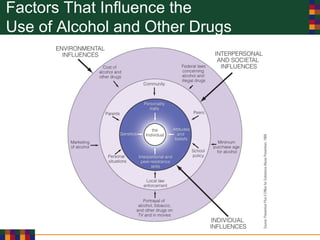
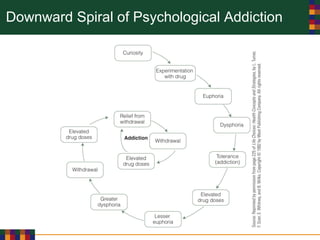
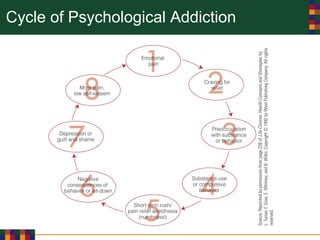
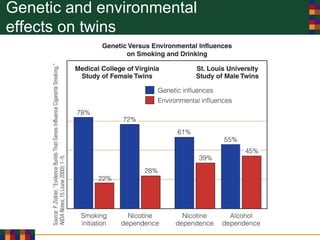
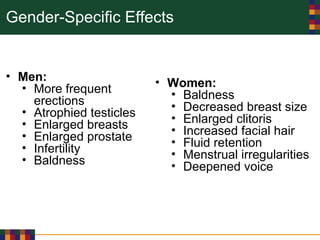
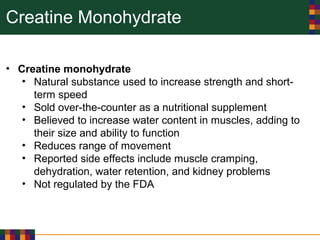
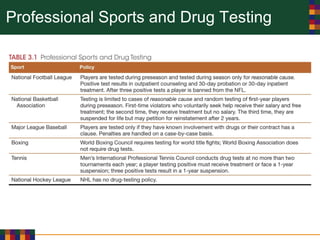
This document discusses various reasons why people use drugs, including experimentation, pleasure-seeking, peer influence, spiritual purposes, and rebelliousness. It also covers the differences between drug dependency and addiction, and discusses several theories for why drug addiction occurs, such as genetic predisposition, personality traits, reinforcement, and social/cultural factors. Finally, it examines the use of performance-enhancing drugs in sports and their associated health risks.