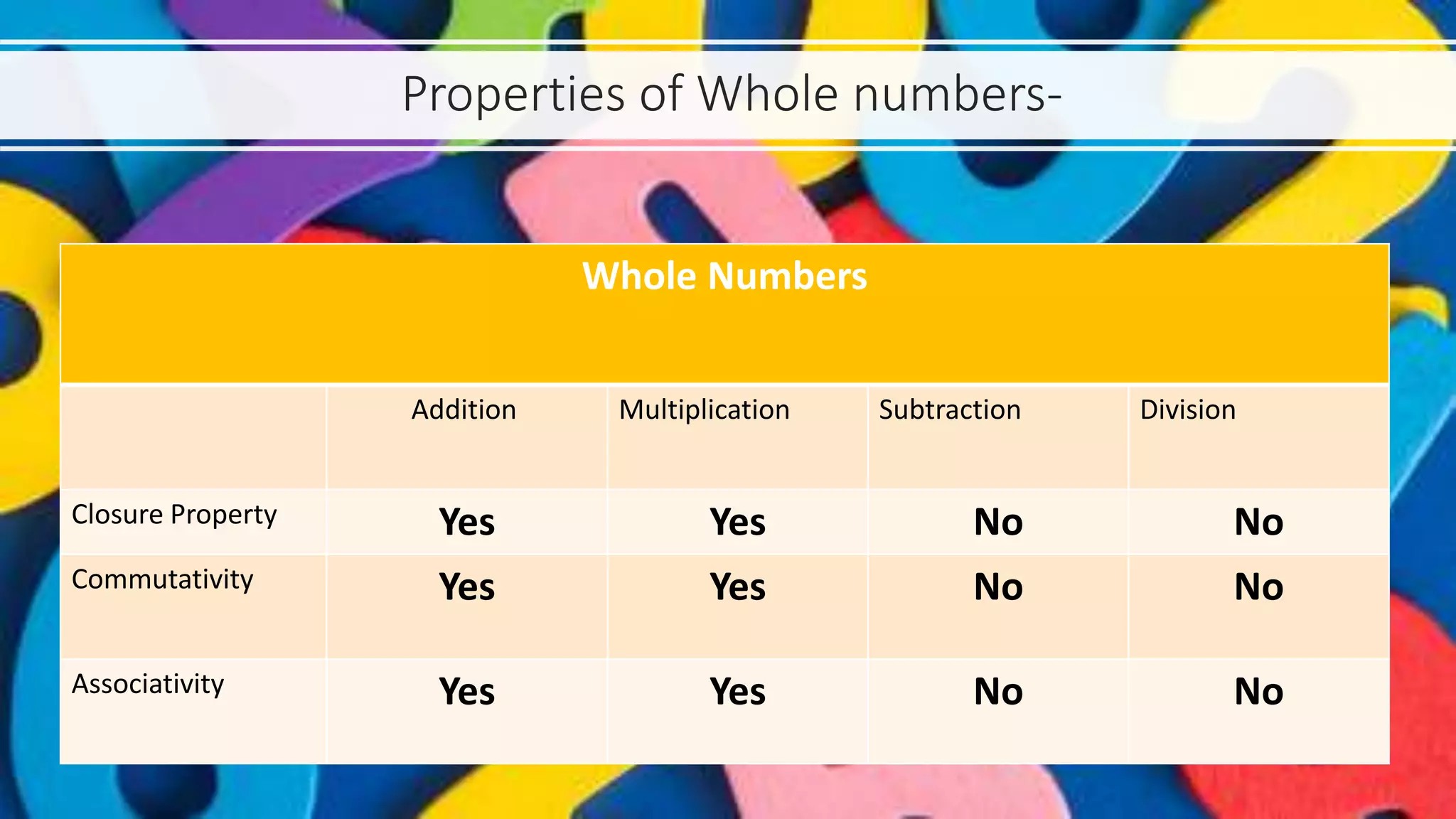
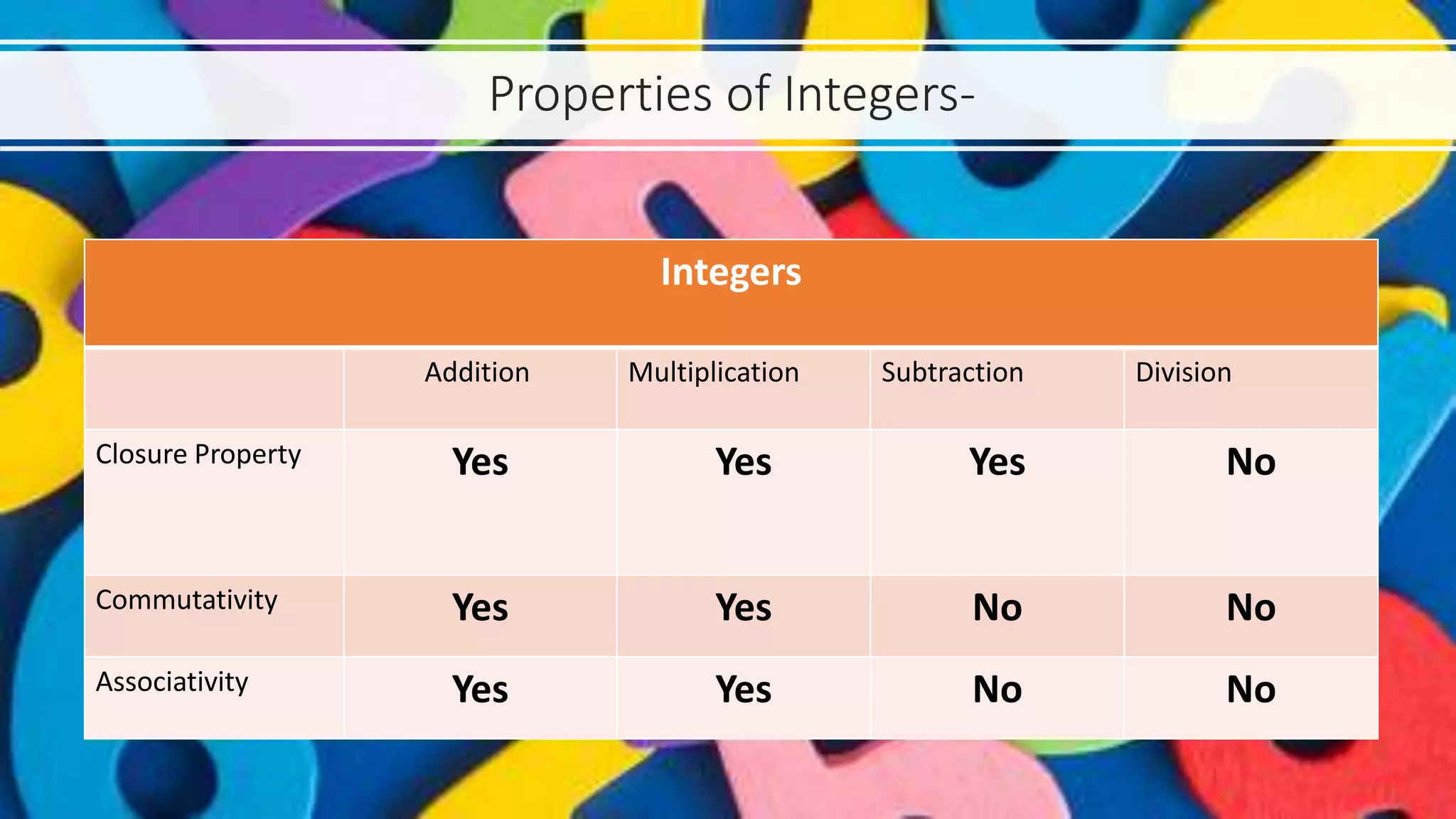
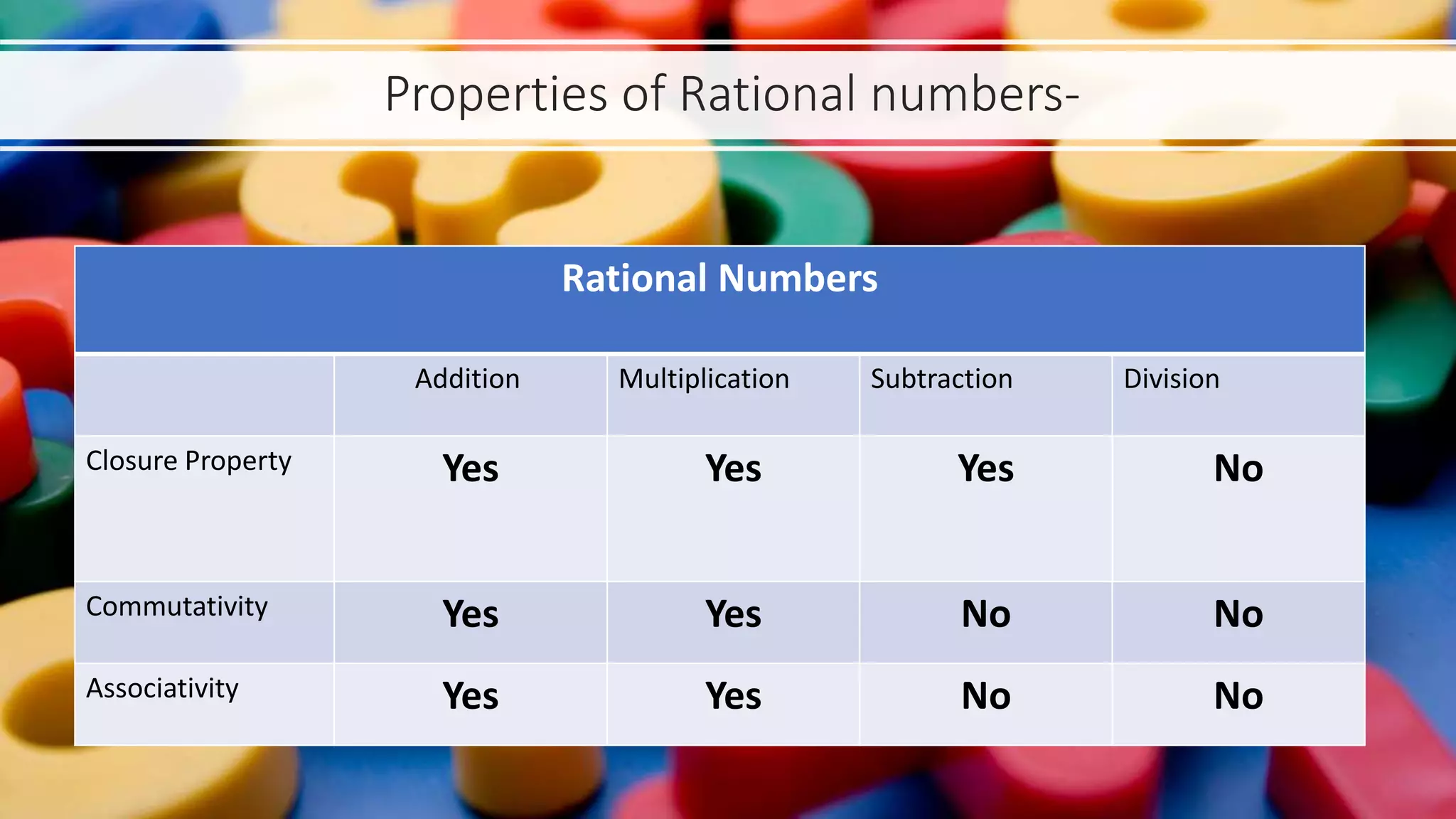
The presentation explores various types of numbers, categorizing them into real and imaginary groups, and detailing subcategories such as natural, whole, integers, rational, and irrational numbers. Each type of number is defined with properties and examples, emphasizing their significance in mathematical calculations. The document also includes games designed to reinforce understanding of these different number types.