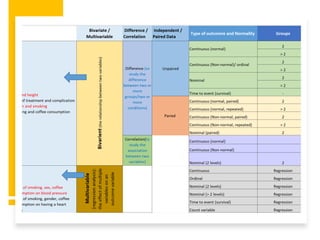
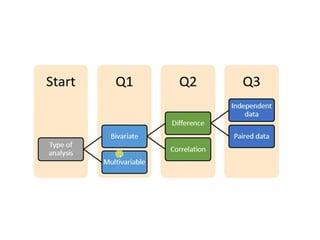
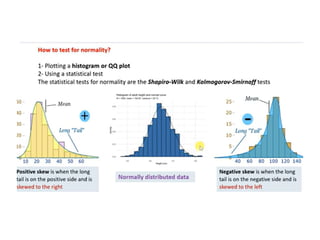
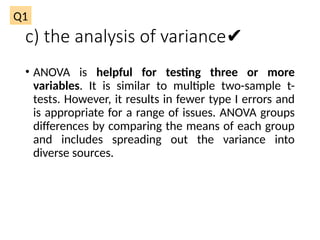
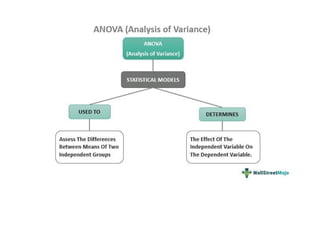
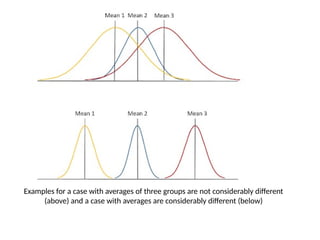
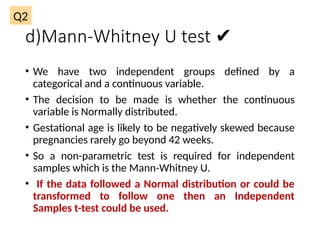
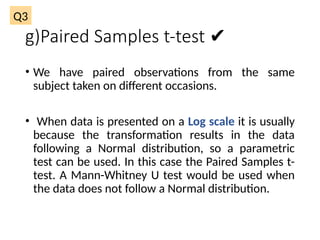
The document outlines various statistical techniques for analyzing independent and paired samples, including applications of ANOVA, Mann-Whitney U test, paired samples t-test, and correlations. It details how to choose appropriate tests based on the distribution of data and relationships between variables, specifically giving guidance on scenarios involving gestational age, anxiety levels, and nutritional supplements. Additionally, it explains the rationale behind using specific tests depending on whether the data is normally distributed or not.