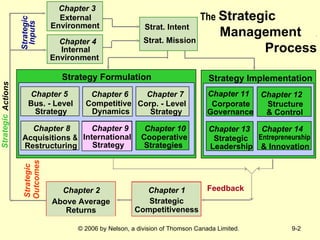
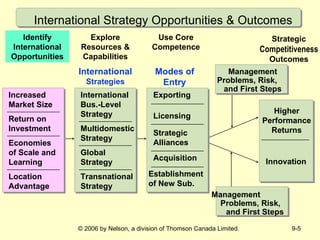
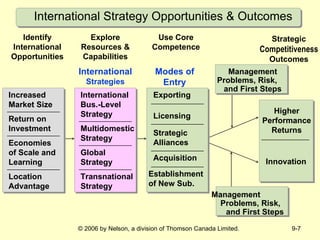
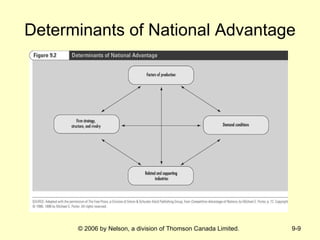
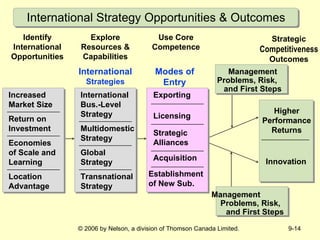
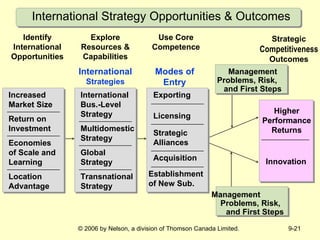
This document discusses international strategy and opportunities for firms. It covers traditional motives for international diversification like accessing larger markets and resources. It also discusses three levels of international strategy - multinational, global, and transnational. Key risks of internationalization include political risks from government instability and economic risks from currency and inflation rate fluctuations. Modes of entering foreign markets addressed include exporting, licensing, strategic alliances, acquisitions, and new wholly-owned subsidiaries.