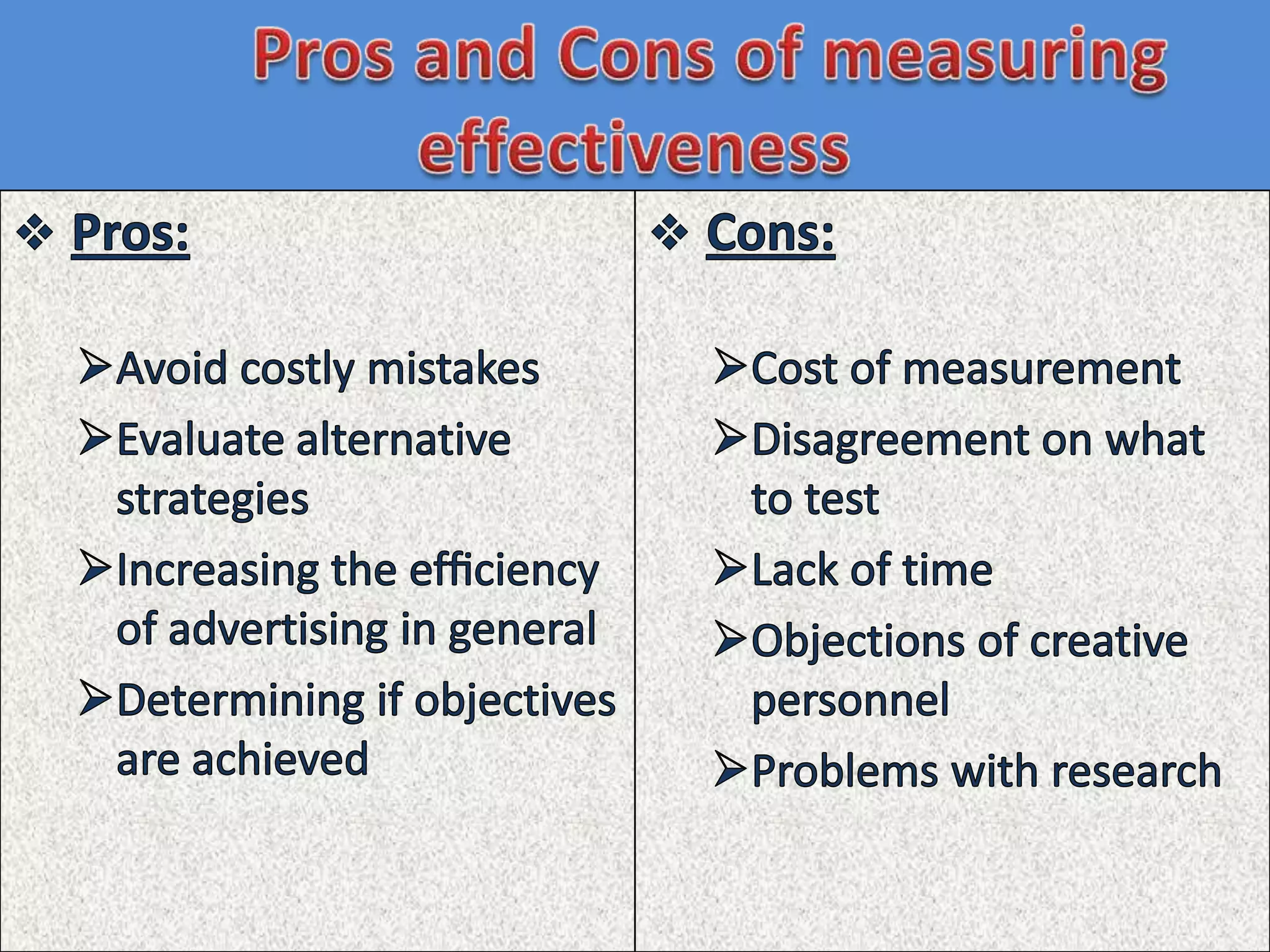
The document discusses testing strategies for advertising campaigns. It describes what should be tested, including source factors, message variables, and media strategies. It recommends testing at different stages of campaign development through laboratory tests, field tests, focus groups, and market testing of finished ads. The document also outlines limitations of certain testing methods and how to properly design testing to reliably and validly measure a campaign's effectiveness.