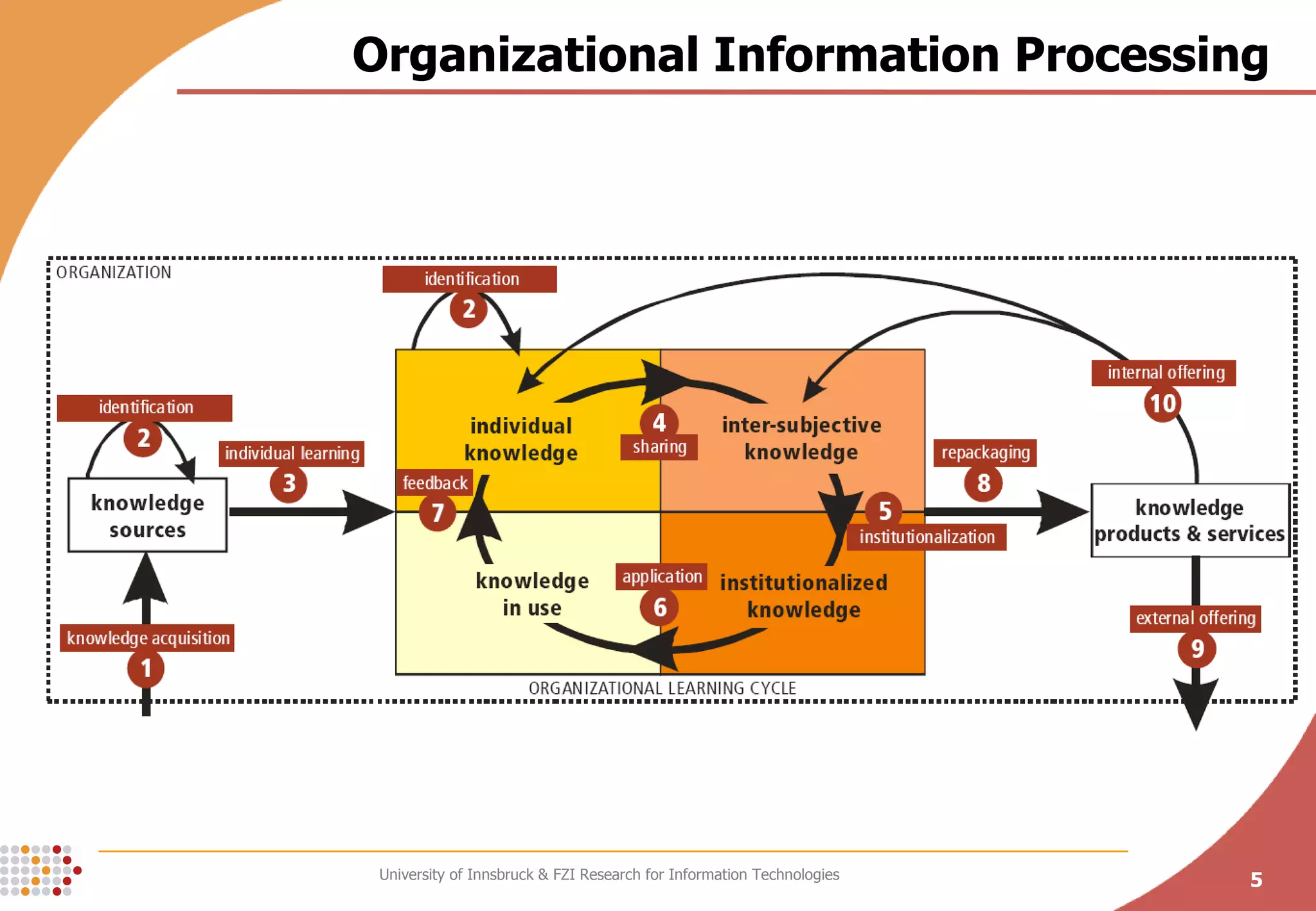
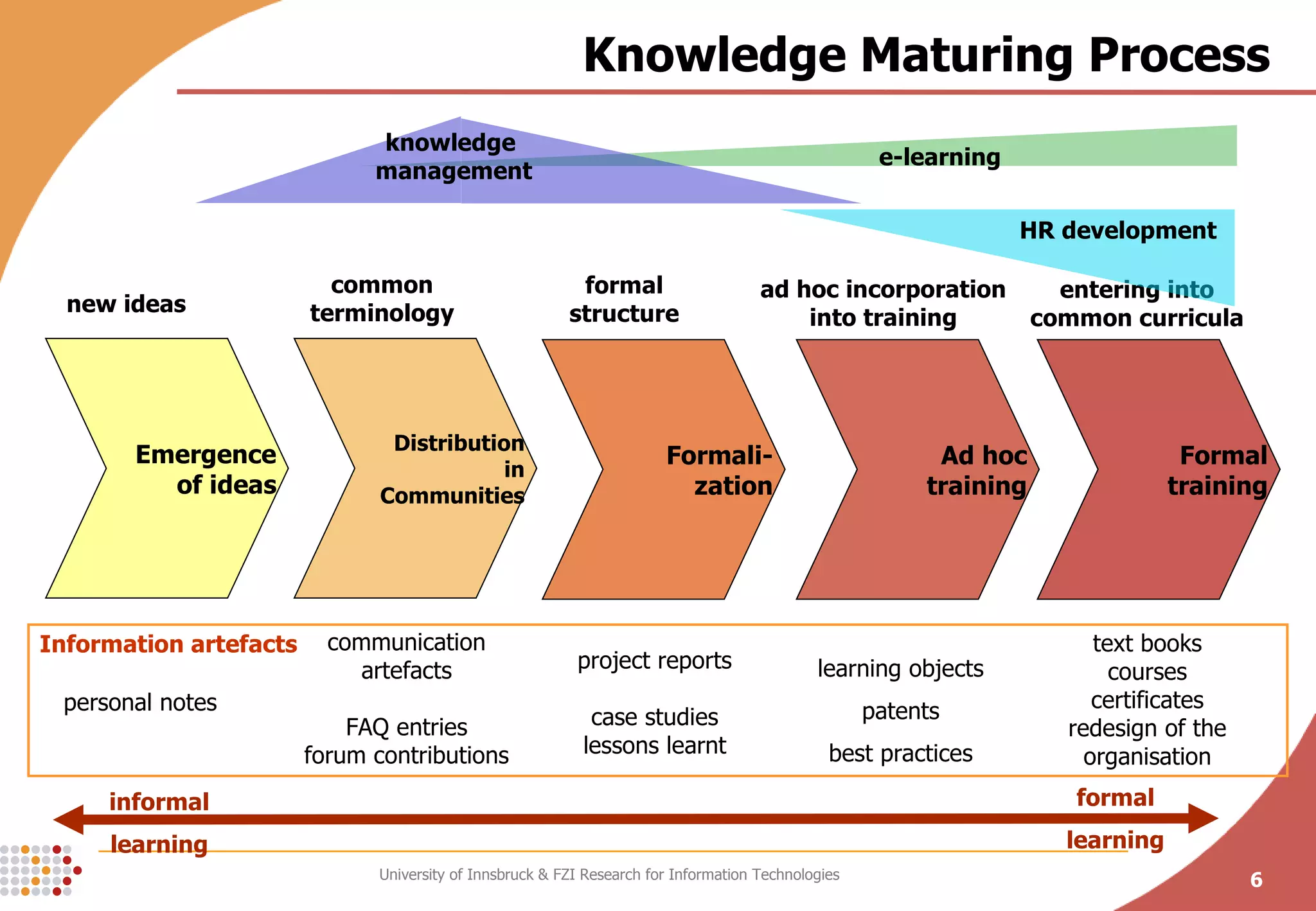
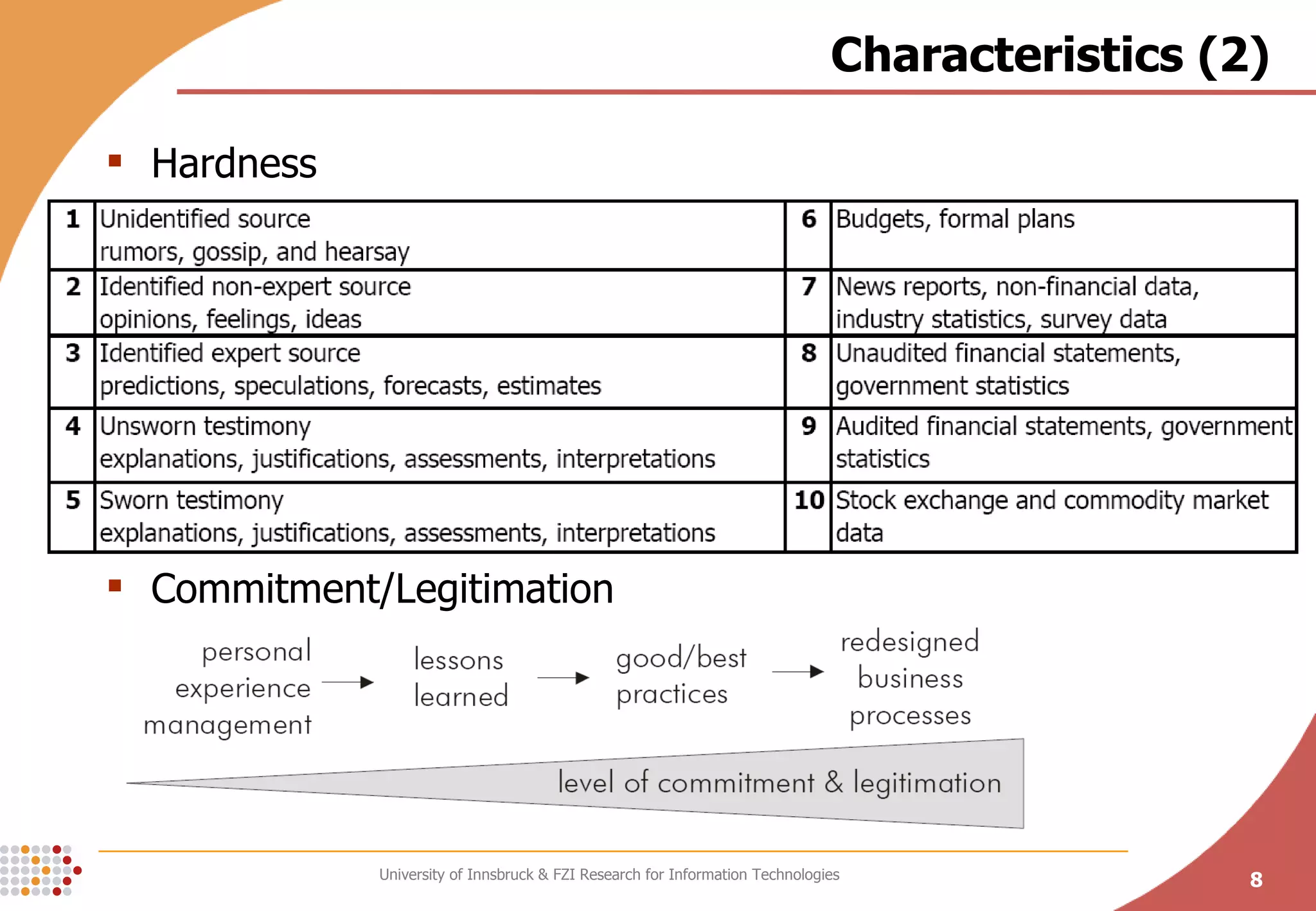
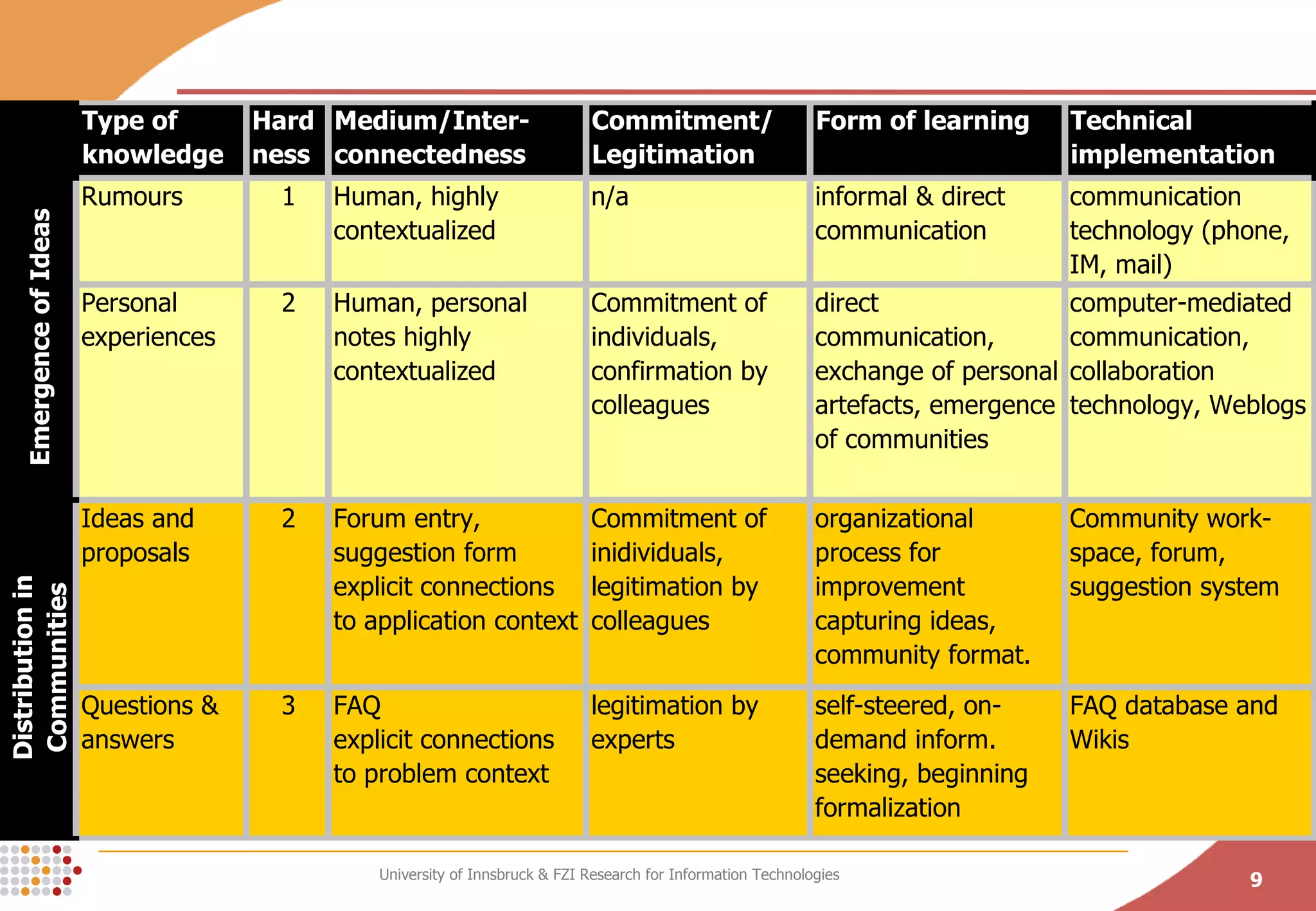
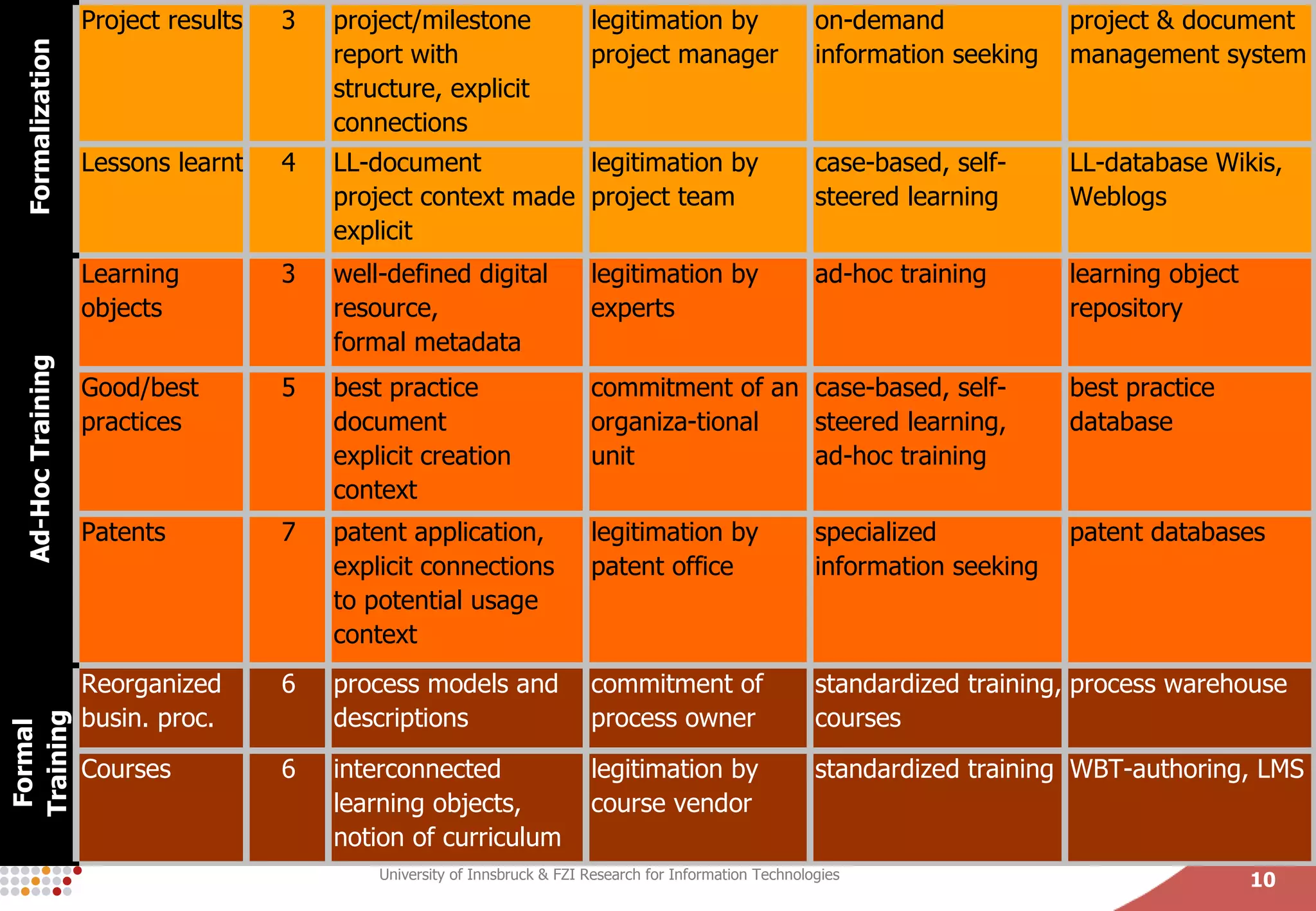
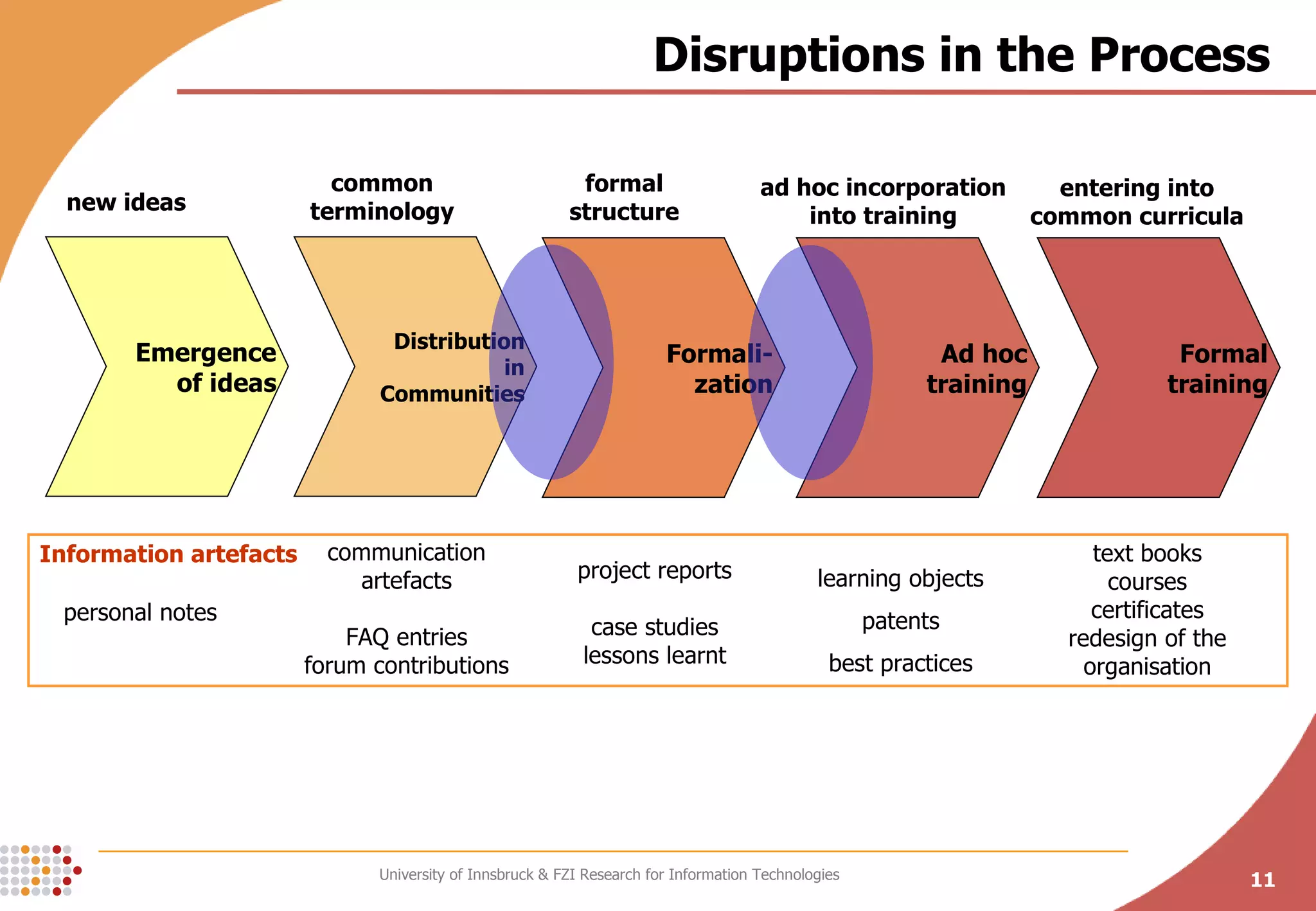
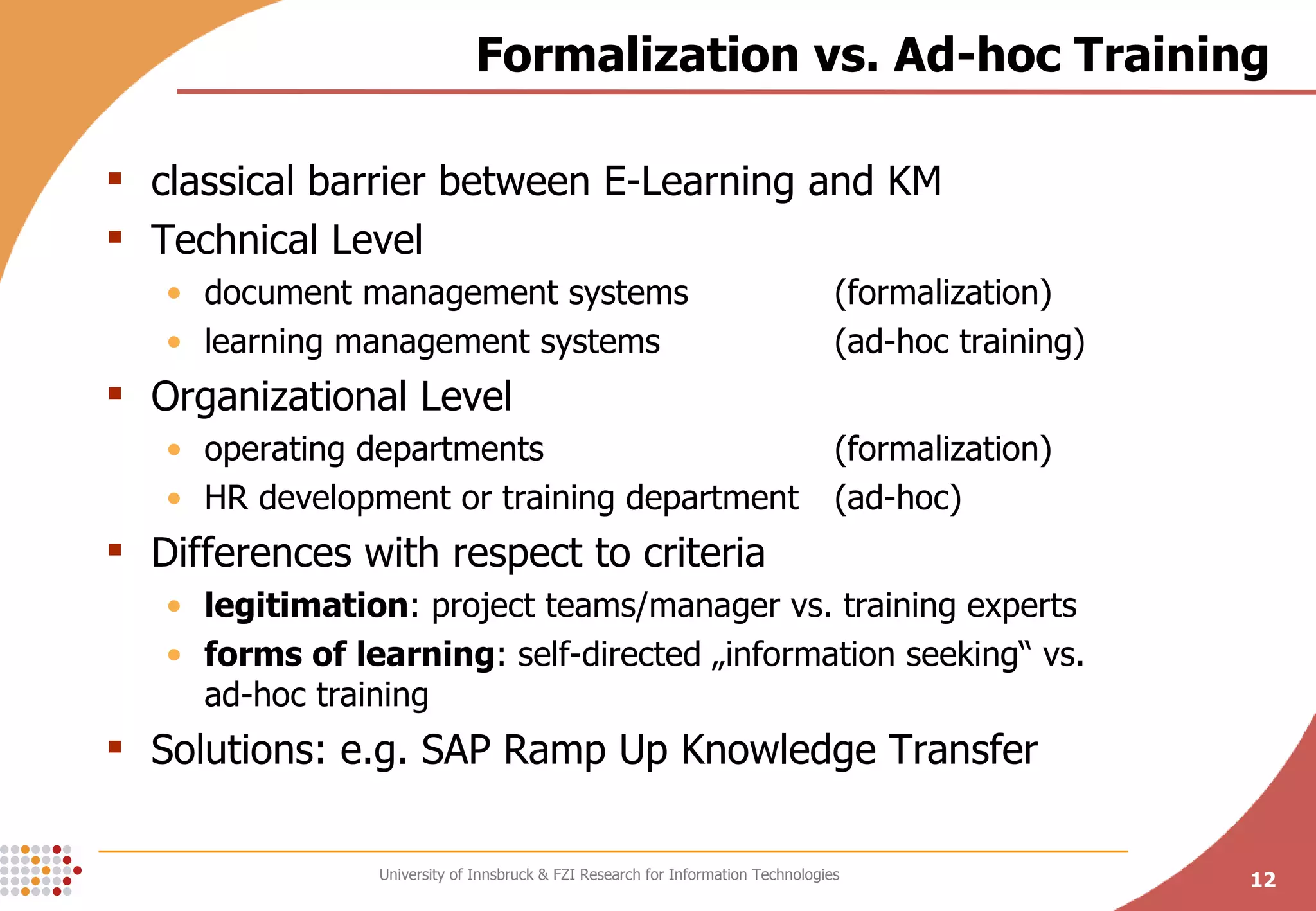
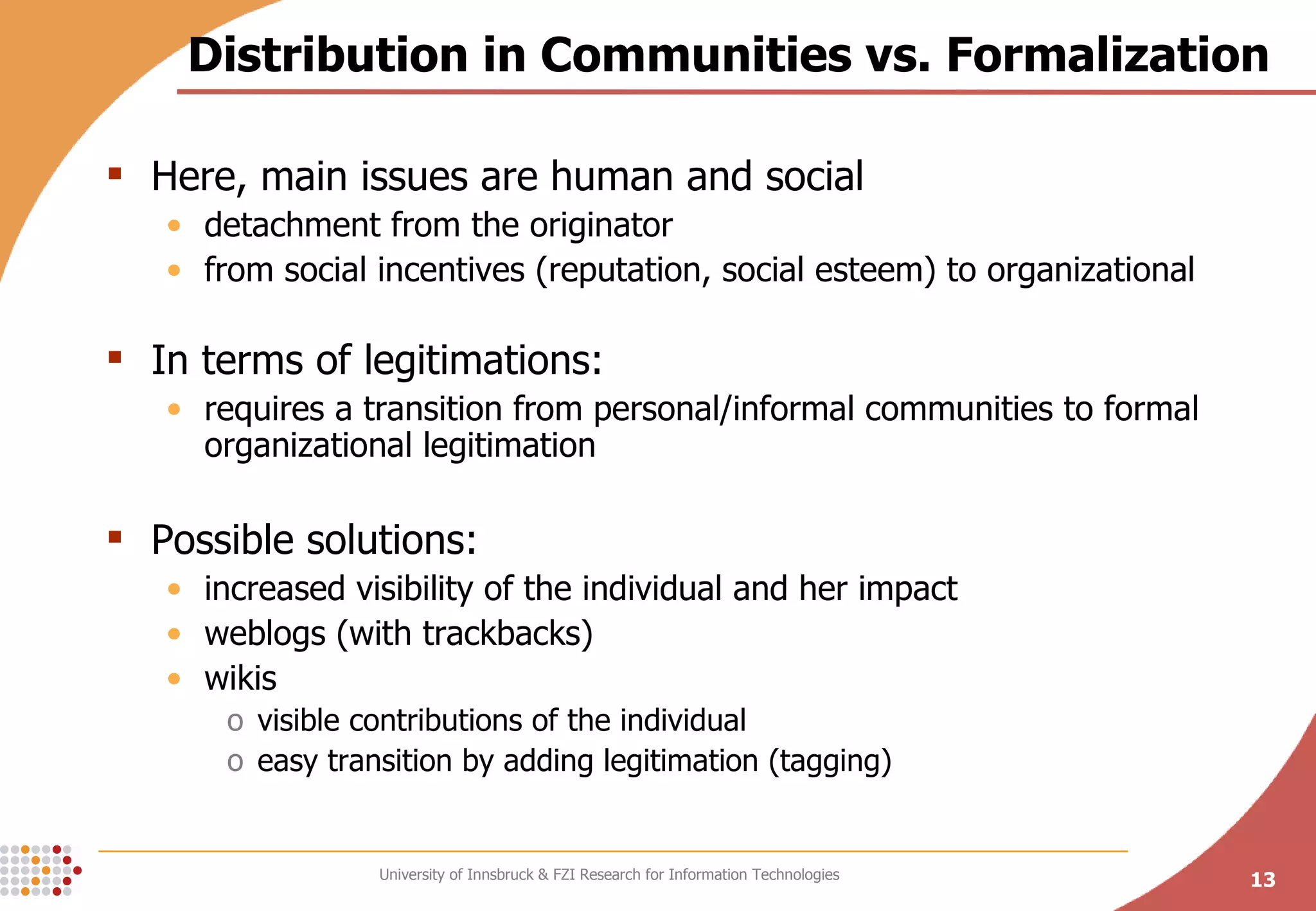
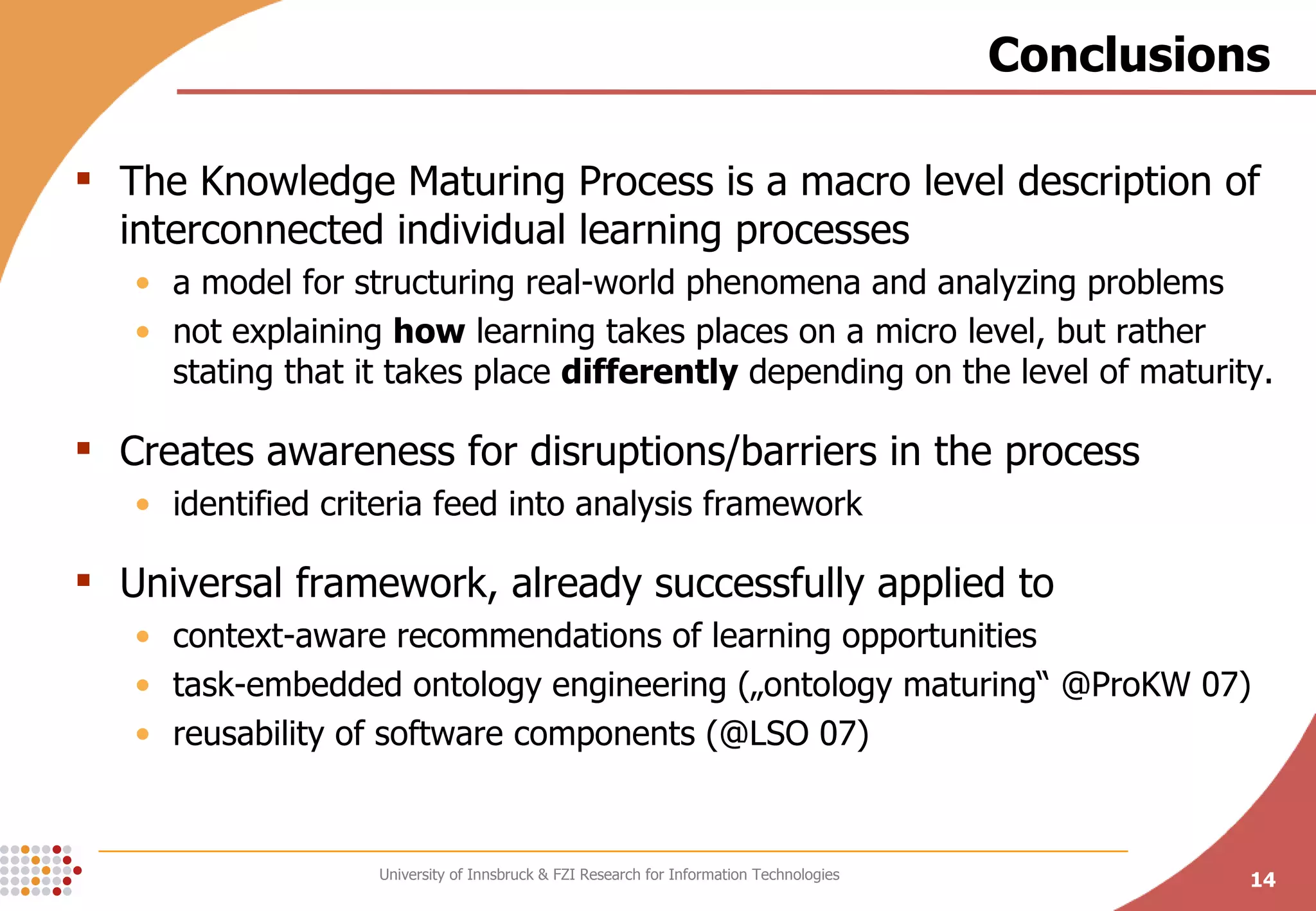
The document presents a conceptual process model called the Knowledge Maturing Process for integrating e-learning and knowledge management. The model characterizes knowledge as progressing through three phases - emergence of ideas, distribution in communities, and formalization. It identifies criteria for characterizing the different phases and discusses potential disruptions between phases, such as between formal training and ad-hoc training or between distribution in communities and formalization. The goal of the model is to provide a framework for analyzing problems in knowledge flow within organizations.
![Characterizing Knowledge Maturing: A Conceptual Process Model for Integrating E-Learning and Knowledge Management 2 University of Innsbruck School of Management Information Systems [email_address] http://iwi.uibk.ac.at/ 2 FZI Research Center for Information Technologies Information Process Engineering Karlsruhe, GERMANY [email_address] http://www.fzi.de/ipe Ronald Maier 1 Andreas Schmidt 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/characterizing-knowledge-maturing-a-conceptual-process-model-integrating-elearning-and-knowledge-management-6455/75/Characterizing-Knowledge-Maturing-A-Conceptual-Process-Model-Integrating-E-Learning-and-Knowledge-Management-1-2048.jpg)