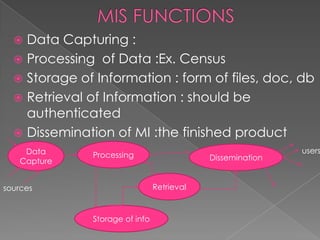
The document outlines key principles for developing a management information system (MIS). It states that an MIS should take a system approach by considering interrelated subsystems, be management-oriented by meeting top-down business needs, and be need-based by providing information to different management levels. An MIS also needs to account for exceptions, future needs, and integrate different functions like production scheduling. It should utilize common data flows, allow for long-term planning, and use subsystem concepts to reduce complexity.