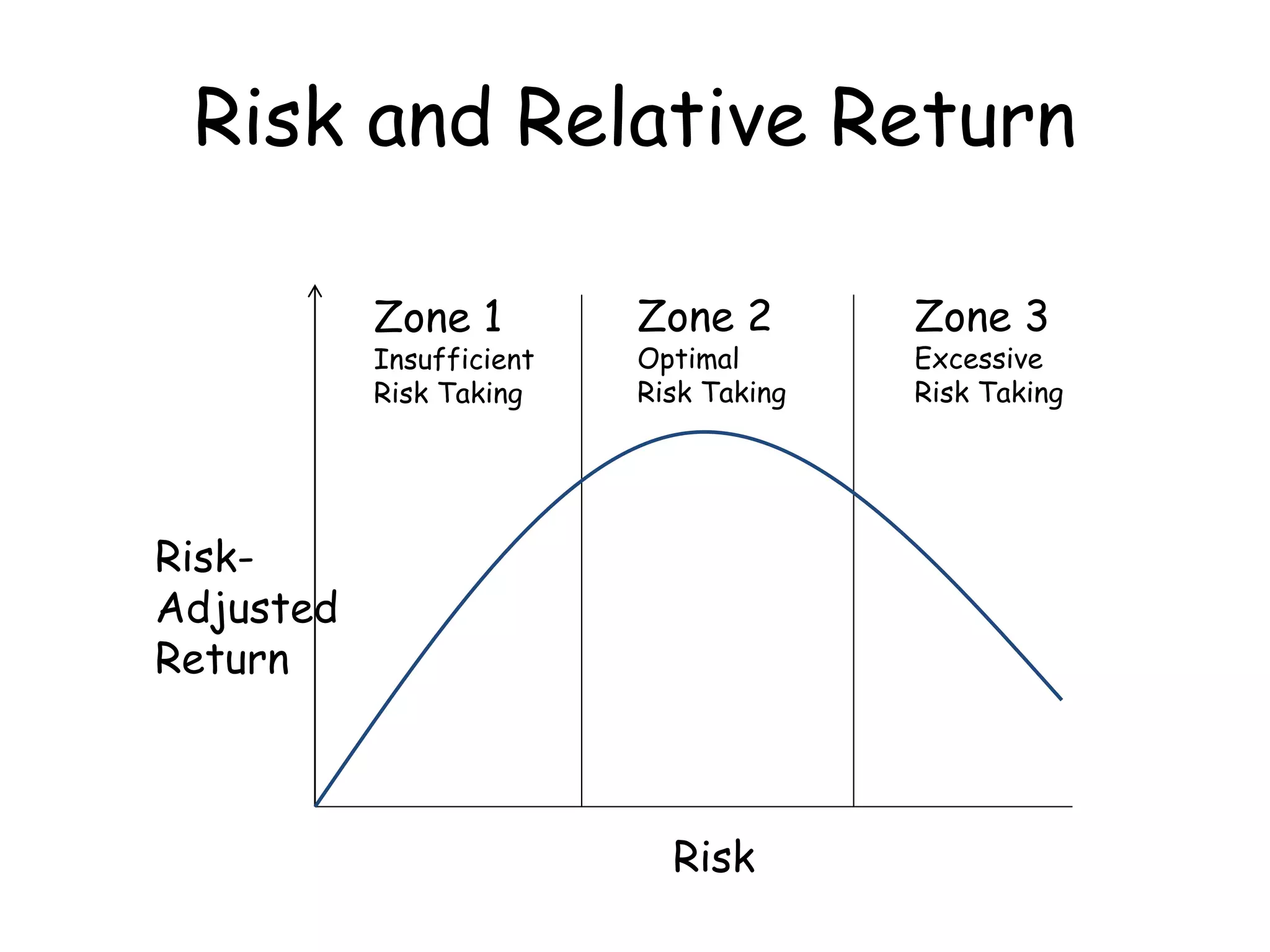
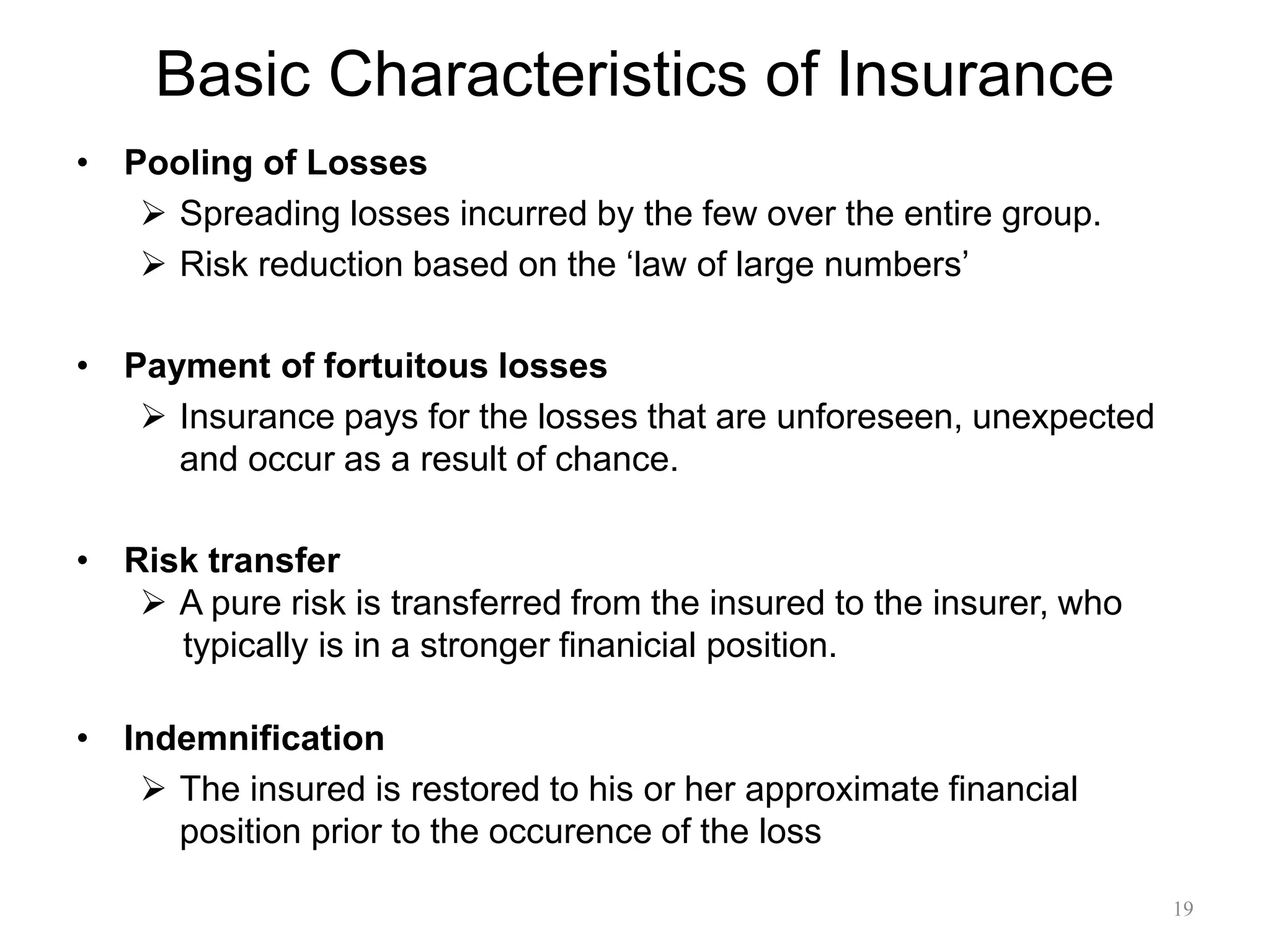
1) Risk is defined as uncertainty of loss and the possibility of unwanted events occurring. Insurance helps manage risk by redistributing the costs of losses across many policyholders.
2) Underwriting is the process used by insurers to evaluate risks, classify them, decide what risks to insure, and determine premiums. It allows insurers to pool risks according to the law of large numbers.
3) The costs of insurance are offset by its benefits, which include peace of mind for individuals and reduced credit risk for businesses. At a societal level, insurance contributes to economic stability.