The document discusses networking on mobile devices. It covers supported networking technologies like cellular data, WiFi, and Bluetooth. It discusses required permissions for network operations and the need to perform networking operations on a separate thread to avoid blocking the UI. It provides an example of using AsyncTask to perform networking operations asynchronously. It also covers best security practices, implementing a network security configuration, checking device connectivity, and using Firebase Cloud Messaging as an alternative to polling for updates from a server.



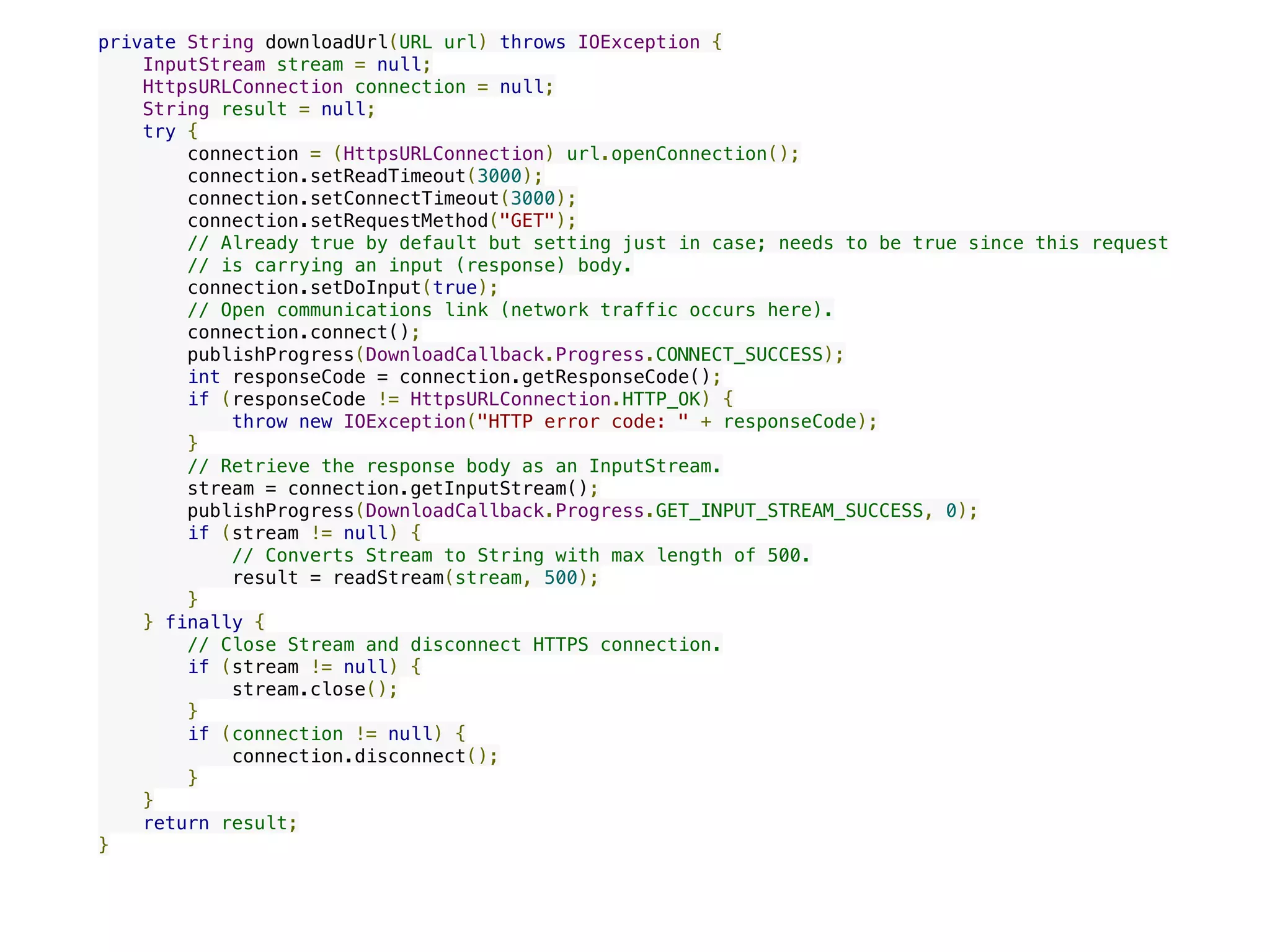



![/**
* Defines work to perform on the background thread.
*/
@Override
protected DownloadTask.Result doInBackground(String... urls) {
Result result = null;
if (!isCancelled() && urls != null && urls.length > 0) {
String urlString = urls[0];
try {
URL url = new URL(urlString);
String resultString = downloadUrl(url);
if (resultString != null) {
result = new Result(resultString);
} else {
throw new IOException("No response received.");
}
} catch(Exception e) {
result = new Result(e);
}
}
return result;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androidnetworking-190401120930/75/Android-Networking-9-2048.jpg)

![Another example of AsyncTask usage
private class DownloadFilesTask extends AsyncTask<URL, Integer, Long> {
protected Long doInBackground(URL... urls) {
int count = urls.length;
long totalSize = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
totalSize += Downloader.downloadFile(urls[i]);
publishProgress((int) ((i / (float) count) * 100));
// Escape early if cancel() is called
if (isCancelled()) break;
}
return totalSize;
}
protected void onProgressUpdate(Integer... progress) {
setProgressPercent(progress[0]);
}
protected void onPostExecute(Long result) {
showDialog("Downloaded " + result + " bytes");
}
}
Usage:
new DownloadFilesTask().execute(url1, url2, url3);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androidnetworking-190401120930/75/Android-Networking-11-2048.jpg)