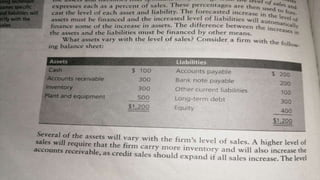
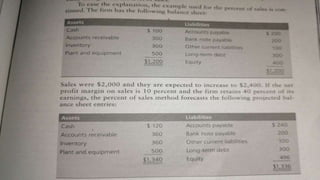
- Management creates strategic plans with goals for the firm that are then executed through operational, marketing, and financial plans. Financial plans must forecast future external financing needs to fit within the strategic goals.
- Some assets like accounts receivable and inventory automatically increase with sales, while others like plant and equipment may require additional investment when capacity is reached from sales growth.
- Forecasting techniques like percentage of sales or regression analysis are used to project future asset and liability levels as sales change, helping identify future financial requirements. This allows creation of projected balance sheets and planning for future external financing needs.