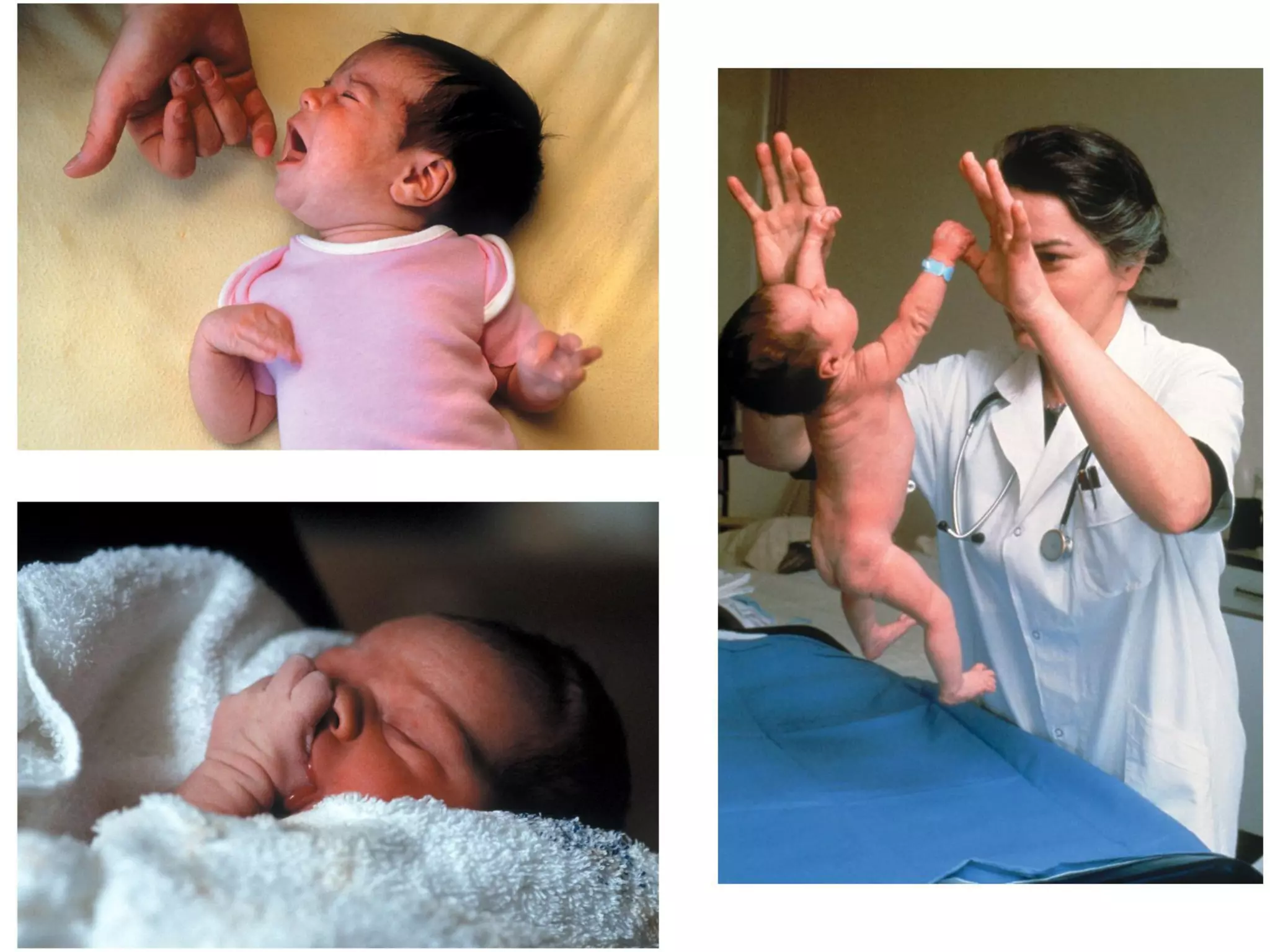
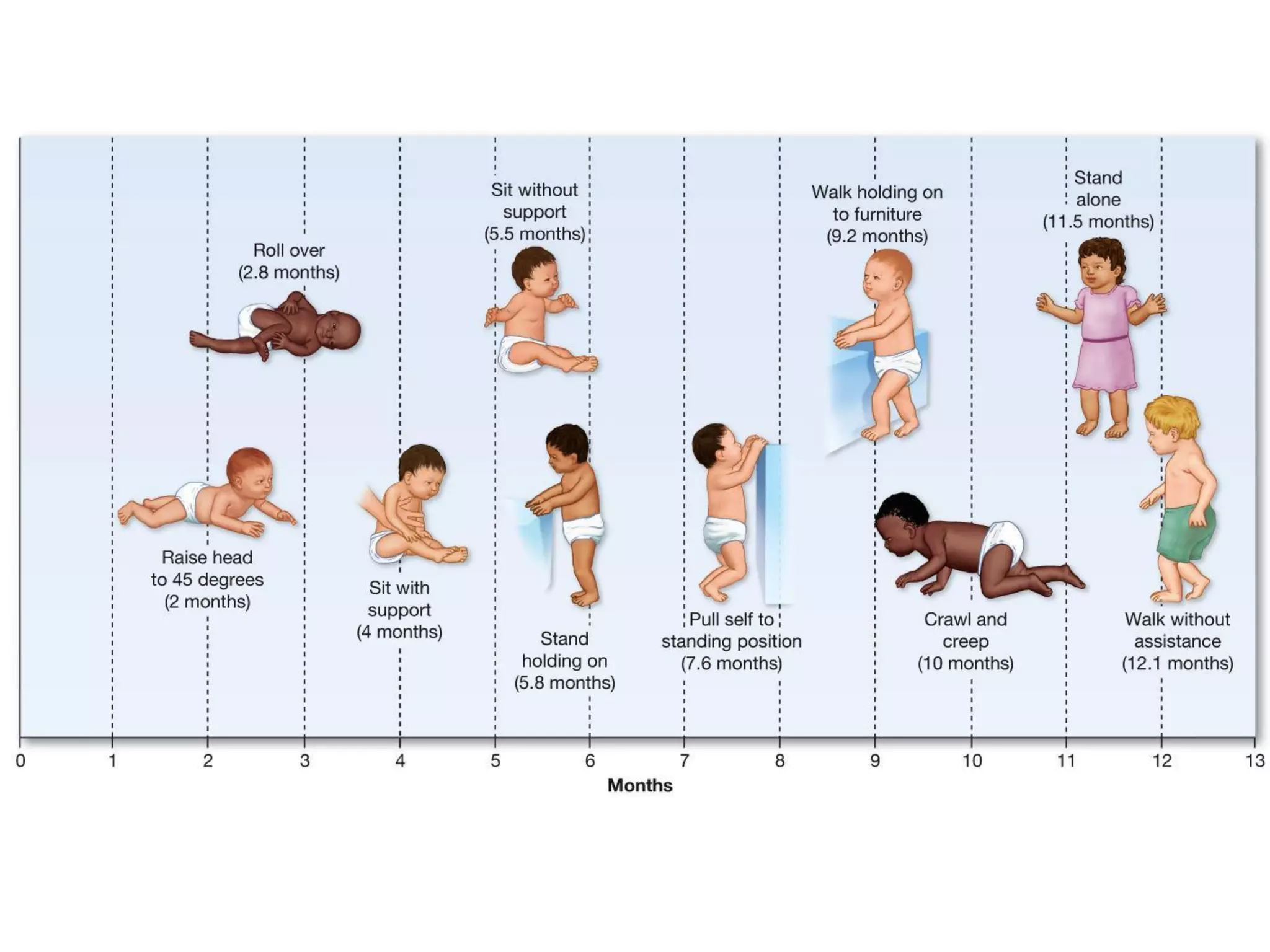
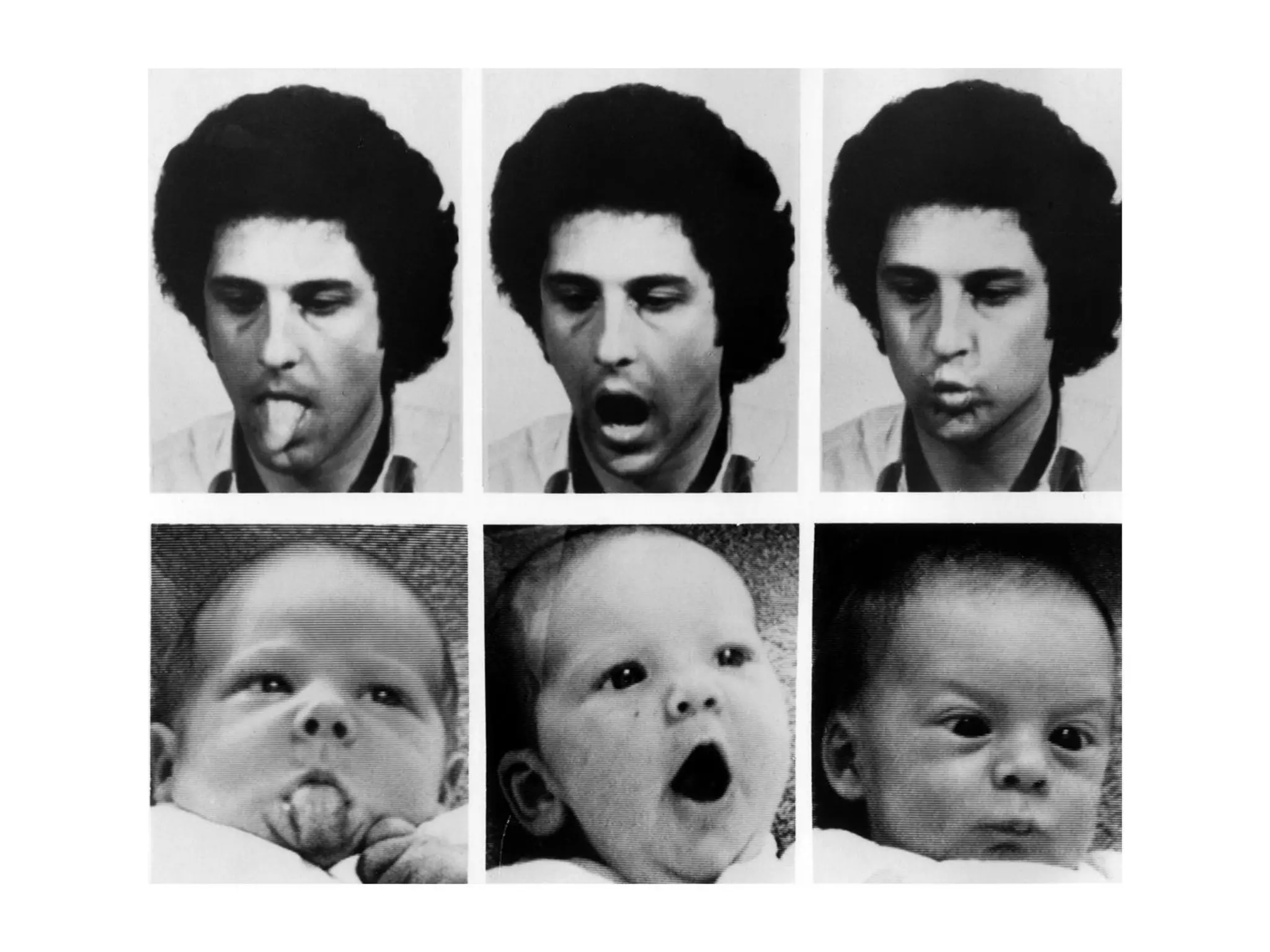
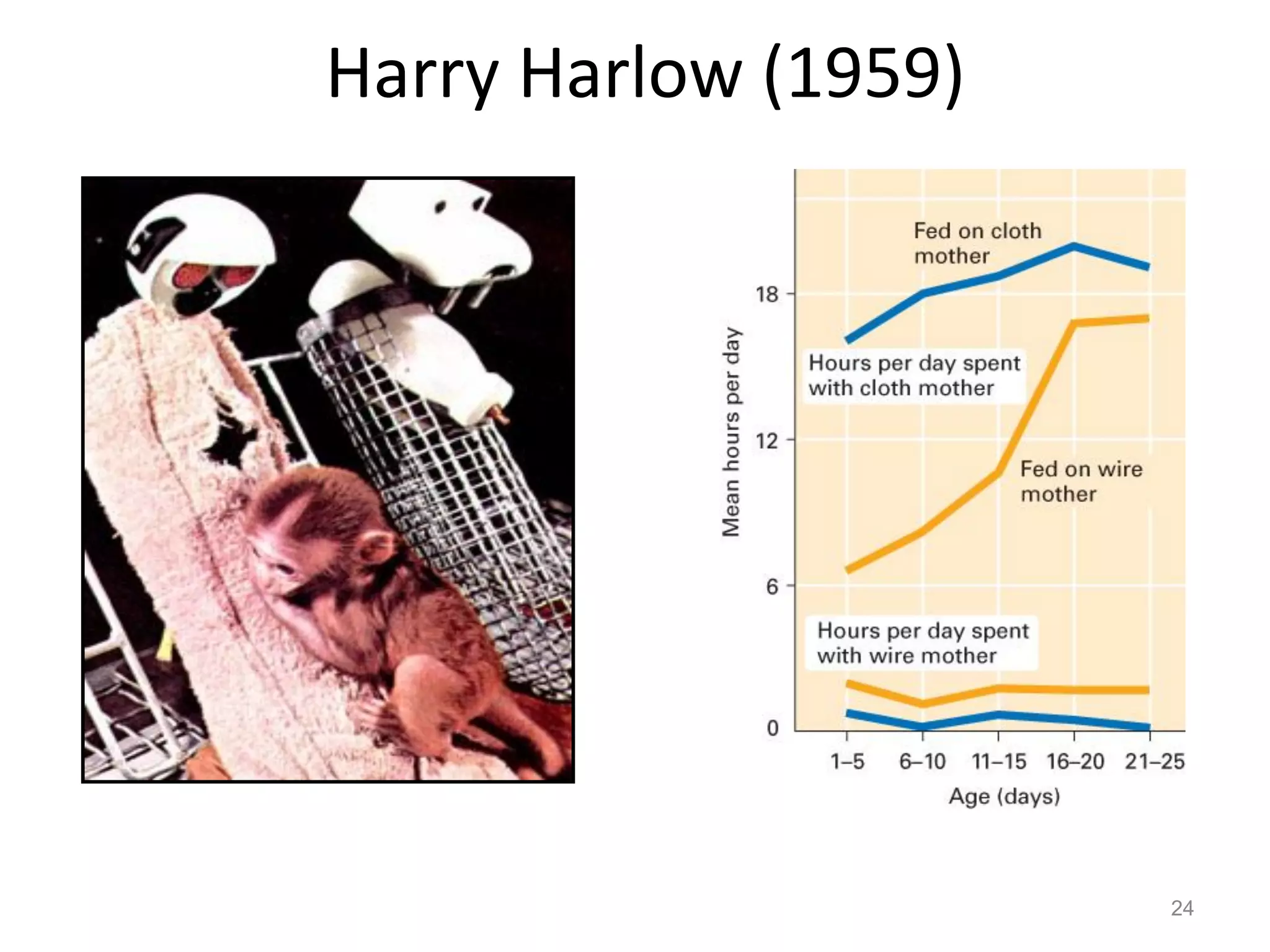
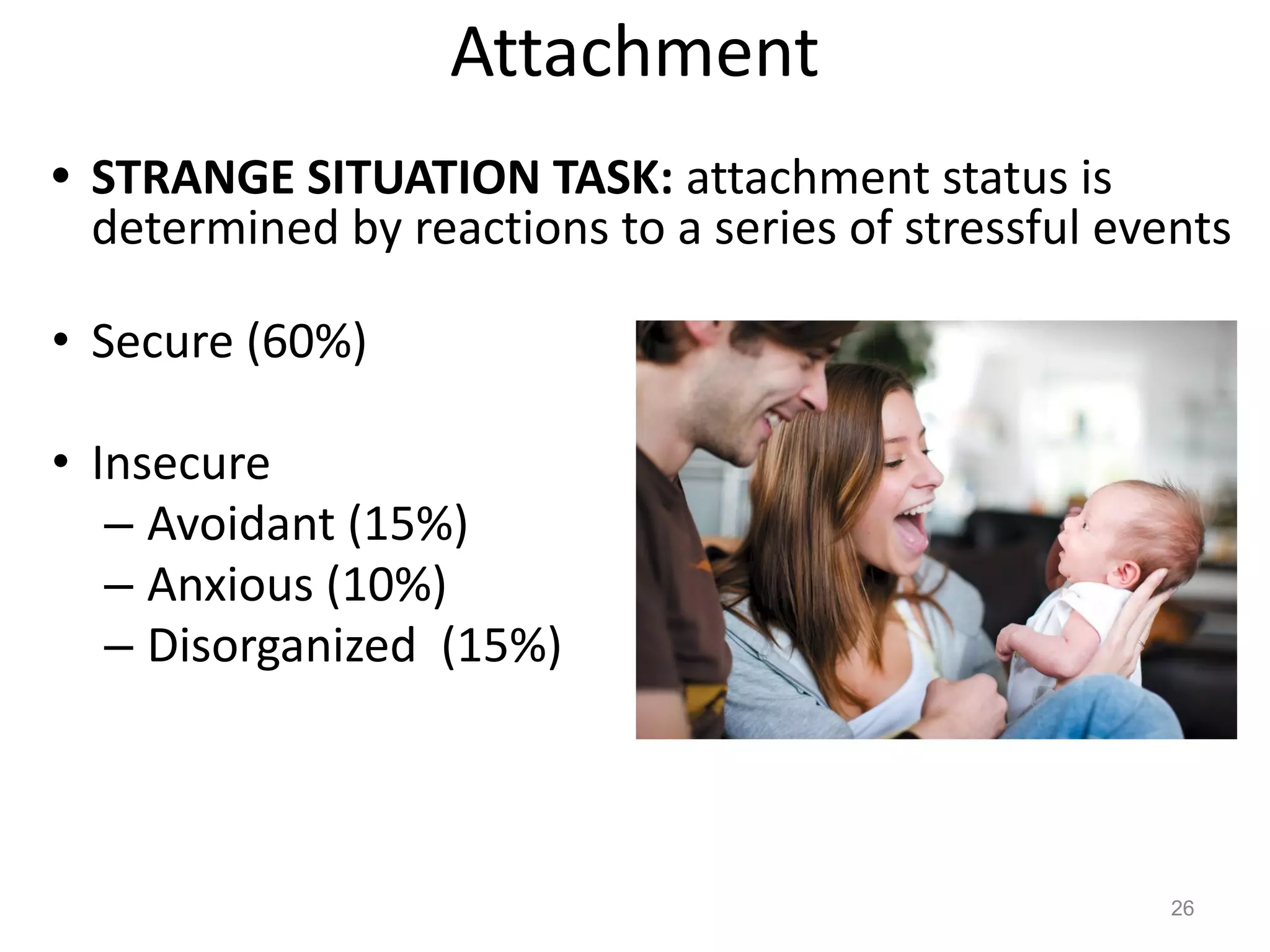
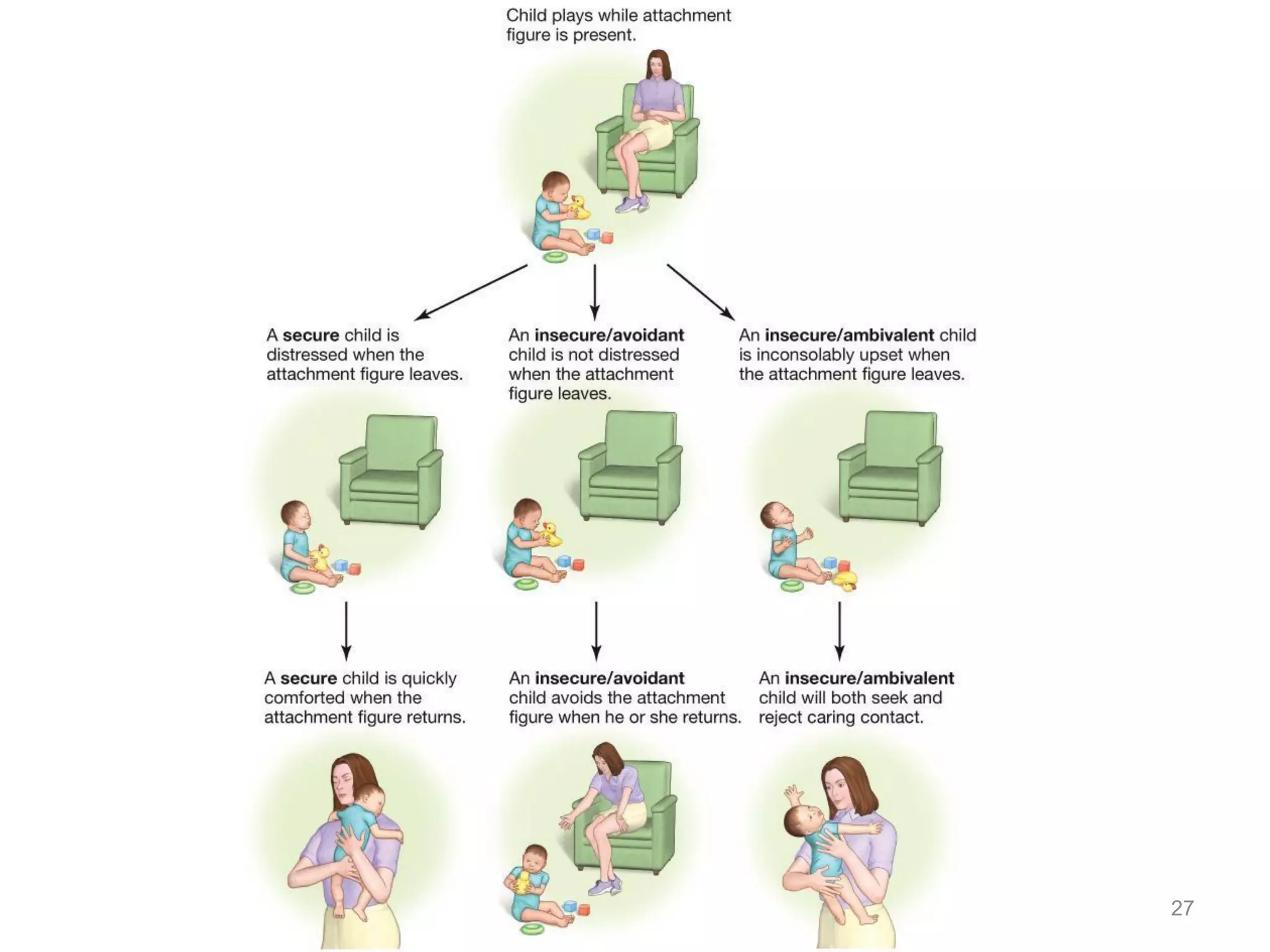
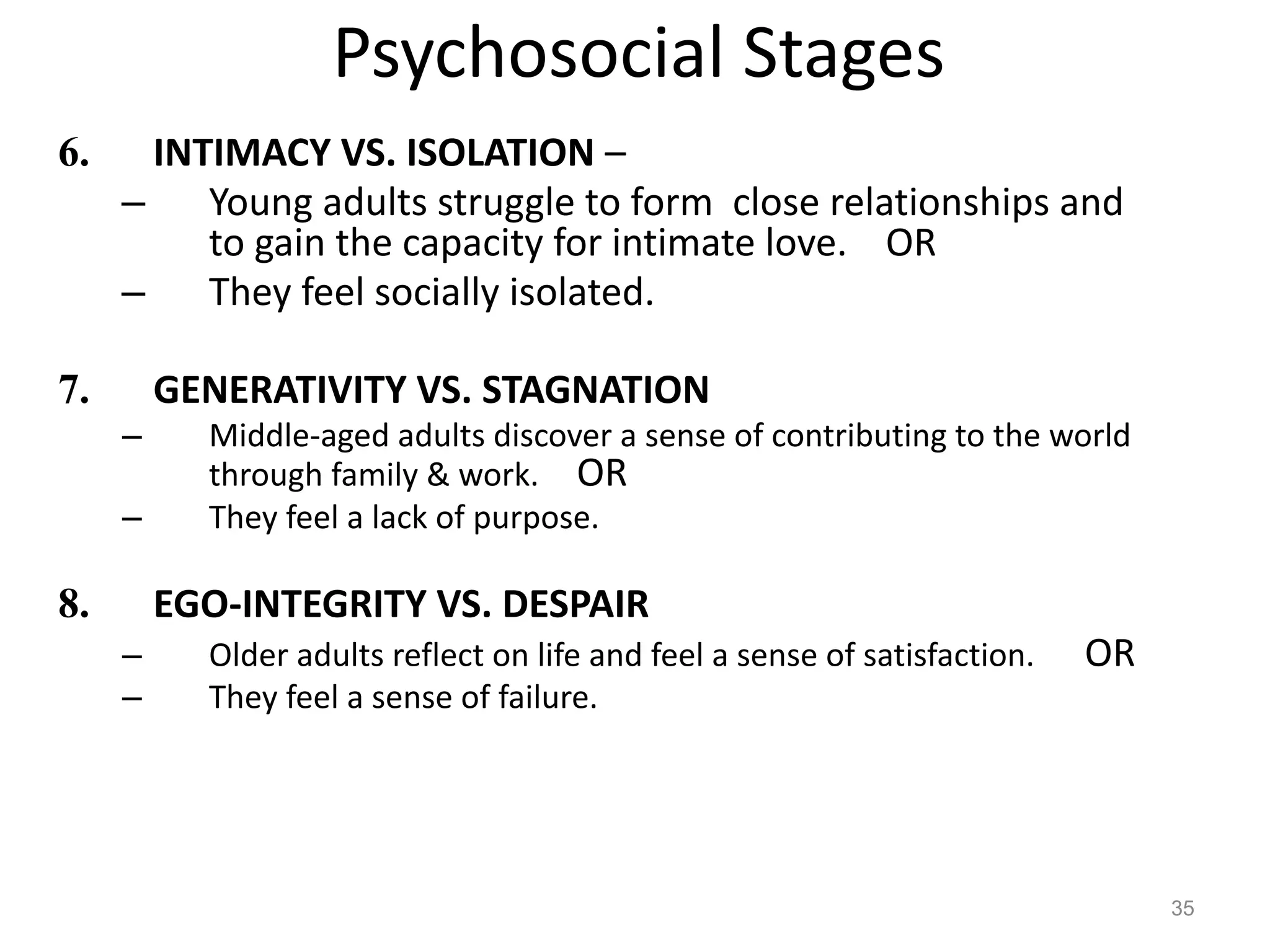
1) Development across the lifespan involves biological, cognitive, and social changes from conception through old age.
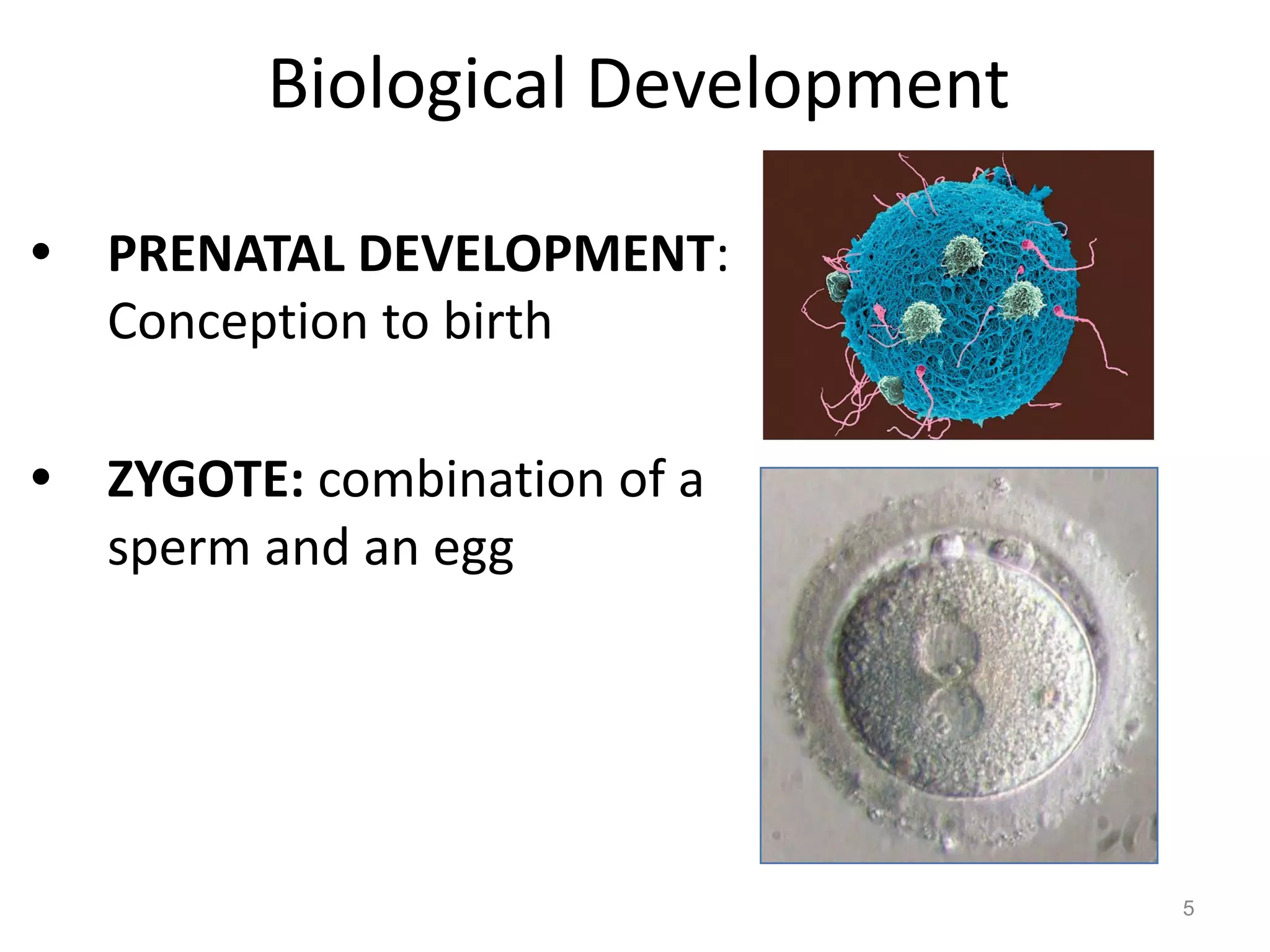
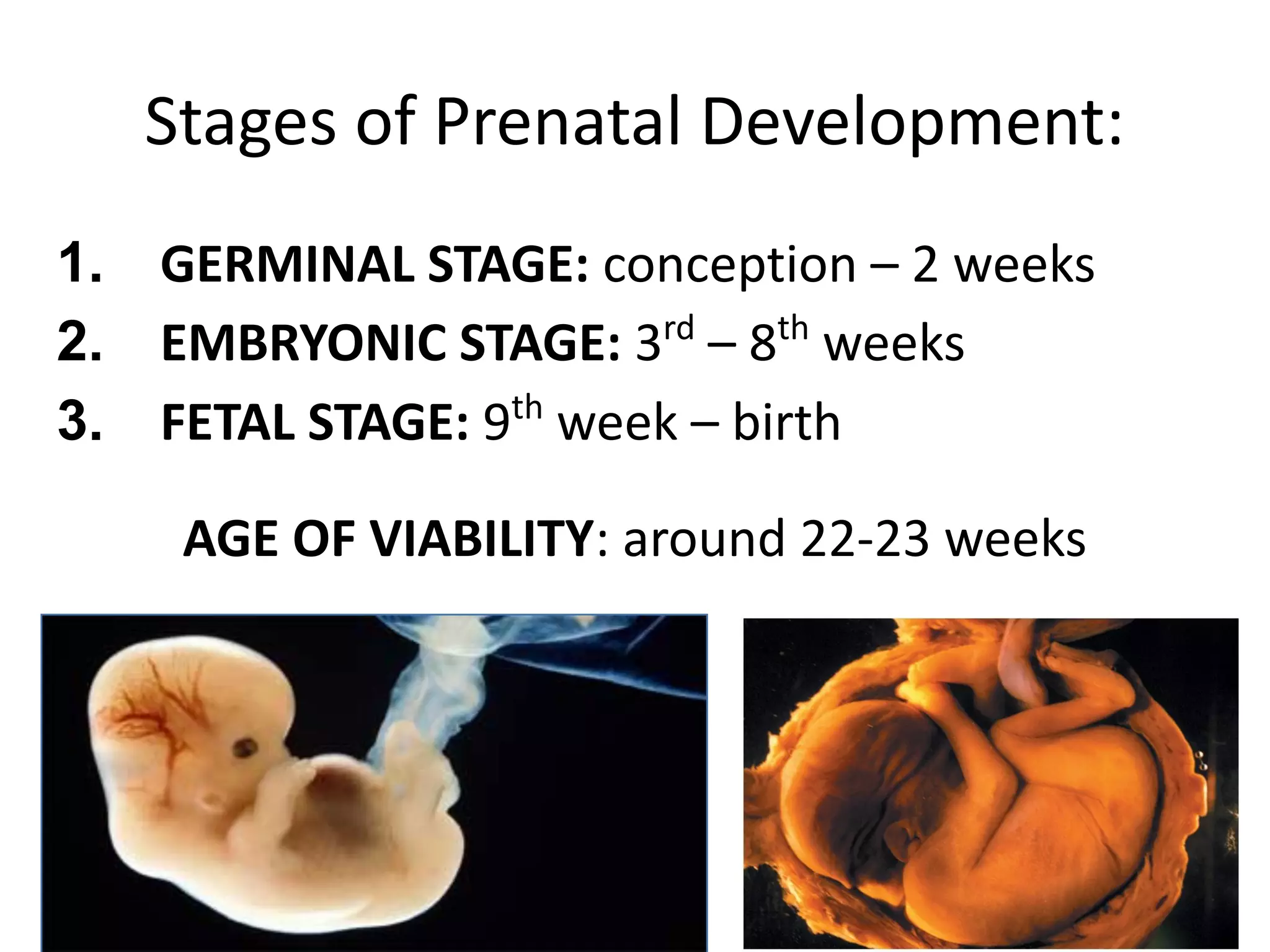
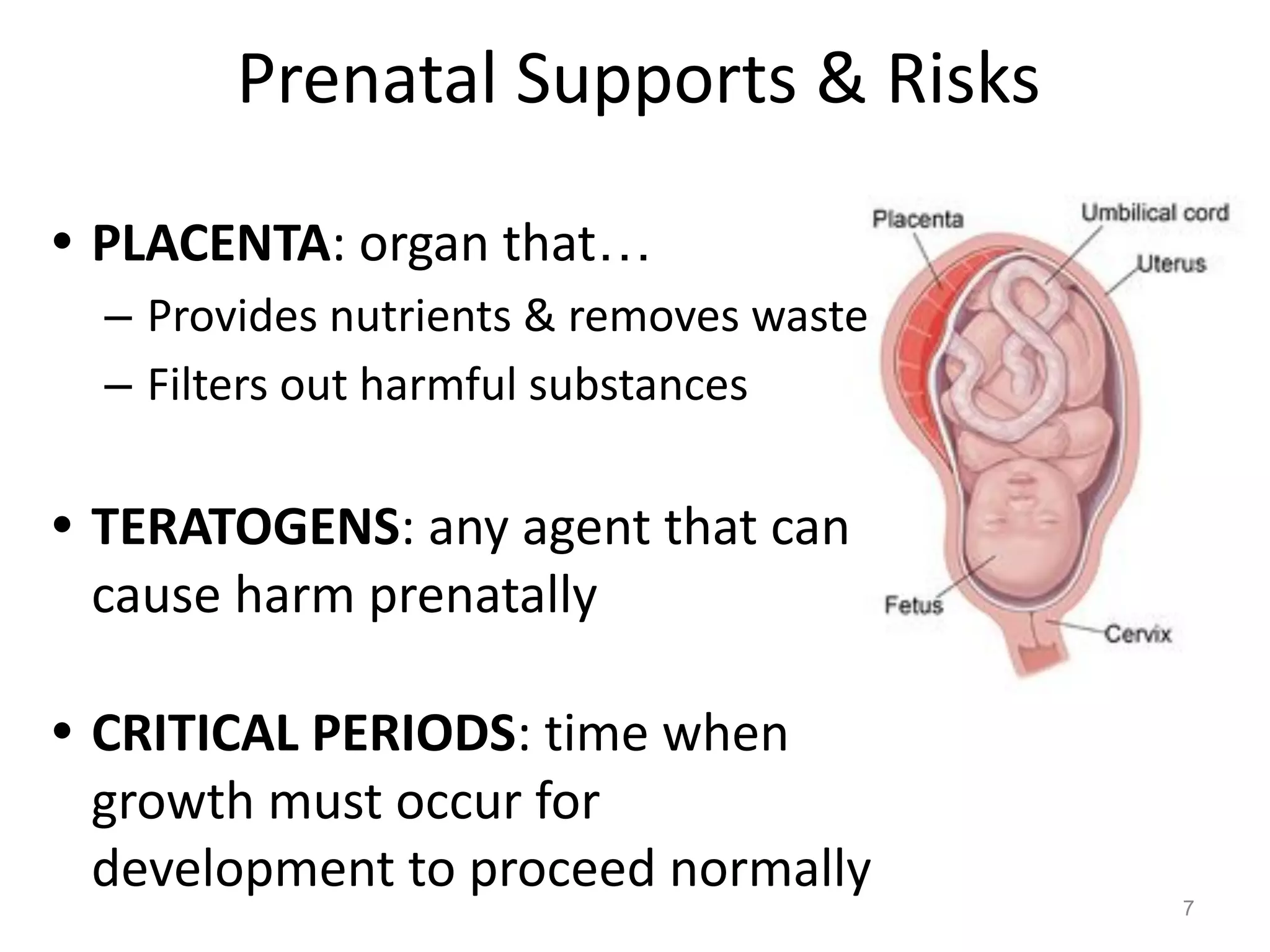
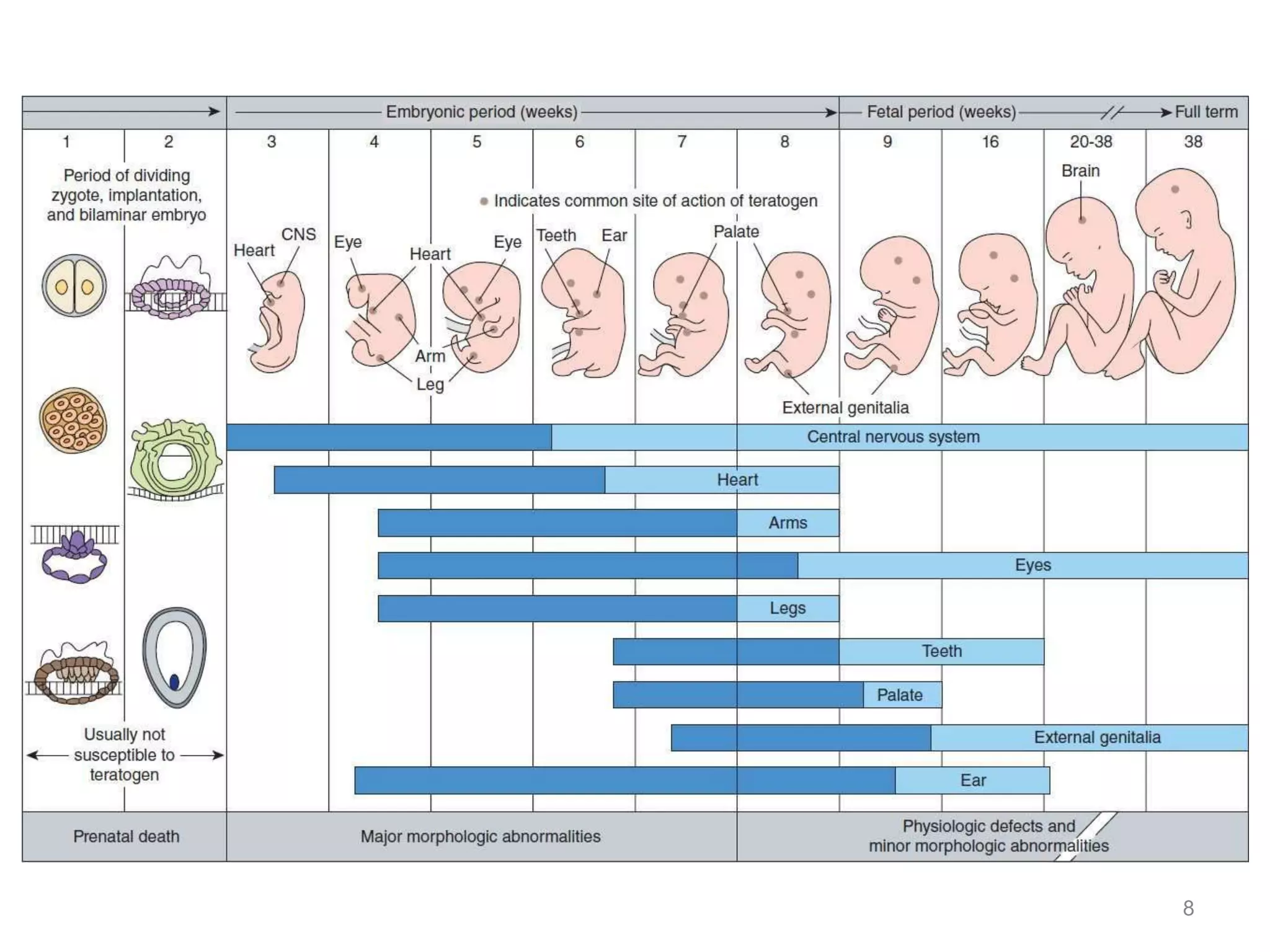
2) Prenatal development proceeds through germinal, embryonic, and fetal stages, with the placenta providing nutrients and filtering substances and certain drugs/illnesses posing risks.
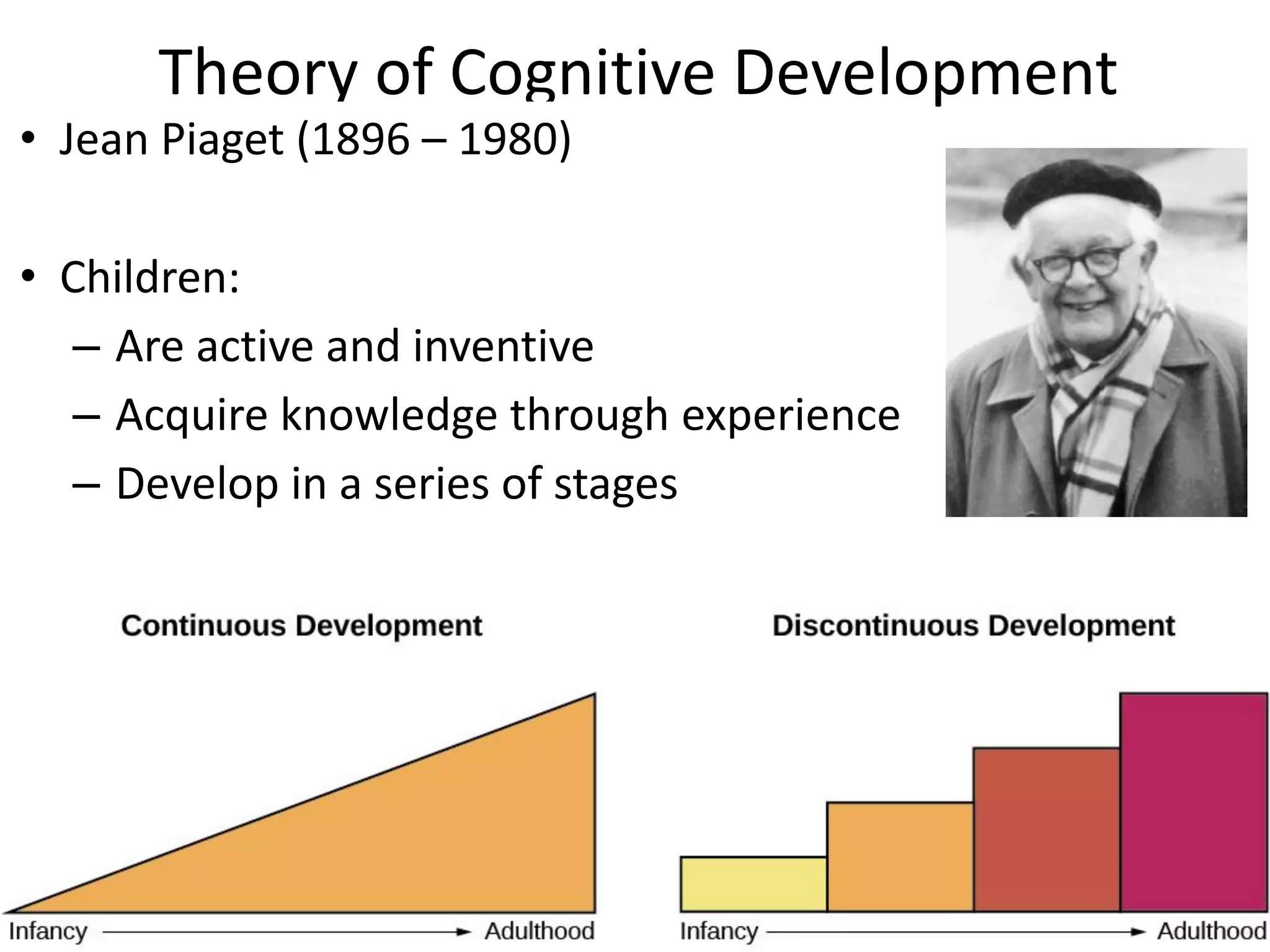
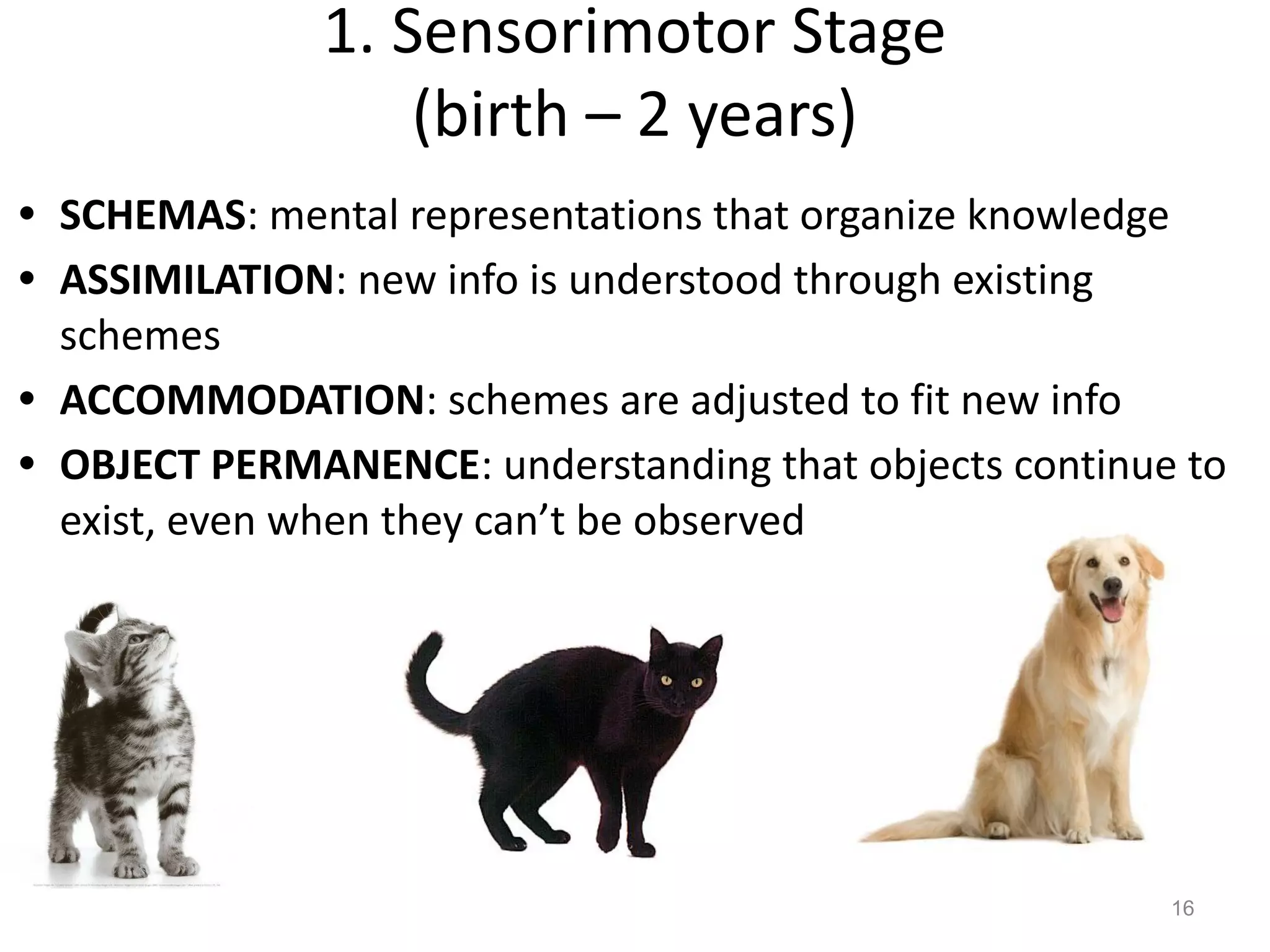
3) Jean Piaget's theory of cognitive development outlined four stages from sensorimotor to formal operations, with knowledge acquired through schemas and accommodation/assimilation.