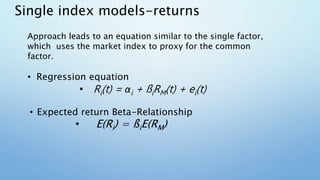
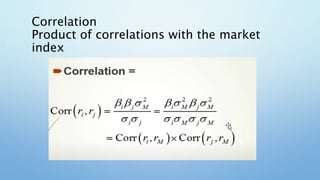
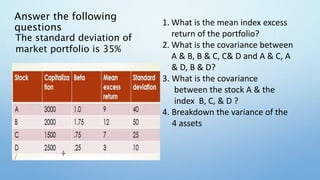
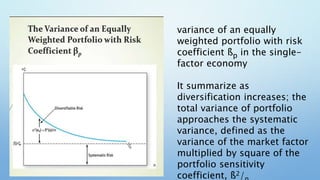
This document provides an overview of the single-factor index model. It discusses how the single-factor model decomposes risk into systematic and firm-specific components. The model uses a common factor, often a stock market index like the S&P 500, to measure systematic risk through securities' betas. It explains how the single-factor model leads to a regression equation relating individual security returns to expected returns and the common factor. The covariance between securities can then be expressed as the product of their betas and the variance of the common factor. The document concludes by noting that as a portfolio becomes more diversified, its total variance approaches only the systematic variance determined by the portfolio's beta and the variance of the market factor.