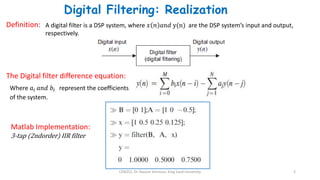
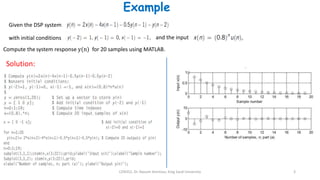
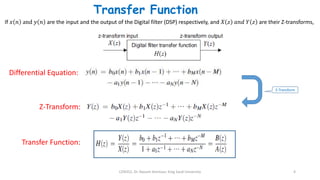
1) Digital filters are discrete-time systems that perform operations on sampled input signals. They are described by difference equations relating the current output to current and previous input/output values.
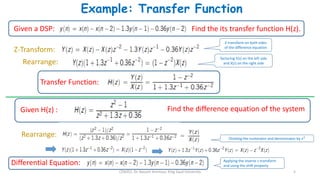
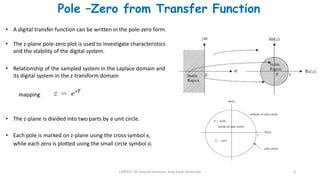
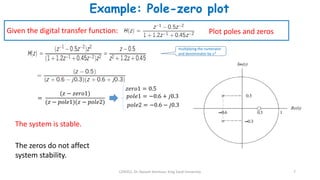
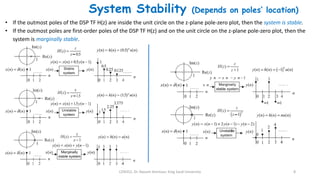
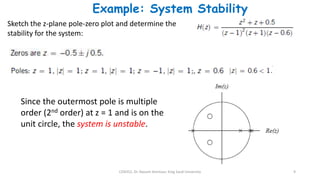
2) The transfer function of a digital filter relates the Z-transform of its input and output and can be used to analyze properties like poles, zeros, and stability.
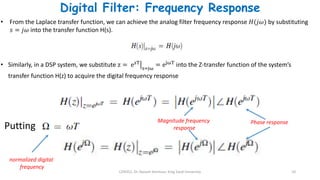
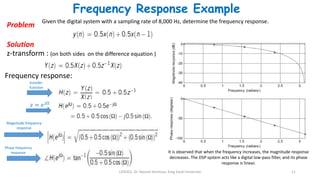
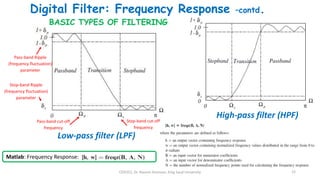
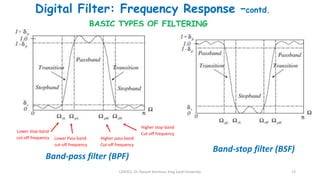
3) The frequency response of a digital filter is obtained by substituting Z = e^jΩ into its transfer function and indicates how the filter affects different frequencies, determining its type (low-pass, high-pass, etc.).