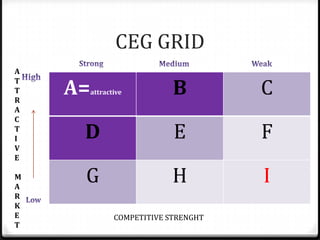
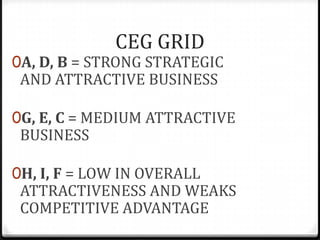
The document provides an overview of key concepts for marketing planning, including defining vision, goals, objectives, strategies, and tactics. It explains the differences between strategic and tactical planning and covers various analyses like SPENT, BCG matrix, GEC grid, Porter's generic strategies, and Ansoff matrix. The marketing planning process is outlined as analyzing the business, market situation, objectives, strategies, and effectiveness. The components of a marketing plan like executive summary, situation analysis, SWOT, objectives, strategies, implementation, and appendices are also described.