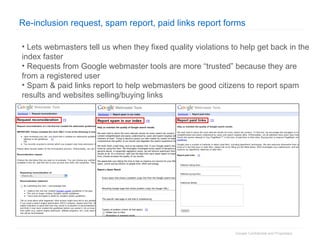
1. The document provides an overview of how Google Search works and guidelines for site owners to ensure their content is discoverable, indexable, and ranks well. It discusses Google's crawling, indexing, and ranking processes.
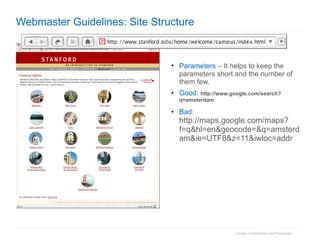
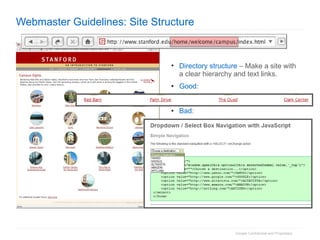
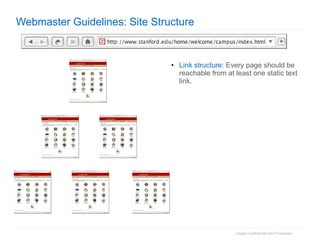
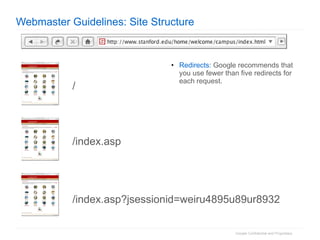
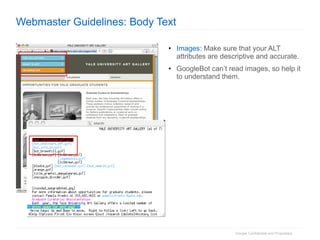
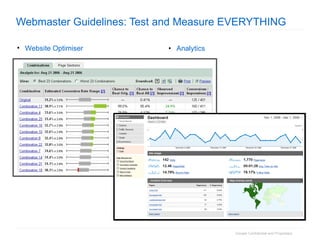
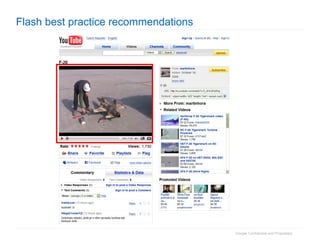
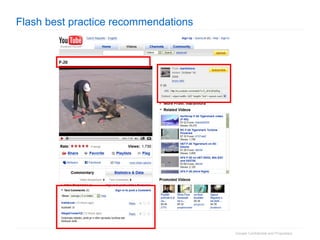
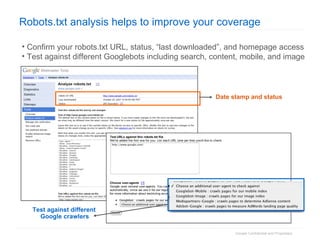
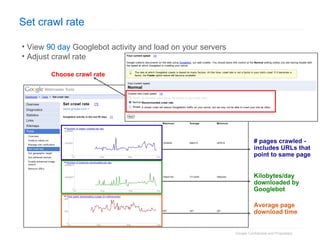
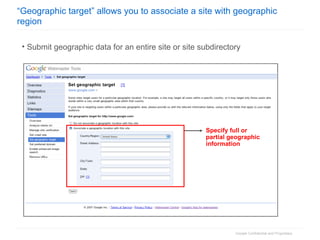
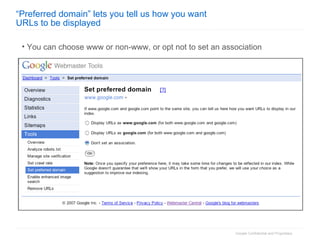
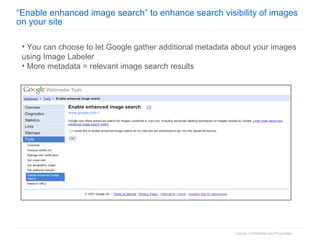
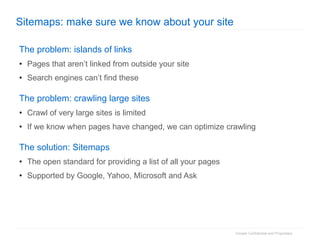
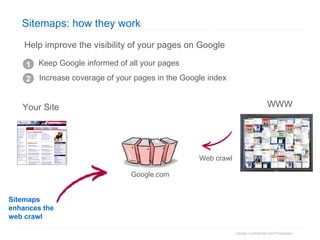
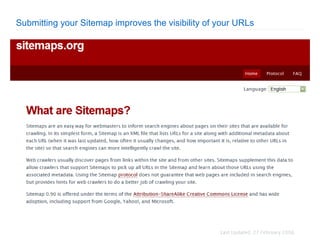
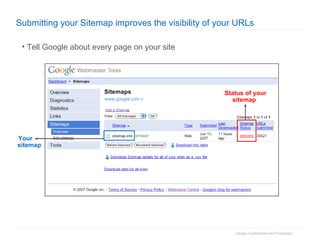
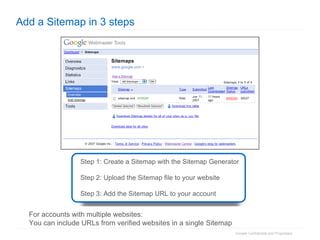
2. The document then outlines Google's Webmaster Guidelines covering site structure, titles, snippets, text, and use of technologies like Flash. It recommends testing sites using analytics and submitting sitemaps to help Google find all pages.
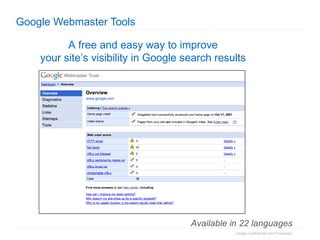
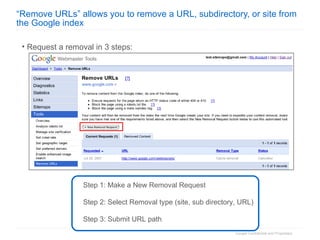
3. The document concludes by summarizing the discussion and providing resources for webmasters to engage with Google through its Webmaster Tools and get support on search visibility.