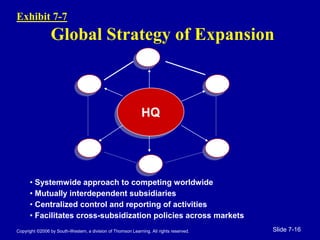
The document discusses strategies for global expansion. It explains that companies expand globally to access new markets as demand becomes more homogeneous worldwide. There are two main strategies - global strategy, which treats the world as a single market, and multidomestic strategy, which customizes approach to local markets. Factors driving globalization include declining costs of transportation, communication, and R&D. Companies must balance benefits of global scale against costs of flexibility and coordination when expanding globally.