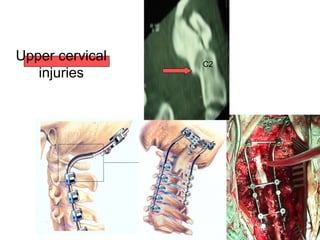
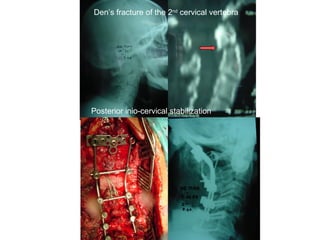
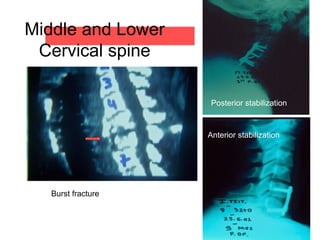
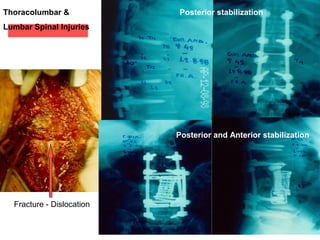
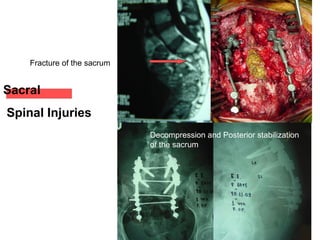
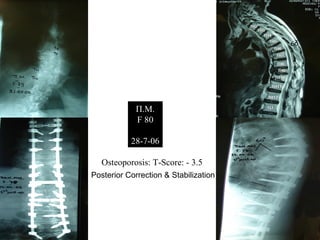
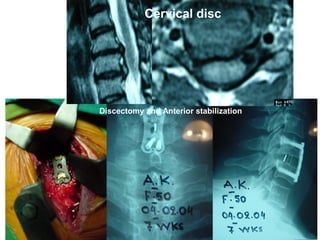
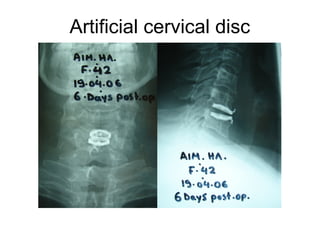
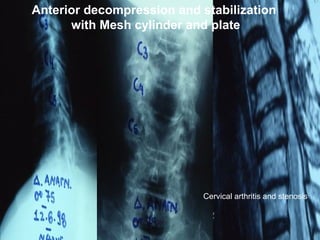
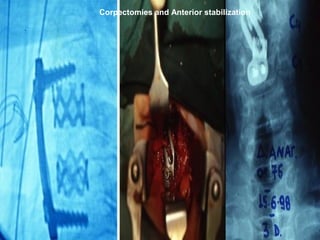
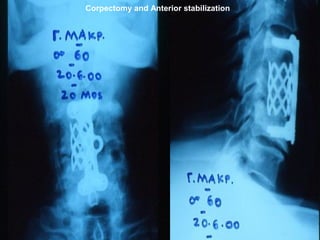
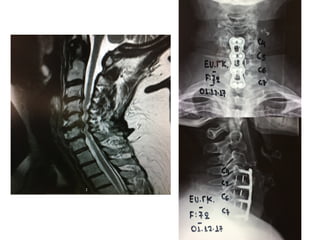
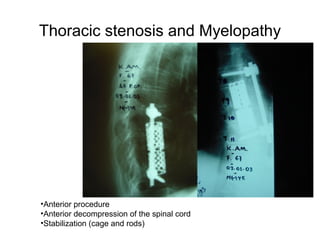
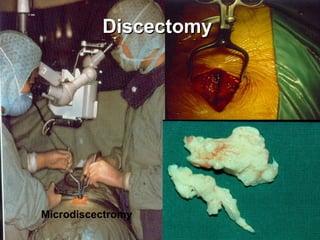
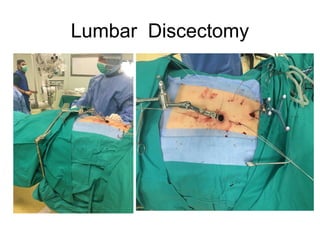
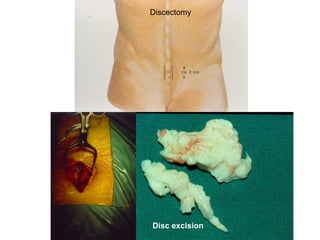
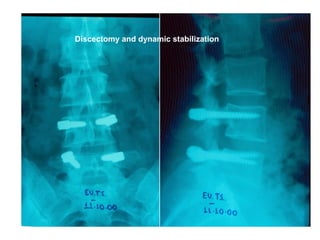
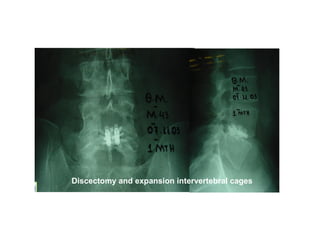
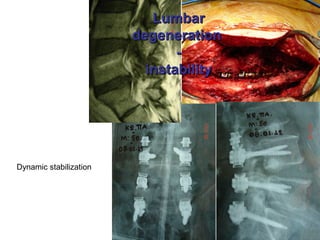
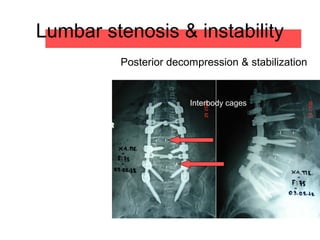
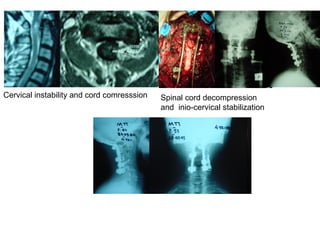
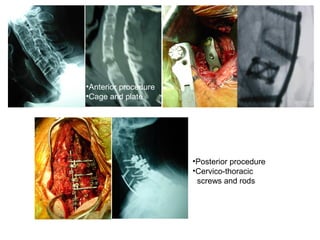
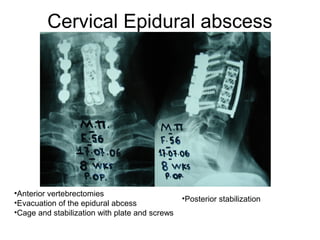
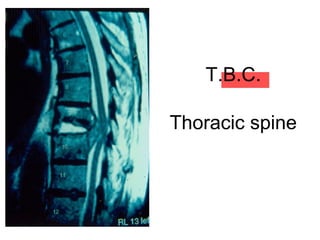
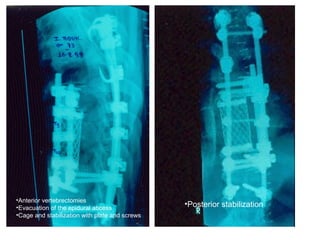
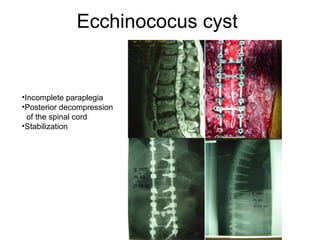
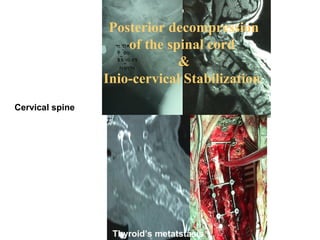
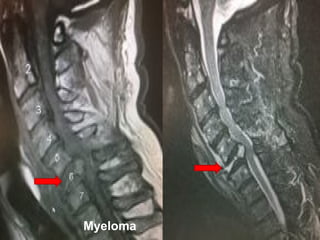
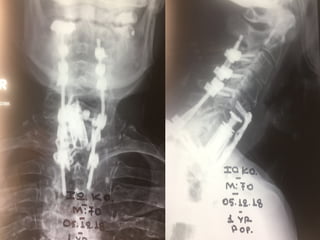
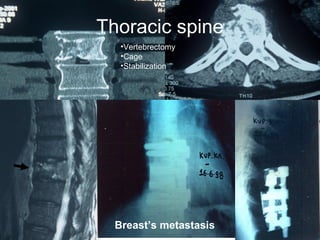
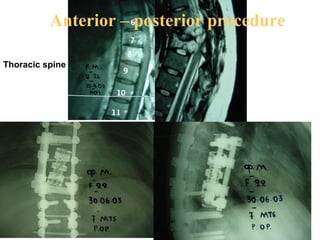
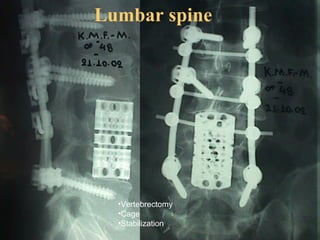
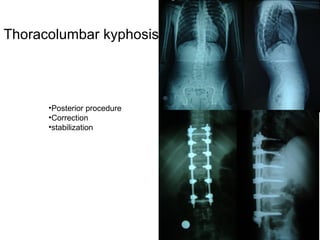
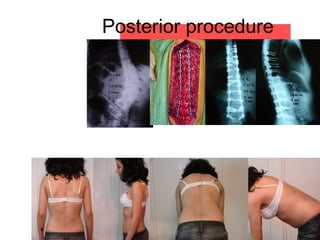
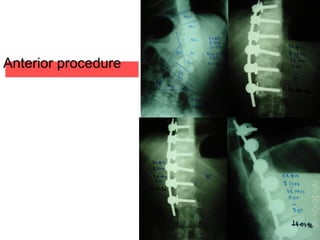
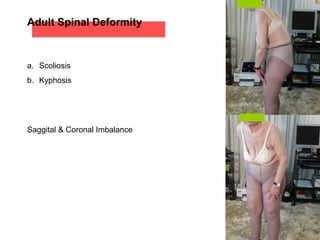
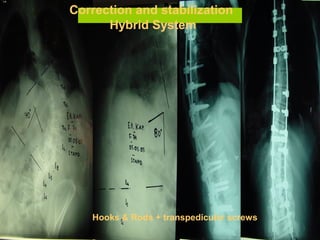
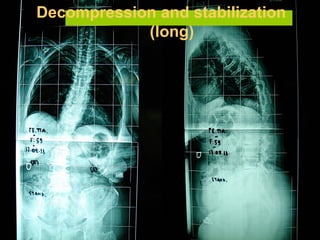
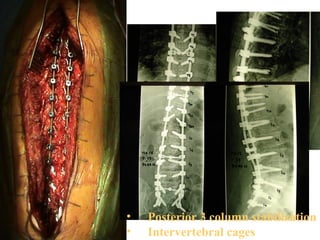
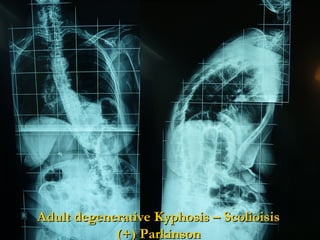
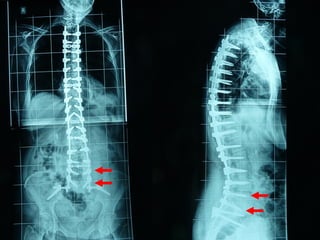
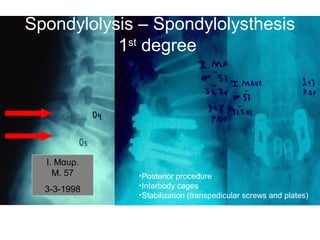
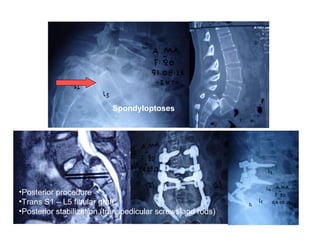
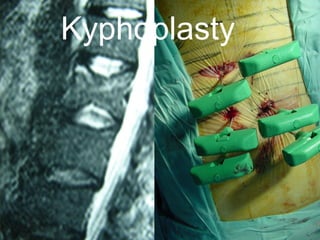
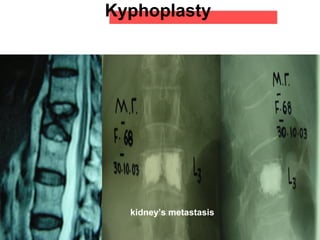
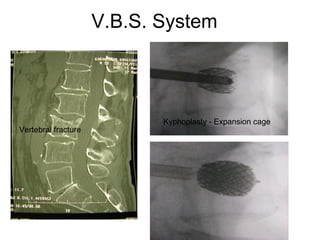
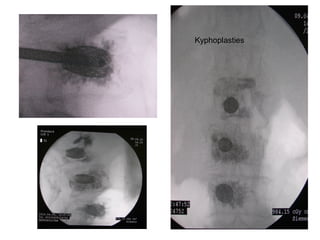
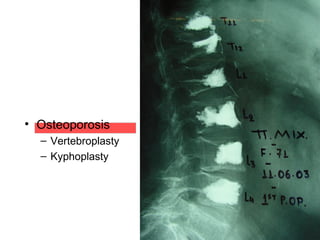
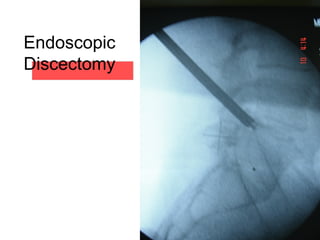
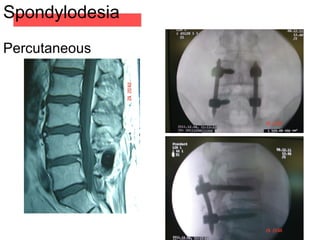
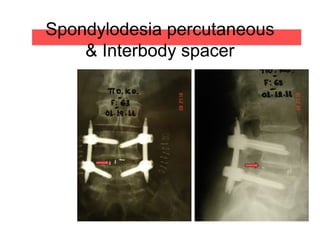
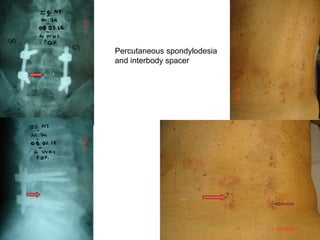
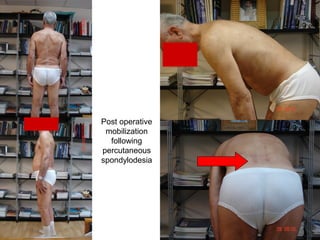
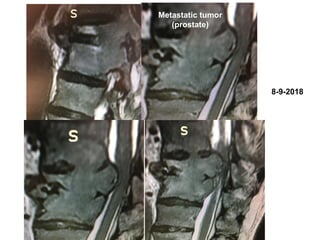
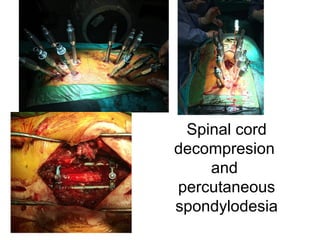
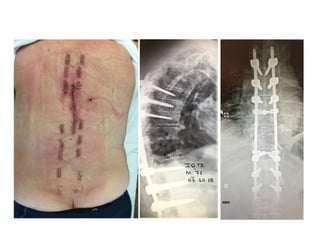
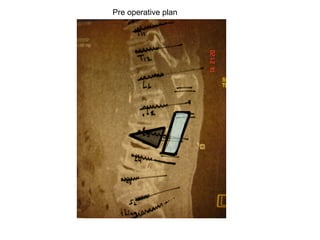
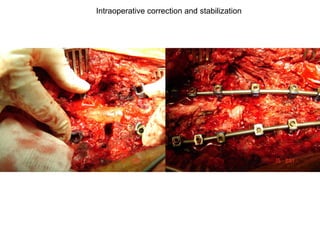
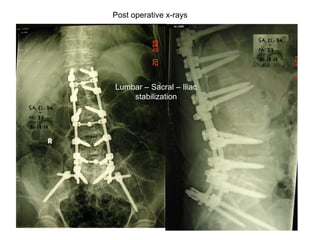
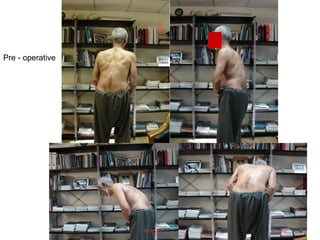
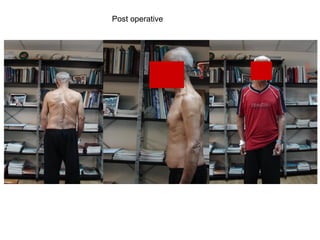
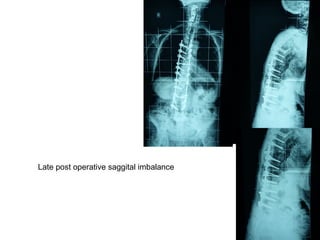
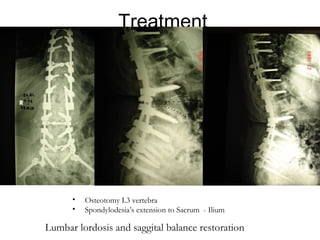
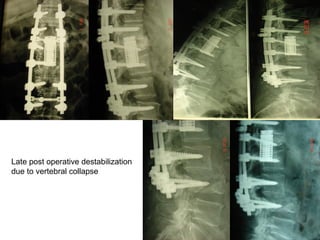
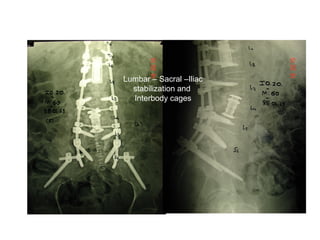
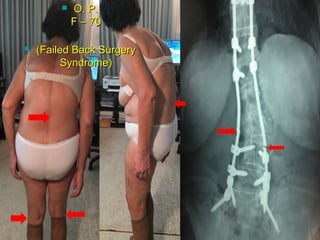
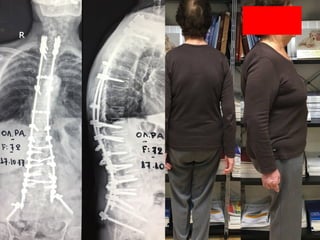
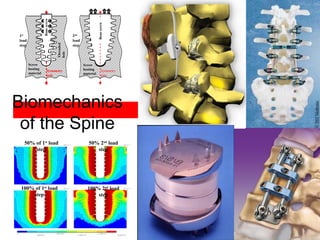
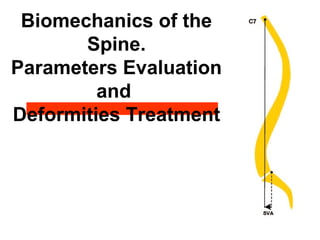
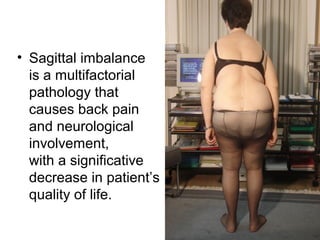
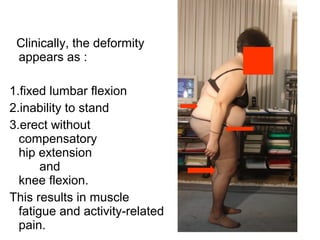
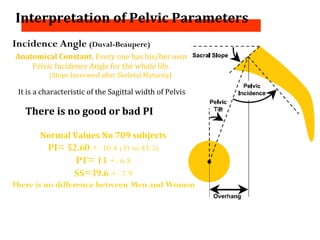
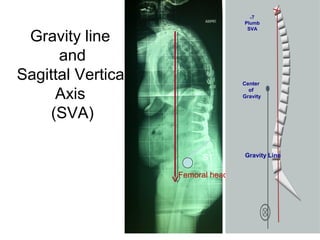
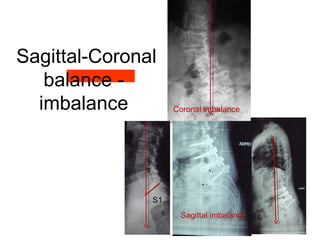
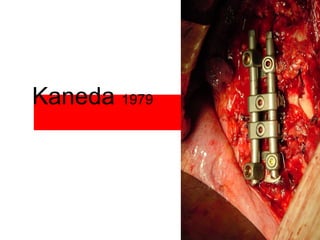
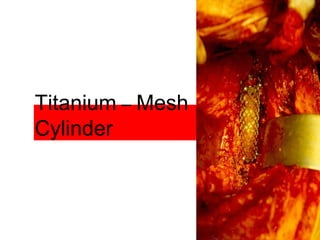
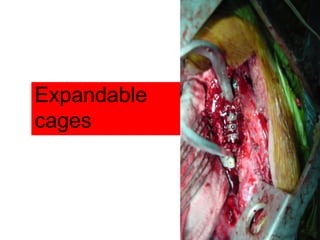
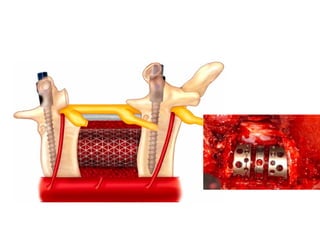
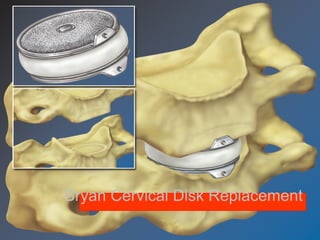
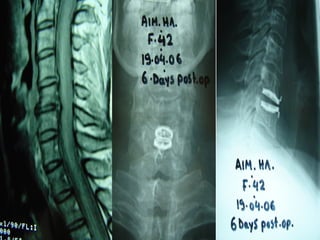
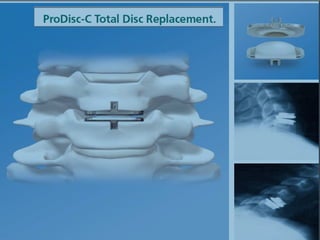
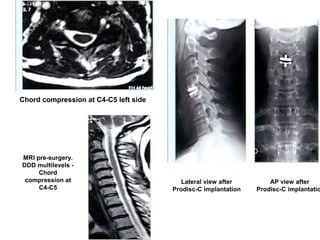
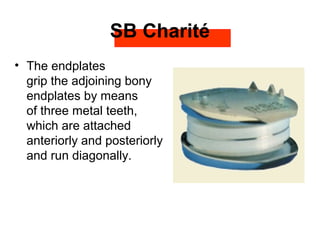
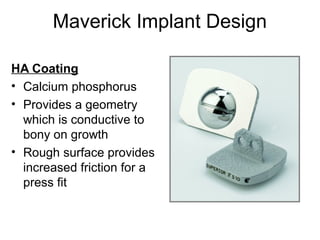
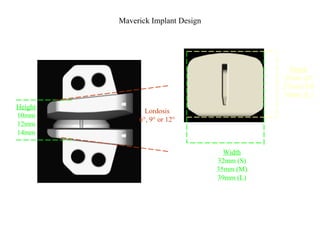
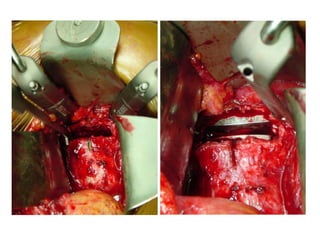
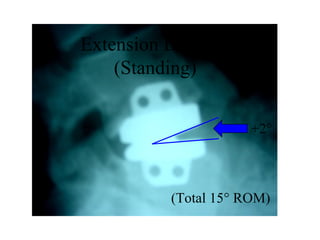
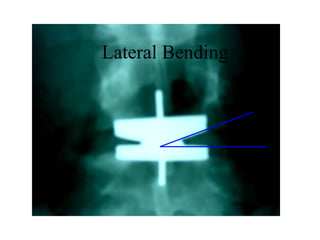
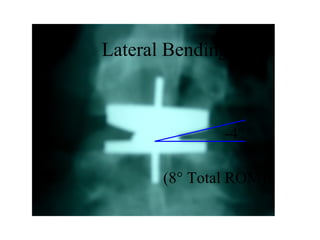
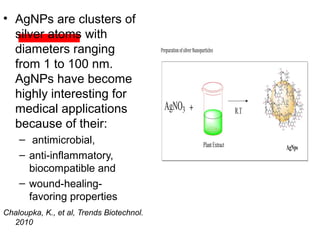
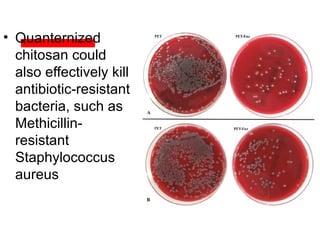
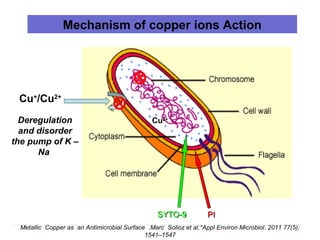
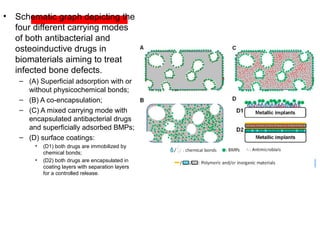
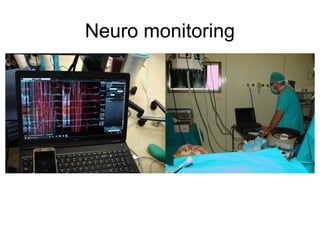
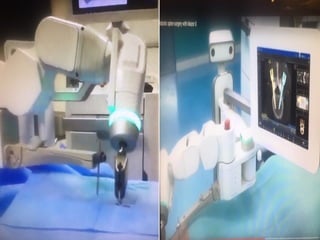
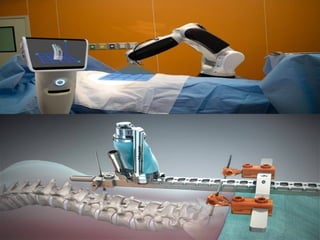
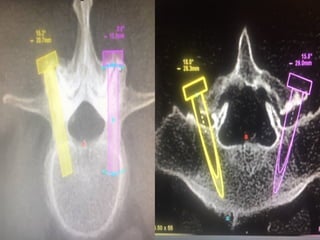
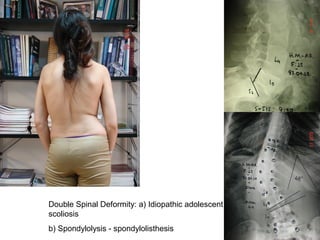
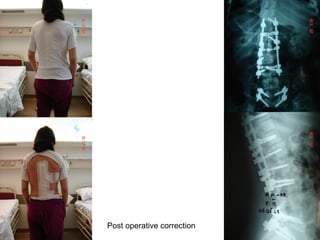
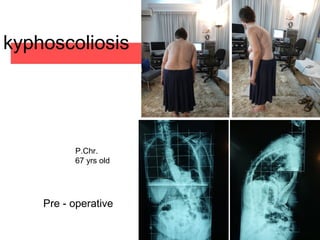
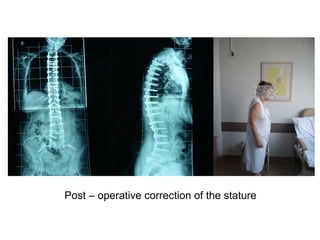
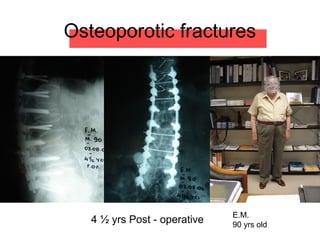
The document details various spinal surgeries performed by Professor George Sapkas, focusing on orthopedic disorders, techniques, and conditions treated, including degenerative diseases, infections, tumors, and deformities. It emphasizes advancements in minimally invasive surgery and innovations in surgical techniques, such as the use of bioengineering and nanotechnology. Additionally, it discusses patient outcomes and the importance of surgical training and support in improving quality of life for patients with spinal issues.