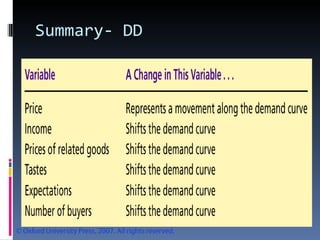
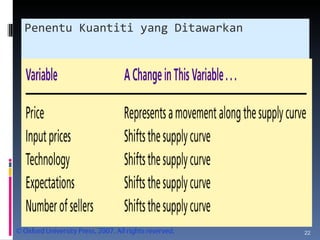
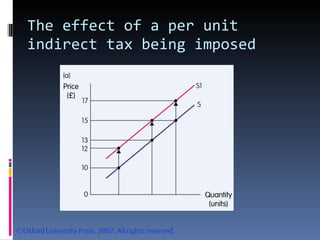
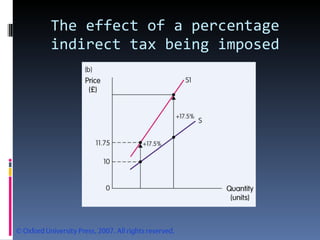
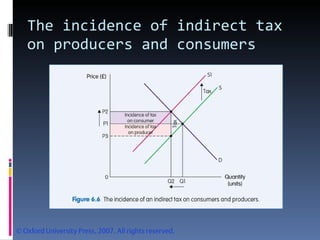
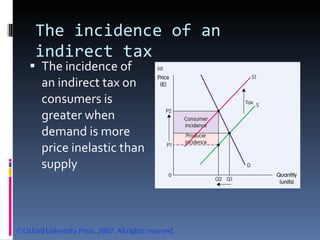
- The document discusses factors that influence demand and supply, including price, income, prices of related goods, and tastes. It explains the concepts of movements and shifts along demand and supply curves.
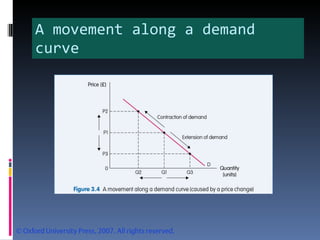
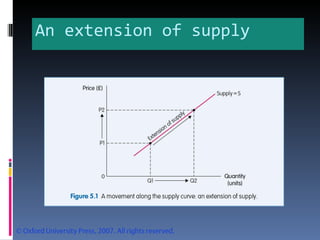
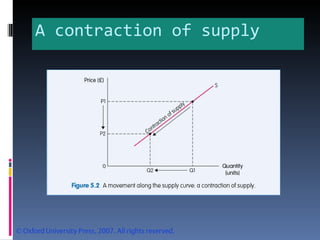
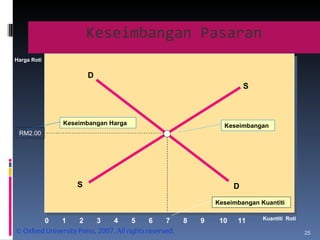
- Demand is represented by a downward-sloping demand curve. The quantity demanded decreases when price increases and increases when price decreases. Supply is represented by an upward-sloping supply curve, with quantity supplied increasing with price.
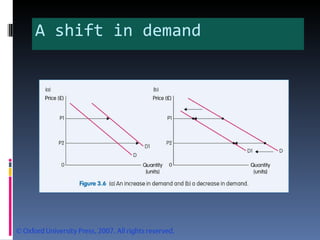
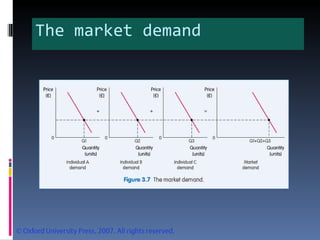
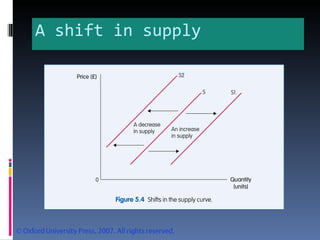
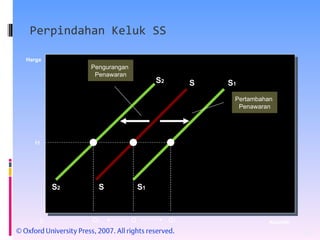
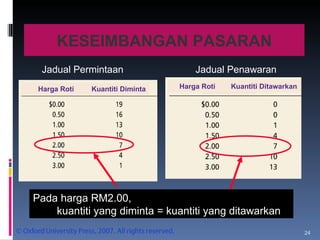
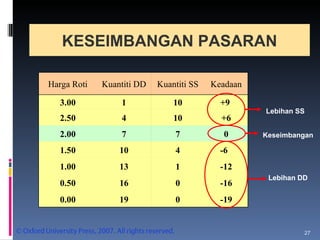
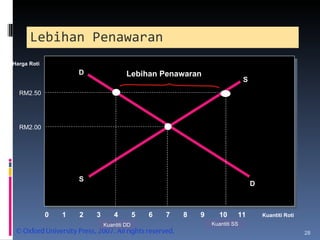
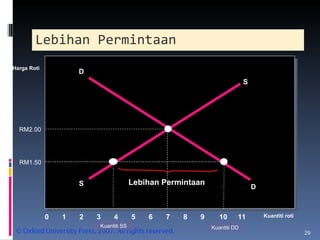
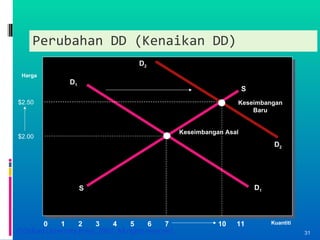
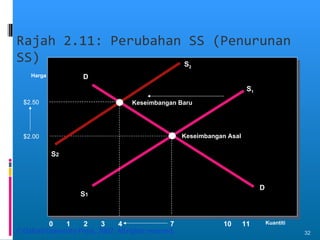
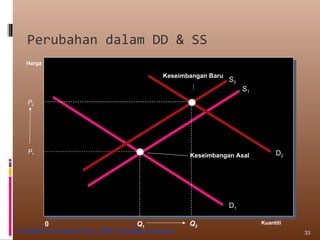
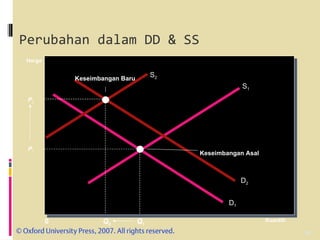
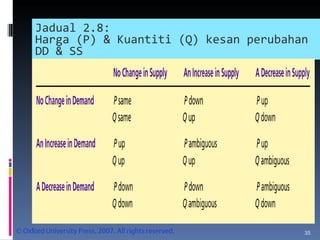
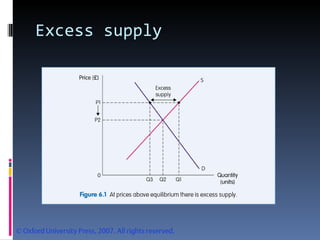
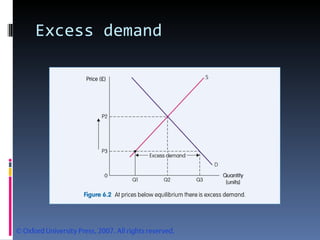
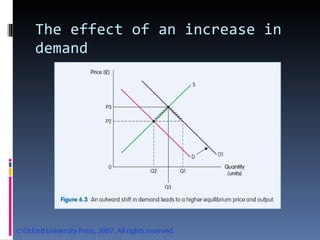
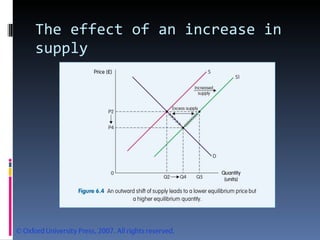
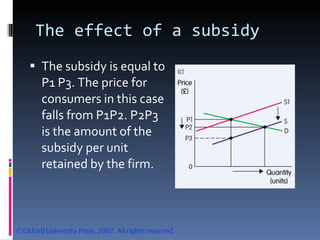
- Market equilibrium occurs where quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. Equilibrium price and quantity can change if demand or supply curves shift due to changes in the factors that influence them.