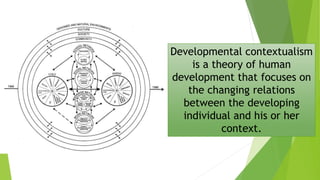
This chapter discusses various perspectives on human development including learning paradigms, socio-cultural theories, ethology-evolutionary and socio-biological approaches, and systems approaches. Learning paradigms focus on interaction with the environment through conditioning, reward/punishment, and observation. Socio-cultural theories emphasize the influence of culture and social interaction. Ethology-evolutionary perspectives account for genetics and adaptation. Systems approaches view human development as resulting from the interaction of nature, nurture, and environmental contexts.