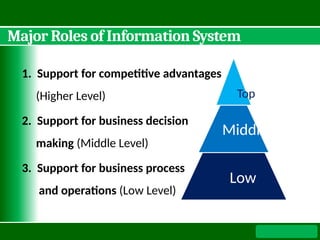
Management involves directing tasks and organizing resources to achieve goals, while information is meaningful data used in decision-making. An information system consists of interrelated components for collecting, processing, storing, and distributing information to support organizational decision-making. The document outlines the types, components, advantages, and disadvantages of information systems, including their role in management information systems.