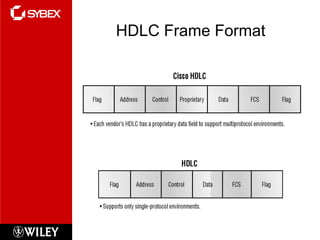
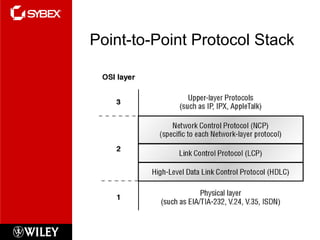
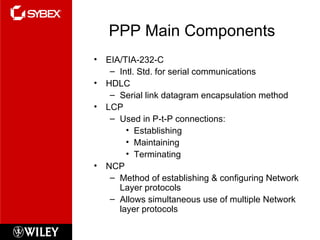
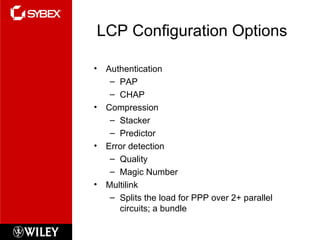
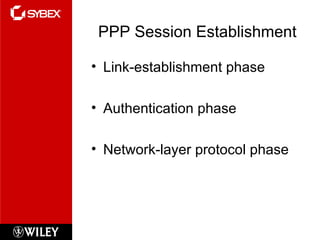
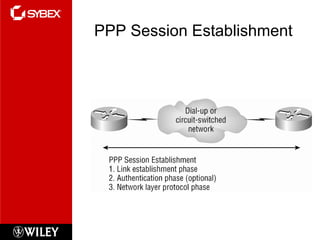
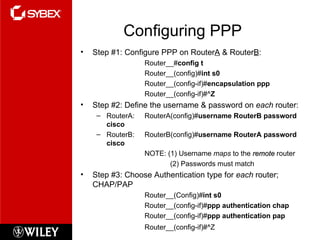
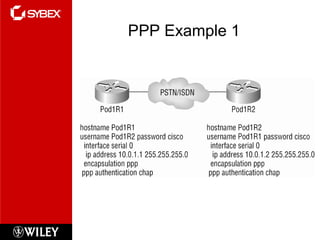
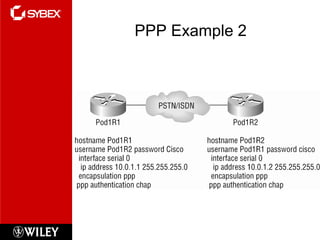
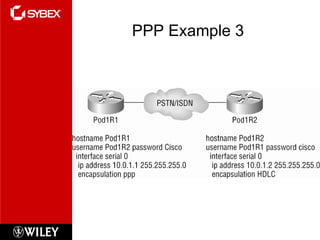
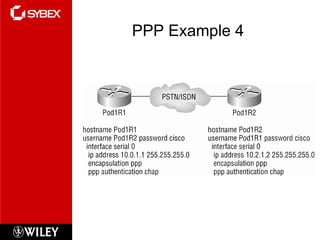
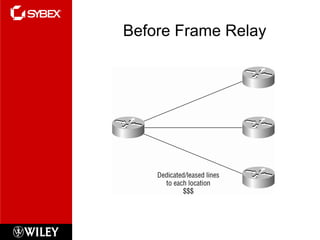
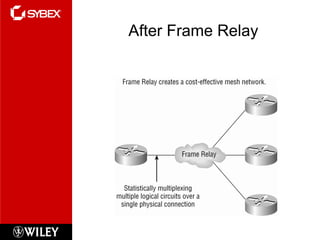
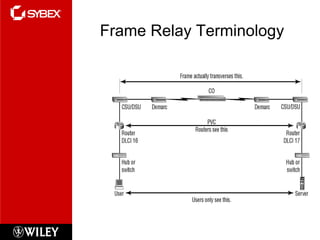
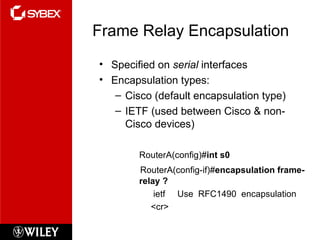
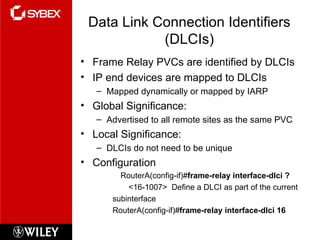
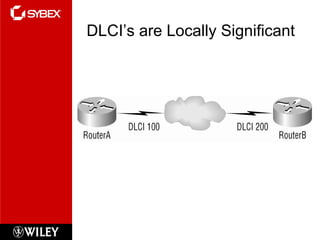
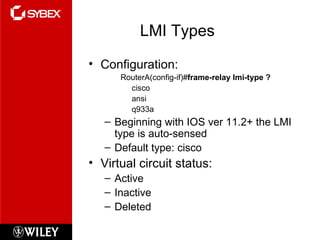
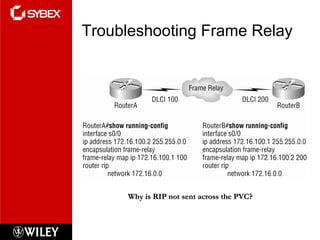
This chapter discusses wide area network (WAN) technologies including HDLC, PPP, Frame Relay, and virtual private networks (VPNs). It defines WAN terminology and components. PPP is described as a protocol used to transport layer 3 packets across point-to-point links. Frame Relay is introduced as a high-performance WAN encapsulation method that provides a connection-oriented data link layer. VPNs allow remote access, site-to-site, and extranet connectivity over public networks like the internet.