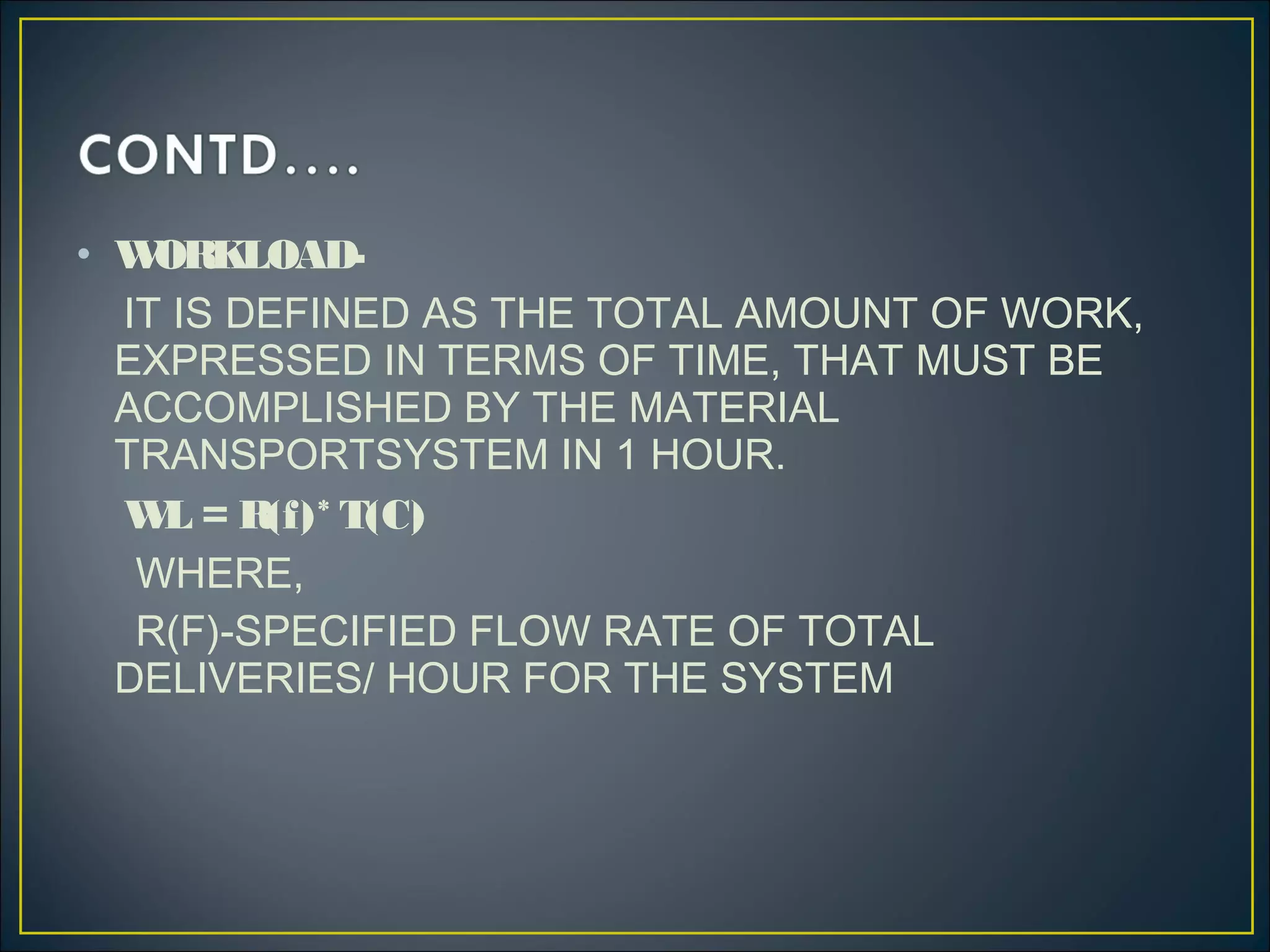
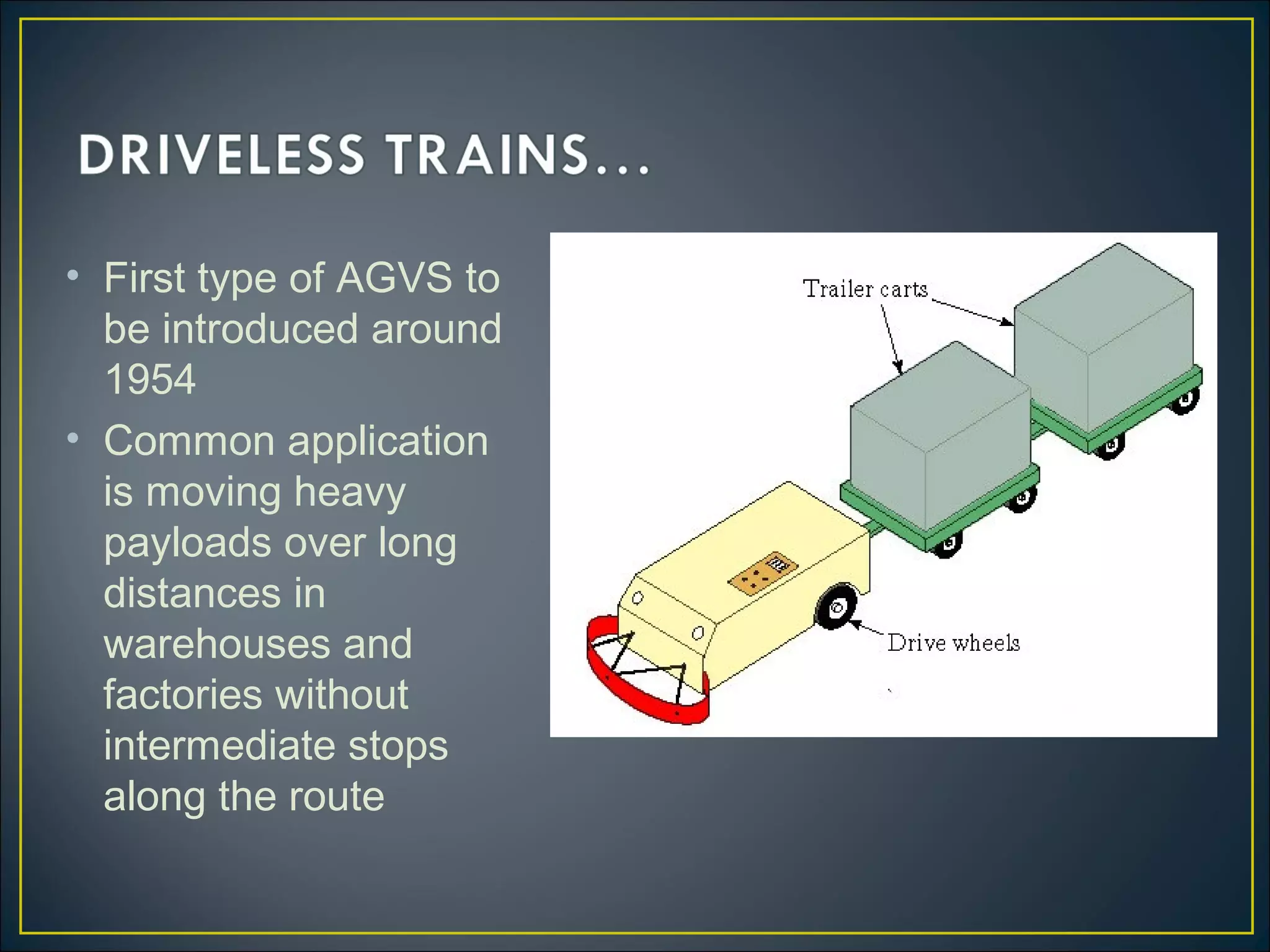
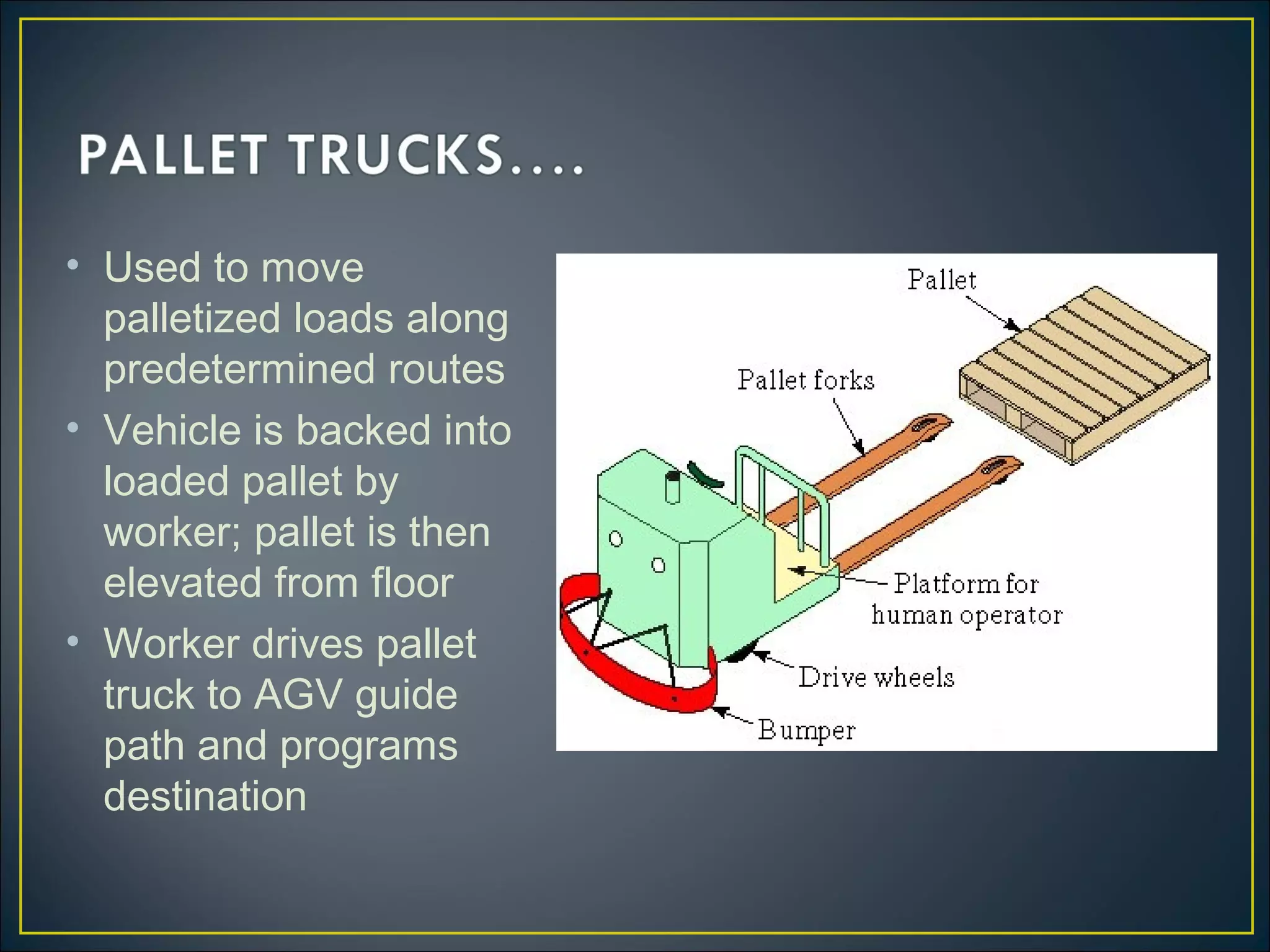
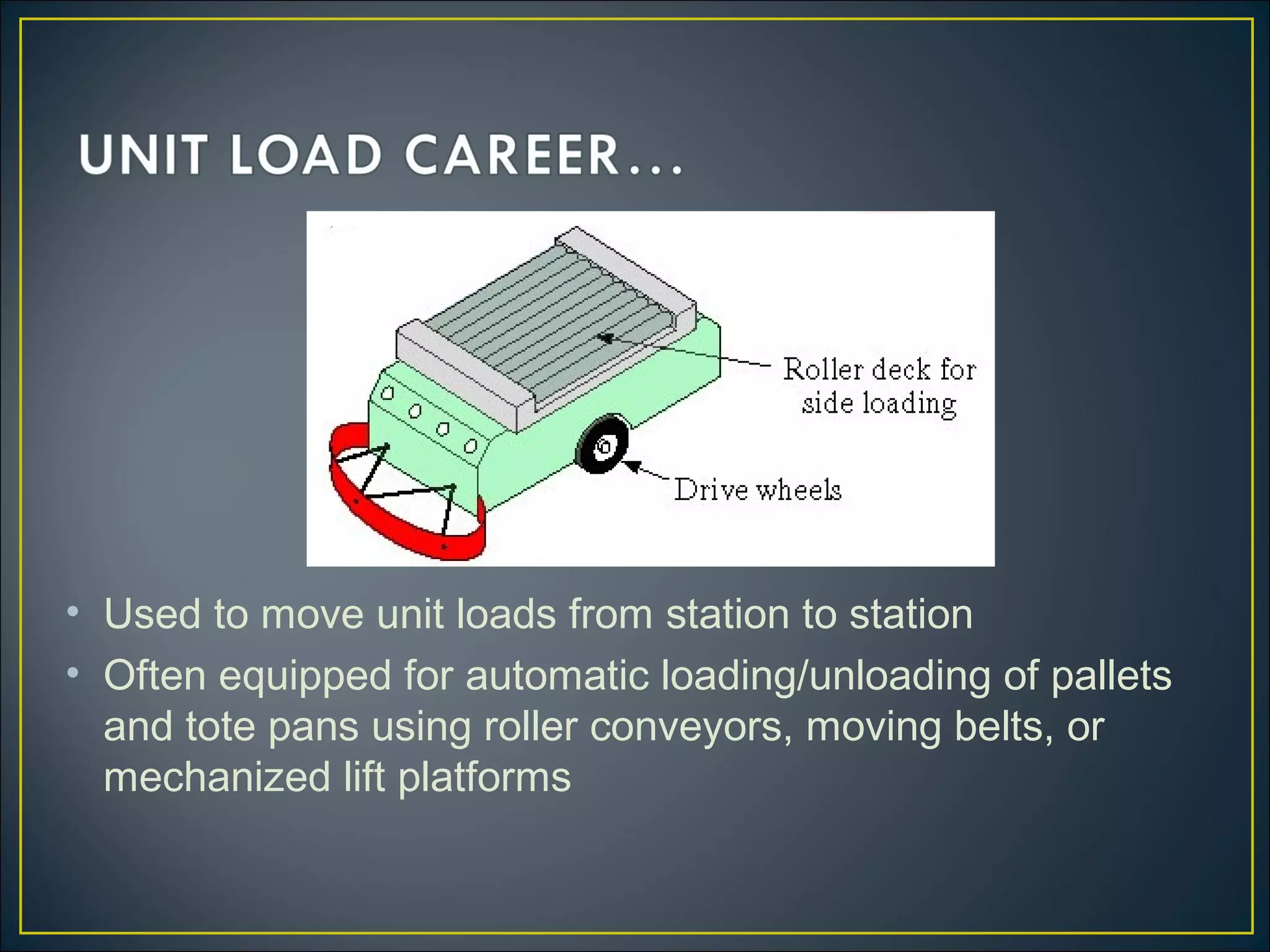
An automated guided vehicle (AGV) is a material handling system that uses independently operated, self-propelled vehicles guided along defined pathways. There are three main types of AGVs: driveless trains for moving heavy payloads over long distances; pallet trucks for moving palletized loads along predetermined routes; and unit load AGVs for moving unit loads between stations, often equipped for automatic loading and unloading. Mathematical equations can describe the operation of AGV systems, taking into account factors like loading/unloading times, travel times and distances, reliability, and traffic congestion. Performance metrics include the rate of deliveries per vehicle, number of vehicles required, and system workload.







![• AVAILABLE TIME-
AT = 60 * A * F(T) * E(W)
WHERE,
AT-AVAILABLE TIME E(W)-WORKER EFFICIENCY
A- AVAILABILITY F(T)-TRAFFIC FACTOR
• RATE OF DELIVERIES PERVEHICLE-
R(DV) = [AT/T(C)]
WHERE,
R(DV)-HOURLY DELIVERY RATE/VEHICLE
T(C)- DELIVERY TIME](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chandrakishore-140430022629-phpapp02/75/Automatic-Guided-Vehicle-13-2048.jpg)