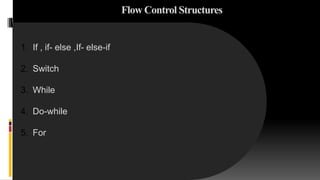
This document provides an introduction to PHP, including its data types, operators, and flow control structures. PHP is a loosely typed scripting language that allows changing a variable's data type. It supports 8 types: 4 scalar (integer, float, string, boolean), 2 compound (array, object), and 2 special (resource, NULL). Operators include arithmetic, string concatenation, comparison, bitwise, and logical. Flow control includes if/else, switch, while, do-while, for, and foreach loops. The document also covers variable scope, date/time functions, and additional PHP concepts.


![1. ScalarData types
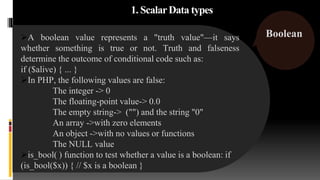
Floating-point numbers are also called real numbers.
They are numbers that have a fractional component.
PHP floating-point numbers are equivalent to the double
data type.
PHP recognizes two types of floating point numbers.
i. The first is a simple numeric literal with a decimal
point. e.g. 3.14, 0.017, -7.1
ii. The second is a floating-point number written in
scientific notation as [number]E[exponent], e.g.
1.75E-2.
Use the is_float( ) function (or its is_real( ) alias) to test
whether a value is a floating point number:
if (is_float($x)) { // $x is a floating-point number }
Floating-
Point
Numbers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap1introppt2phpfinallydone-200716103923/85/Chap1introppt2php-finally-done-5-320.jpg)


![2. Compound Data types
ArraysAn array is a variable that holds a group of values. By
referring to their index position we can access the
individual elements.
The position is either specified numerically or by name.
An array with a numeric index is commonly called an
indexed array while one that has named positions is called
an associative array.
In PHP, all arrays are associative, but you can still use a
numeric index to access them.
Referencing array elements:
$arrayName[index];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap1introppt2phpfinallydone-200716103923/85/Chap1introppt2php-finally-done-9-320.jpg)
![2. Compound Data types
Arraysis_array( ) function to test whether a value is an array:
if (is_array($x)) { // $x is an array }
indexed array
$item[0] = “Pen"; $item[1] = “Pencil";
$item[2] = “Notebook";
associative array
$book[‘C’] = “Richie”; $book[‘CPP’] = “Bjarne”;
$book[‘Java’] = “Sun”;
The array( ) construct creates an array:
$item = array(‘Pen’, ‘Pencil’, ‘Notebook’);
$book = array(‘C’ => ‘Richie’ , ‘CPP’ => ‘Bjarne’,
‘Java’ => ‘Sun’);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap1introppt2phpfinallydone-200716103923/85/Chap1introppt2php-finally-done-10-320.jpg)