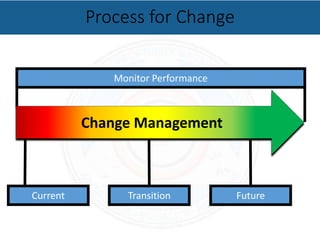
Change management is the process of managing people through organizational change. It incorporates tools to help people successfully transition to new changes. Reasons for change include leadership changes, mission changes, resource changes, and significant events. Barriers to change can include resistance to new ideas and reluctance to adapt to different ways of doing things. The process for change management involves monitoring performance, planning for the future and managing the current transition. Strategies for effective change include preparing people, getting buy-in, and reinforcing commitment. Follow-up is important to ensure the success of changes.