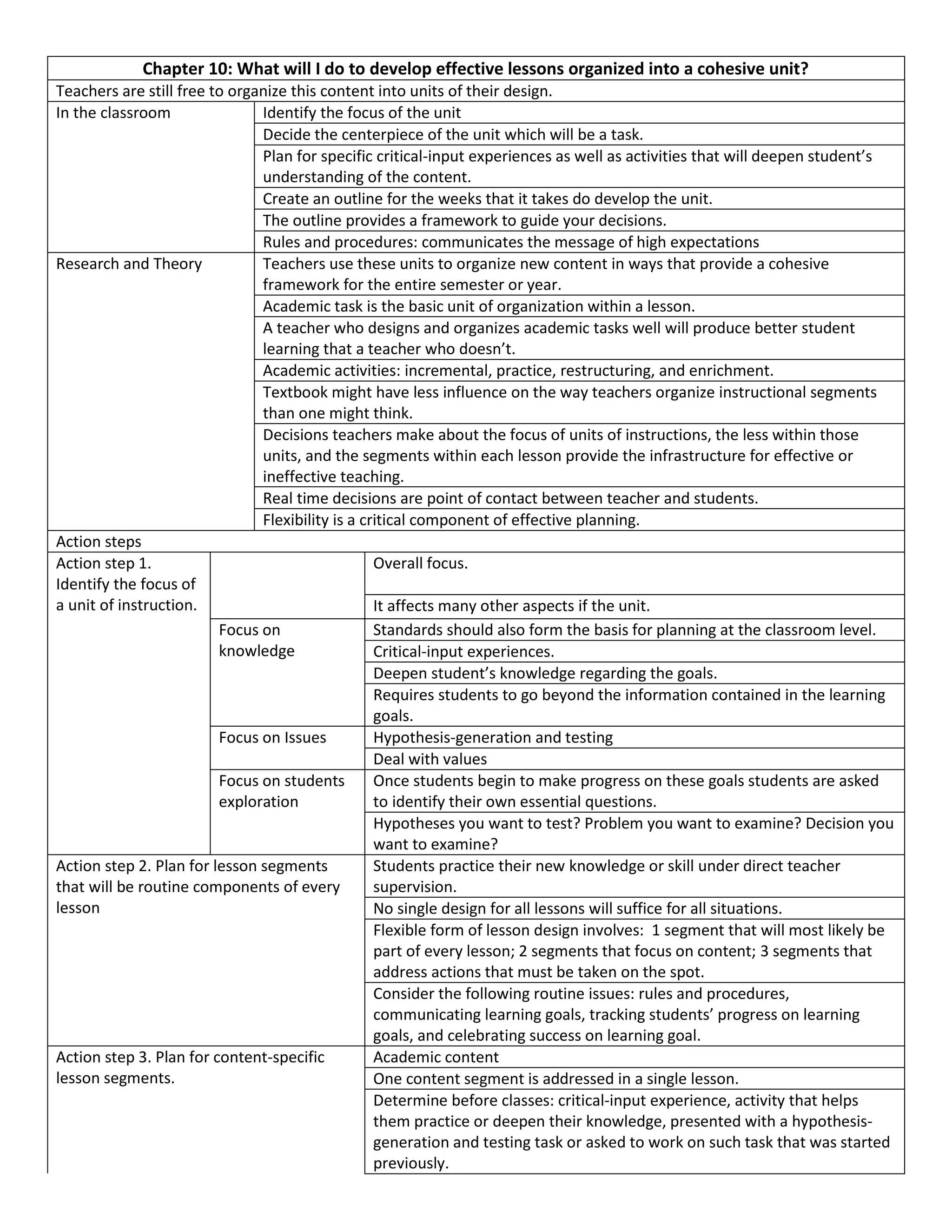
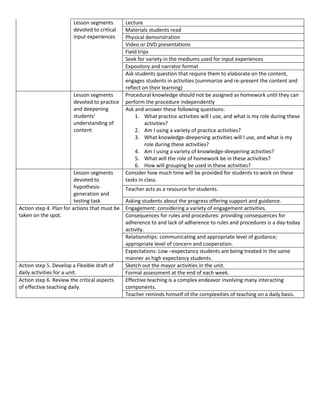
This document provides guidance on developing effective lesson units organized into a cohesive framework. It recommends identifying the unit focus, deciding on a central task, and planning critical input experiences and activities. Teachers should create an outline guiding weekly development. The document also suggests planning for routine lesson components like rules and procedures, as well as content-specific segments involving input, practice, and hypothesis generation. Flexibility is important when designing segments to address issues as they arise. Teachers are advised to review critical aspects of teaching daily.