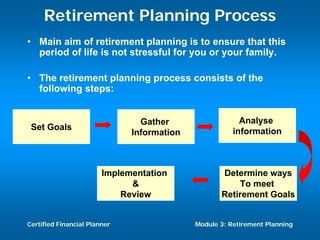
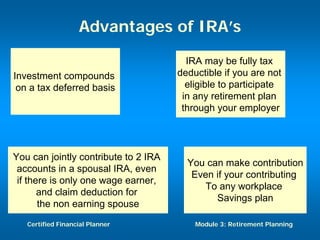
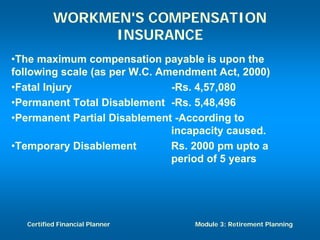
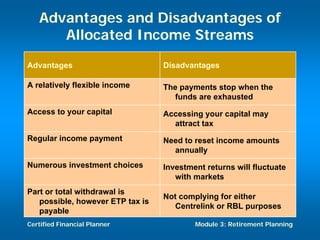
The document discusses retirement planning and provides information about retirement benefits. It covers topics such as the importance of retirement planning, sources of retirement income like government and company programs, retirement benefit schemes, and strategies for retirement planning such as maximizing workplace savings and establishing IRAs. The document aims to help people understand retirement and the need for financial planning to ensure a comfortable retirement.