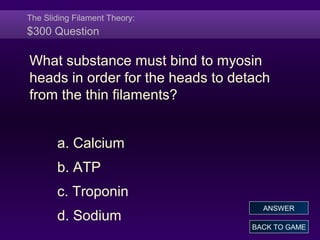
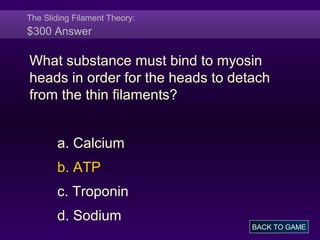
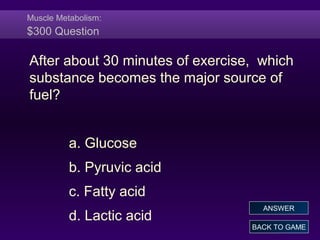
This document provides information about muscle tissues in the human body. It discusses the anatomy of skeletal muscle fibers and their organization into fascicles. It describes the sliding filament theory of muscle contraction, how calcium ions trigger the interaction of actin and myosin filaments. It also covers muscle metabolism and the different pathways that generate ATP during muscle contraction. The document concludes with characteristics of smooth muscle fibers and how they contract through calcium binding to calmodulin rather than troponin.