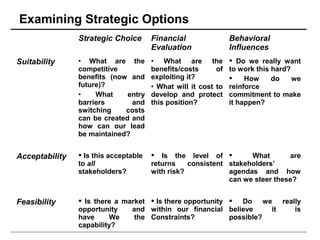
Strategic Financial Management (SFM) examines how strategic and financial analysis can be integrated to create practical value. SFM looks at links between corporate strategy and financial management, managing for value, strategic management accounting, strategic and financial planning, and key applications like strategic investment decisions and acquisitions. Implementing SFM requires analyzing the links between strategy and finance, examining strategic options through both strategic choice and financial evaluation, and aligning organizational structure, resource allocation, and change management with strategic goals and financial performance.