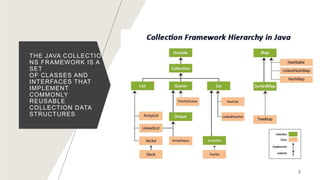
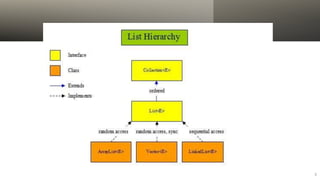
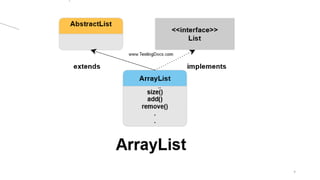
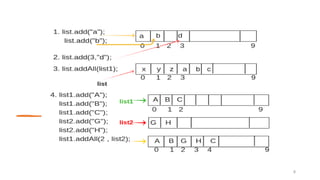
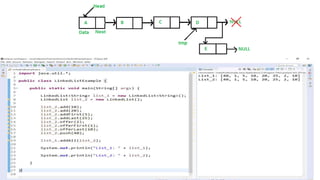
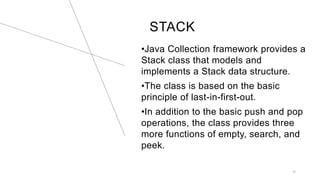
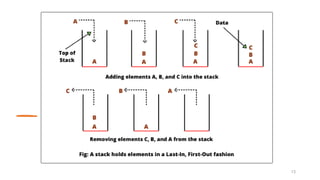
The Java Collections Framework provides a set of classes and interfaces for implementing reusable collection data structures, including the List interface which allows ordered storage, element access by index, and supports duplicates. It includes various implementations like ArrayList, LinkedList, Vector, and Stack, each with distinct characteristics such as thread safety and dynamic resizing. Methods for creating unmodifiable lists and abstract implementations for different access patterns are also described.