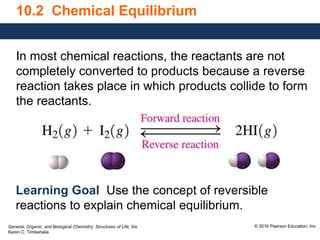
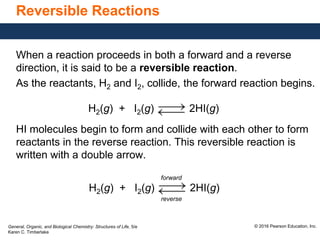
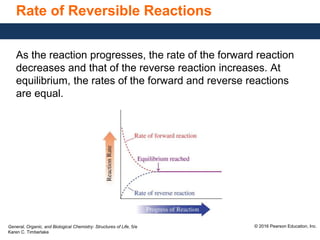
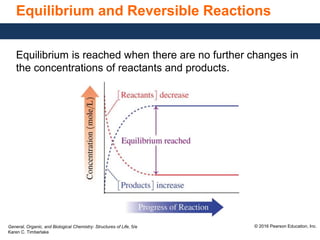
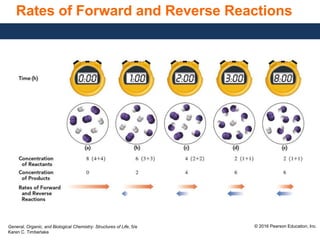
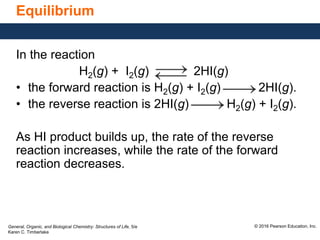
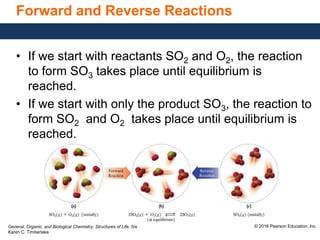
This document discusses chemical equilibrium in reversible reactions. It explains that in reversible reactions, the forward and reverse reactions occur simultaneously until equilibrium is reached, where the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal. It provides examples of reversible reactions, such as H2(g) + I2(g) ⇌ 2HI(g), and explains that at equilibrium the concentrations of reactants and products stop changing.