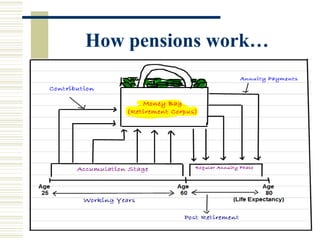
The document provides information about pension plans in India. It discusses that PFRDA regulates the pension sector in India and was established in 2003. It then explains what pension plans are, how they provide individuals with a regular income in retirement. It also discusses the history of pension plans shifting from employer-provided to individual plans. Finally, it outlines the key factors to consider to calculate a retirement corpus and describes different types of pension plans and annuity options available.