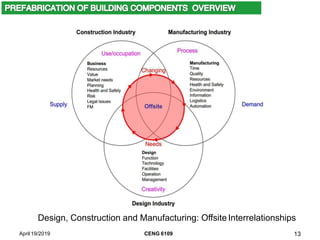
This document contains lecture notes for a course on industrialized building and maintenance. It introduces prefabricated construction and the industrialized building system. Some key points covered include:
- The benefits of prefabricated construction like reduced construction time, consistent quality, and improved safety.
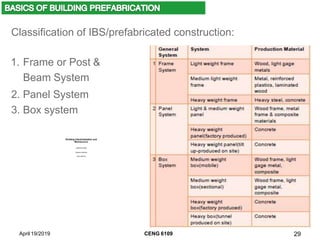
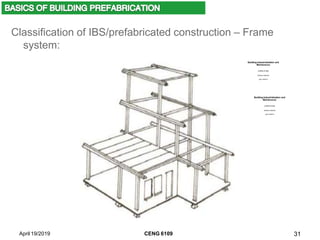
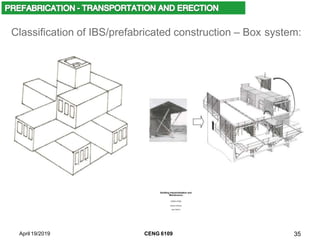
- Different classifications of prefabricated systems including frame, panel, and box systems.
- The process of prefabricated building construction from foundation work to connections of beams and slabs.
- Potential barriers to the use of prefabricated construction like poor skills/knowledge and a lack of integration among professionals in design.