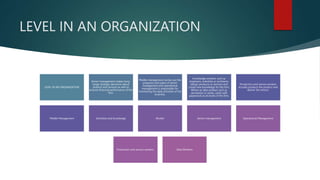
The document explores the interplay between information systems and organizations, highlighting how managers create systems to support business needs while needing to adapt to technological changes. It categorizes information systems into transaction processing systems, management information systems, executive information systems, and decision support systems, each serving different managerial levels and decision-making processes. Additionally, it discusses both the advantages, such as improved planning and decentralization, and drawbacks, such as vulnerabilities to cybercrime and system malfunctions.