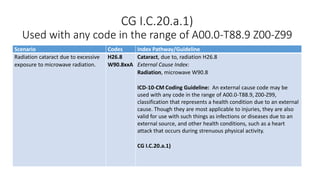
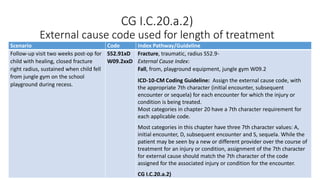
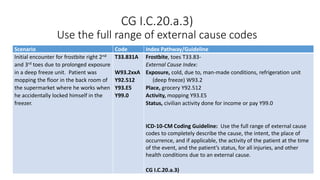
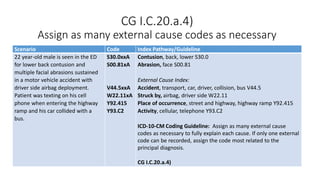
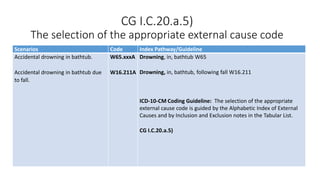
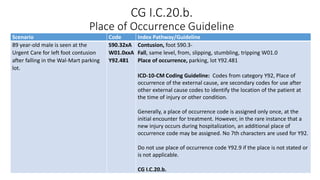
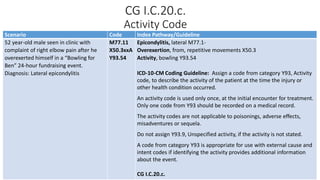
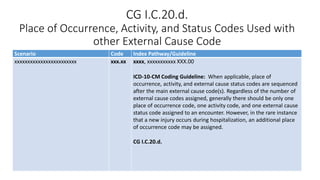
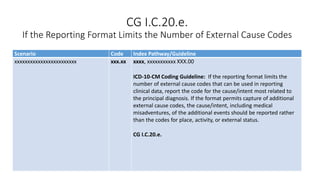
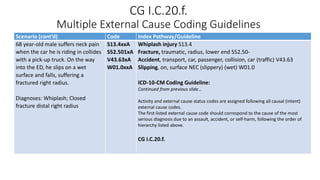
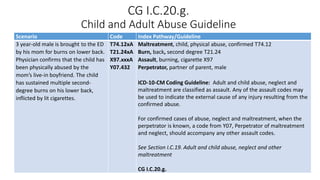
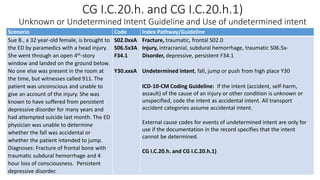
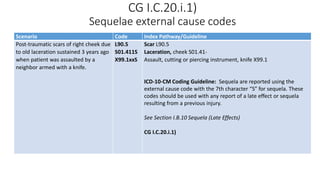
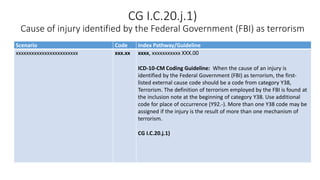
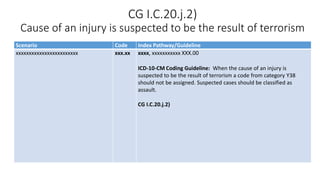
This document provides guidance on using external cause of morbidity codes from ICD-10-CM Chapter 20. It explains that these codes classify environmental events, circumstances, and intent of injury. They are always used as secondary codes along with a code for the nature of the condition. The document outlines the blocks of codes in Chapter 20 and provides coding guidelines on proper use of external cause codes, such as always assigning as many codes as needed to fully describe the cause of injury.