This document provides an overview of PHP (Hypertext Preprocessor) including its introduction, syntax, variables, data types, operators, control flow statements and functions. PHP is a widely used open source scripting language that allows developers to execute code server-side to generate dynamic web page content. Some key points covered include:
- PHP code is placed within <?php ?> tags in HTML documents and executed on the server.
- It supports common data types like strings, integers, arrays and objects that can be stored and manipulated using variables and operators.
- Control structures allow conditional execution and loops like if/else, switch, while, do/while and for to control program flow.
- Functions
















![PHP Data Types
Boolean
A Boolean represents two possible states: TRUE or FALSE.
Used in conditional Testing.
$x = true;
$y = false;
Array
Stores multiple values in one single variable.
Example
<?php
$cars = array("Volvo","BMW","Toyota");
var_dump($cars);
?>
Output:
array(3) { [0]=> string(5) "Volvo" [1]=> string(3) "BMW" [2]=> string(6) "Toyota" }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpppt-190412102026/85/PHP-Basics-17-320.jpg)






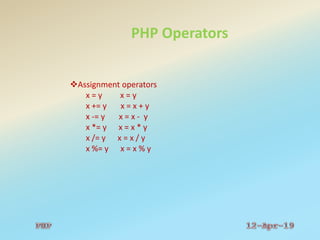







![PHP Operators
Array operators
+ Union $x + $y
<?php
$x = array("a" => "red", "b" => "green");
$y = array("c" => "blue", "d" => "yellow");
print_r($x + $y); // union of $x and $y
?>
Output:
Array ( [a] => red [b] => green [c] => blue [d] =>
yellow )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpppt-190412102026/85/PHP-Basics-32-320.jpg)



















![PHP Arrays
An array is a special variable, which can hold more than one value
at a time.
Types:
Indexed arrays - Arrays with a numeric index
Associative arrays - Arrays with named keys
Multidimensional arrays - Containing one or more arrays
Example
<?php
$cars = array("Volvo", "BMW”);
echo "I like " . $cars[0] . ”and " . $cars[1] . ".";
$age = array("Peter"=>"35", "Ben"=>"37", "Joe"=>"43");
echo "Peter is " . $age['Peter'] . " years old.";
?>
Output:
I like Volvo and BMW.
Peter is 35 years old.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpppt-190412102026/85/PHP-Basics-52-320.jpg)

![PHP - A Simple HTML Form
Example
Welcome.php
<html>
<body>
Welcome <?php echo $_POST["name"]; ?><br>
Your email address is: <?php echo $_POST["email"]; ?>
</body>
</html>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpppt-190412102026/85/PHP-Basics-55-320.jpg)

![PHP - A Simple HTML Form
Example
welget.php
<html>
<body>
Welcome <?php echo $_GET["name"]; ?><br>
Your email address is: <?php echo $_GET["email"]; ?>
</body>
</html>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/phpppt-190412102026/85/PHP-Basics-59-320.jpg)