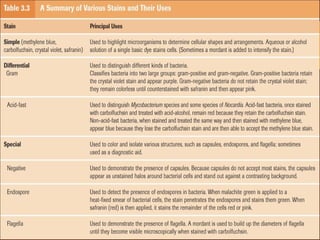
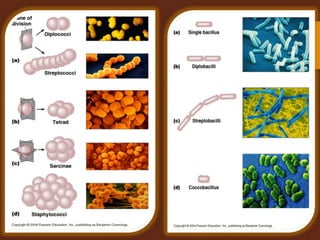
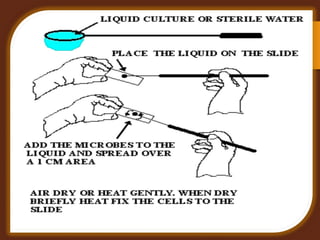
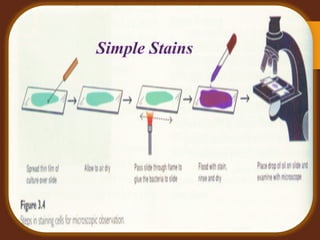
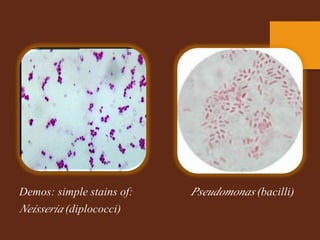
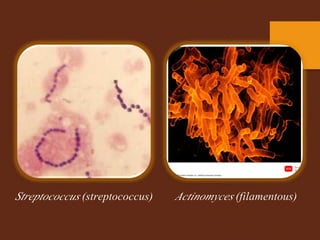
Staining is a crucial technique in microbiology that enhances the visibility of bacterial cells and their structures for observation under a microscope. Different stains, composed of chromogen and auxochrome, have specific affinities for various cell components, allowing categorization of bacteria based on morphology and structure. The process involves preparing a bacterial smear, heat-fixing, and applying stains like basic or acidic dyes to differentiate cellular features.