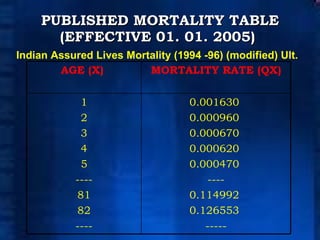
The document discusses actuarial principles and the role of actuaries. It explains that actuaries apply statistical methods to assess financial risks related to insurance, retirement benefits, and investments. Actuaries calculate premiums based on assumptions about mortality, interest, and expenses. They must ensure the ongoing solvency of insurance companies and certify various reports and returns. The duties of appointed actuaries in India are also outlined.