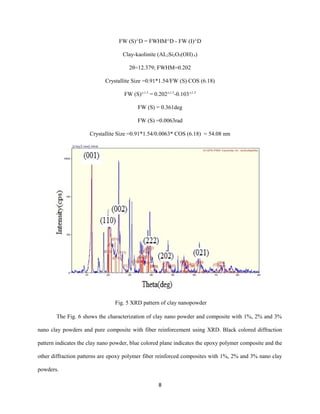
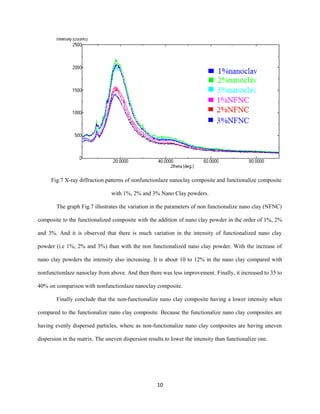
This document summarizes a study on the structural properties and characterization of clay-based hybrid nanocomposites. Glass-epoxy composites were fabricated with halloysite nanotubular clay particles using hand lay-up technique. The composites containing 1%, 2%, and 3% halloysite nanoclay by weight were characterized using X-ray diffraction. XRD analysis showed that the intensity of diffraction peaks increased with higher nanoclay content, indicating improved dispersion of clay particles in the matrix. Pin-on-disk wear tests found that composite with 2% nanoclay exhibited the lowest wear rate, as clay particles improved the mechanical properties and wear resistance of the epoxy polymer matrix.
![SOME STUDIES ON STRUCTURAL PROPERTIES AND CHARACTRIZATION
ISSUES OF CLAY BASED HYBRID NANOCOMPOSITES
ABSTRACT:
The hybrid composite of glass-epoxy is fabricated by the use of halloysite nanotubular particles
by hand lay-up technique. Actually the direction of nano-clay particles may lead to agglomeration, to
overcome this problem, the epoxy is need to be chemically treated. The chemical reaction of unsaturated
polyester with the epoxy resin was carried out thermally in presence of benzyl peroxide-radical initiator
and the resulting product was analyzed by X-Ray Diffractometer. Epoxy and unsaturated polyester
toughened epoxy systems were further modified with 1, 2 and 3% (by wt) of Halloysite nano tubular
(HNT) clay. Mainly this paper deals with the characterization and wear properties of epoxy polymer and
glass fiber-reinforced epoxy-clay hybrid composites. Characterization is done with the help of X-Ray
Diffraction and performance levels of the composite at different percentage of nano clay addition are
observed. Under this wear test have been conducted in the Pin-on-disc type at different loads and time for
different percentage composition of nano clay particles addition and respective changes are studied.
Keywords: Halloysite nano clay, polymer-clay nanocomposite, X-ray diffraction, pin-on-disk.
1. Introduction
Epoxy resin is a versatile and widely accepted matrix material for the fabrication of advanced
composites, hardware components, electronic circuit board materials, radomes and missile equipment
components because of its excellent bonding, physico-chemical, thermal, mechanical, dielectric and aging
characteristics [1–7]. The inorganic hallow site nano tubes (HNT) clay has been used as reinforcement
material for number of polymers due to their nanoscale size and intercalation behaviors [8]. The HNT
clay is modified with cetyltrimethylammonium ions to facilitate its interaction with polymer matrix and
1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projects1-161208015353/85/chemistry-final-year-1-320.jpg)
![become organophilic. Fictionalization of the clay surface by ion exchange method is made with cationic
surfactants which lowers the surface energy of the clay and increases the compatibility between the clay
surface and polymer matrix.
Hence, the addition of organophilic HNT clay into epoxy resin helps to recover the impact
strength and thermal stability lost due to the absence of rigid chemical modifier like bismaleimide. The
modified organophilic HNT clay reinforced epoxy nanocomposites exhibit significant improvements in
thermal and mechanical properties like high temperature durability, enhanced barrier properties, reduced
flammability and other characteristics [9].
Recently, organic-inorganic nanocomposites have attracted attention. Their remarkable properties
and unique structure have led to the synthesis and study of a variety of hybrid composite materials [10].
The intercalation of inorganic materials by organic guest species is a way to construct an ordered organic-
inorganic assembly [11].
Epoxy resins are the preferred matrix material since they possess better mechanical and thermal
properties. Further, they wet many substrate materials, absorb less moisture. The other advantages worth
mentioning are that they possess excellent chemical resistance coupled with good electrical properties
[12]. The wear of polymeric composites with different reinforcements has been the topic of investigation
in recent times [13]. When particles added to polymers have proven to be effective in reducing the
coefficient of friction and wear rate of composites. The use of SiC as a filler material is known to improve
the mechanical and tribological properties of metal–matrix composites [14]. When the filler has a
nanometer thickness and a high aspect ratio (30–1000) plate-like structure, it is classified as a layered
nanomaterial (such as an organosilicate) [15]. In general, nanomaterials provide reinforcing efficiency
because of their high aspect ratios [16].
The properties of a nanocomposite are greatly influenced by the size of its component phases and
the degree of mixing between the two phases. Depending on the nature of the components used (layered
silicate or nanofiber, cation exchange capacity and polymer matrix) and the method of preparation,
significant differences in composite properties can be obtained [17].
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projects1-161208015353/85/chemistry-final-year-2-320.jpg)
![X-ray diffraction technique (XRD), which determines the d001 spacing in the modified clay and
provides information on the degree of hybrid structure generated [16].
Wide angle X-ray diffraction measurements were accomplished using Rigaku D/MAX-2000 X-ray
diffractometer with Cu Kα radiation (λ = 0.154nm) and a scanning rate of 1°/min. Bragg’s law, λ =
2dsinθ, was used to calculate the crystallographic spacing “d” [17].
To characterization of clay studied by X-ray diffraction The layer silicates observed in the
untreated clay Sialupe (39/80) are mica, kaolinite and 14 Å layer silicates, mainly chlorite. Amphiboles
and feldspars are also present. Already after heating to 300°C, the typical kaolinite peak is diminished in
intensity, after heating to 400°C only traces of it are left. Kaolinite is supposed to transform to
metakaolinite shortly below 450°C , but in the present case may do so at lower temperatures due to the
long duration of the heating [18 and 19].
Tribology is a science that deals with design, friction, wear and lubricating surfaces in relative
motion [20]. Polymer nanocomposites based on layered nano clays have attracted a great deal of interest
because they exhibit remarkable improvement of physical properties when compared with those of pure
polymer or conventional composites. These improvements include high modulus, increased strength,
toughness, heat resistance and fire retardancy, and decreased gas permeability. Three main types of
structures can be obtained when layered clay is associated with a polymer: (і) a phase-separated structure,
(іі) an intercalated structure and (ііі) an exfoliated or delaminated structure (iv) achieves pure
nanocomposites [21]. For tribological loaded components, the coefficient of friction, the mechanical load
carrying capacity, and the wear rate of the materials determine their acceptability for industrial
applications. Polymer based composite materials are employed in tribological applications owing to their
ever increasing demand in terms of stability at higher loads, temperatures, better lubrication and wear
properties [22 and 23].
The effect of clay addition improves the mechanical properties of epoxy polymer and glass fiber-
reinforced epoxy-clay hybrid composites. The clays used in the present system were alkyl ammonium
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projects1-161208015353/85/chemistry-final-year-3-320.jpg)
![treated montmorillonite (MMT) based organoclay (OC) and unmodified MMT clay (UC). The addition of
OC increases the thermal properties of epoxy-glass fiber more than that of UC filled hybrids [24].
In the present paper discussed with the effects of Halloysite Nano clay particles as fillers in
glass–epoxy composite systems on the characterization and tribological properties have been discussed in
the present investigation. The composites employed in the study have been fabricated using hand lay-up
technique. This work deals with the Nanocomposites with 1%, 2% and 3% nanoclay powder and epoxy
polymer (matrix phase) are characterized by using X-Ray diffraction technique. The phases present in the
composite are identified by X-Ray diffractometer and crystallite sizes are calculated by Scherer formula.
The diffraction patterns of 1%, 2% and 3% nanoclay composites are compared, and effect of clay addition
on improving the mechanical properties of epoxy polymer and glass fiber-reinforced epoxy-clay hybrid
composites. The effect of variants in sliding speed, time and applied load on the wear behavior of
polymer nanocomposites is studied by measuring the wear rate. Sliding speed, time and loads in the range
of 640-1000 RPM, 300-900 sec and 5-25 N respectively were used in the experiments with wear test pin
having flat face in contact with hardening rotating steel disc. It is observed that wear rate increases with
the increasing applied load, time and sliding speeds.
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/projects1-161208015353/85/chemistry-final-year-4-320.jpg)