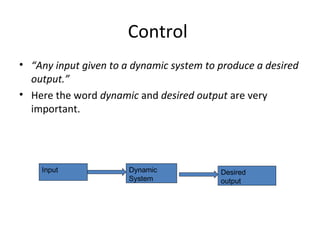
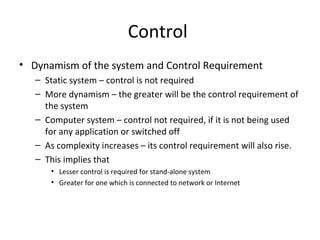
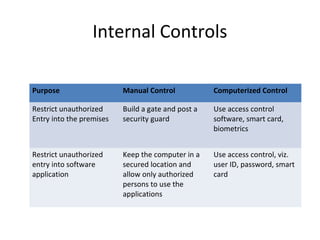
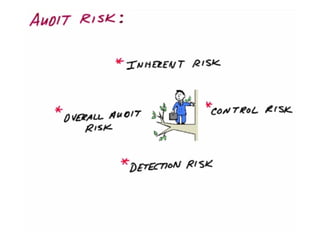
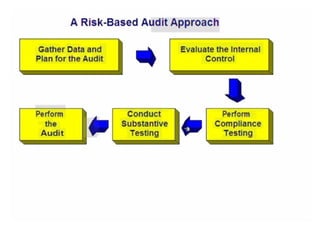
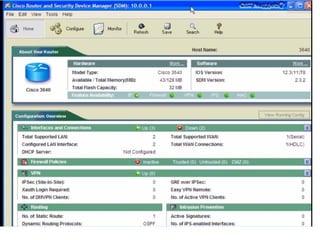
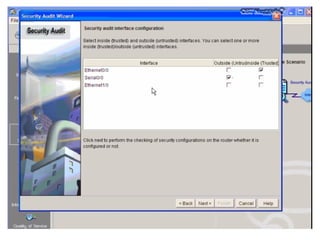
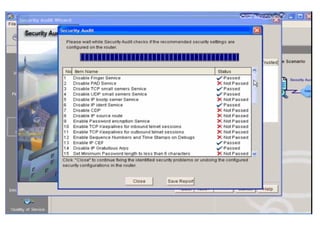
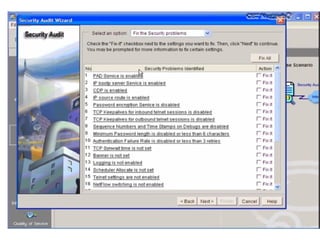
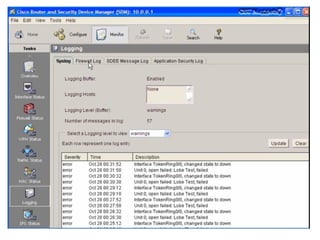
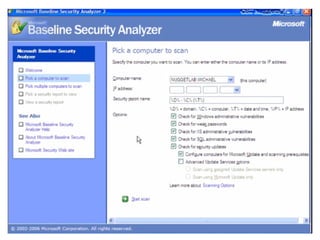
This document discusses internal controls and information system (IS) audits. It defines control as any input given to a dynamic system to produce a desired output. The level of control required increases as a system becomes more dynamic and complex. Effective controls require understanding a system's dynamism so control measures can operate effectively. Controls should be focused on specific outputs and evaluated to provide further appropriate inputs. Internal controls aim to ensure business objectives are achieved and undesired risks prevented or detected and corrected through policies, procedures and organizational structure. Controls can be preventive, detective, or corrective and take both manual and automated forms depending on the environment.