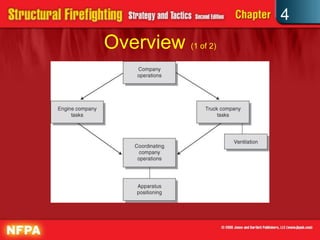
This document outlines the division of labor concept for structuring firefighting operations. It describes how an incident commander coordinates engine and truck company functions. The engine company is responsible for obtaining a water source, setting up pumps, advancing hose lines into structures, and fulfilling the life safety priority through extinguishment. The truck company conducts search and rescue operations through ventilation and forcible entry. Proper apparatus positioning and coordination of company tasks are essential to safely and effectively battling structure fires.