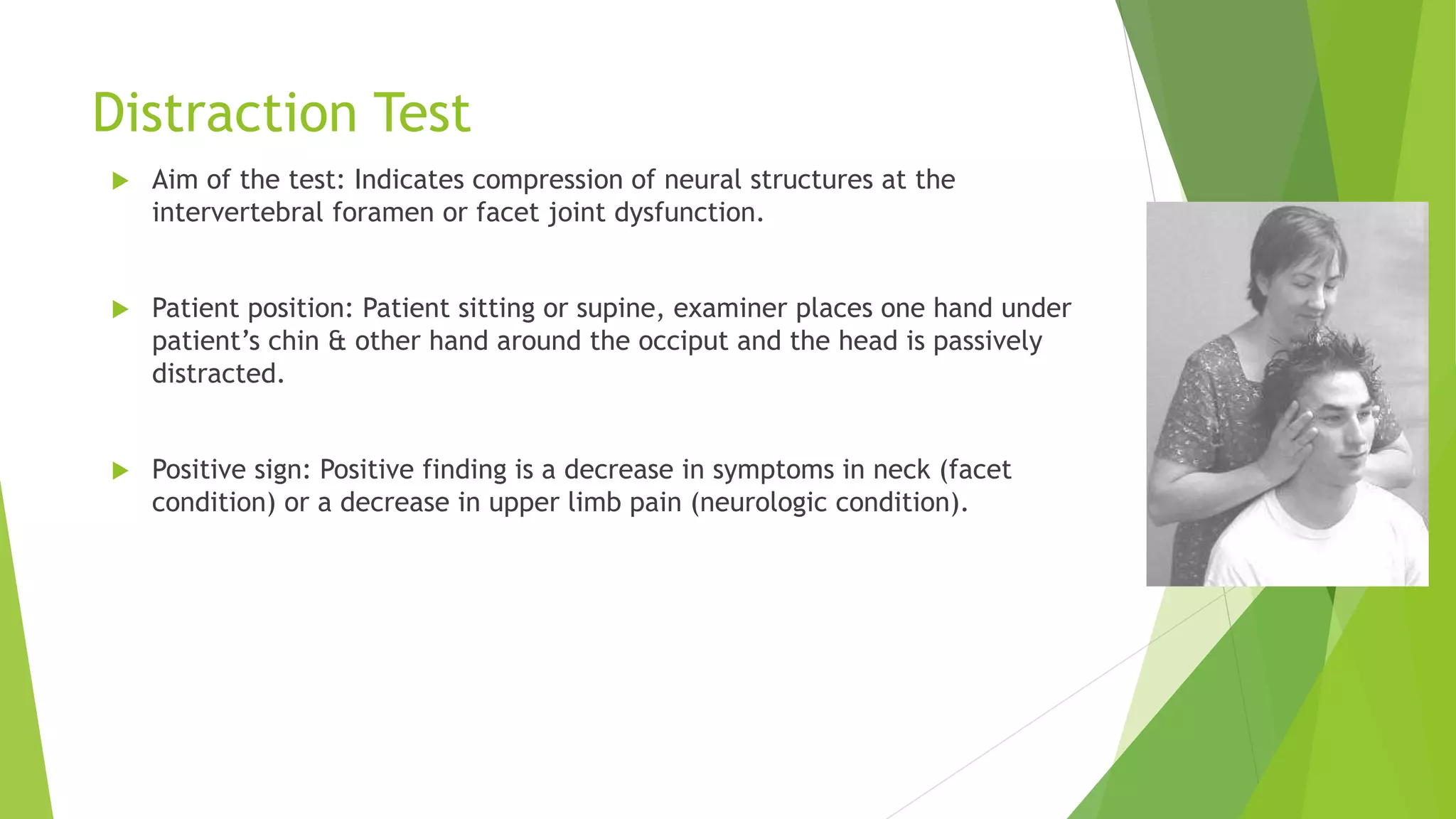
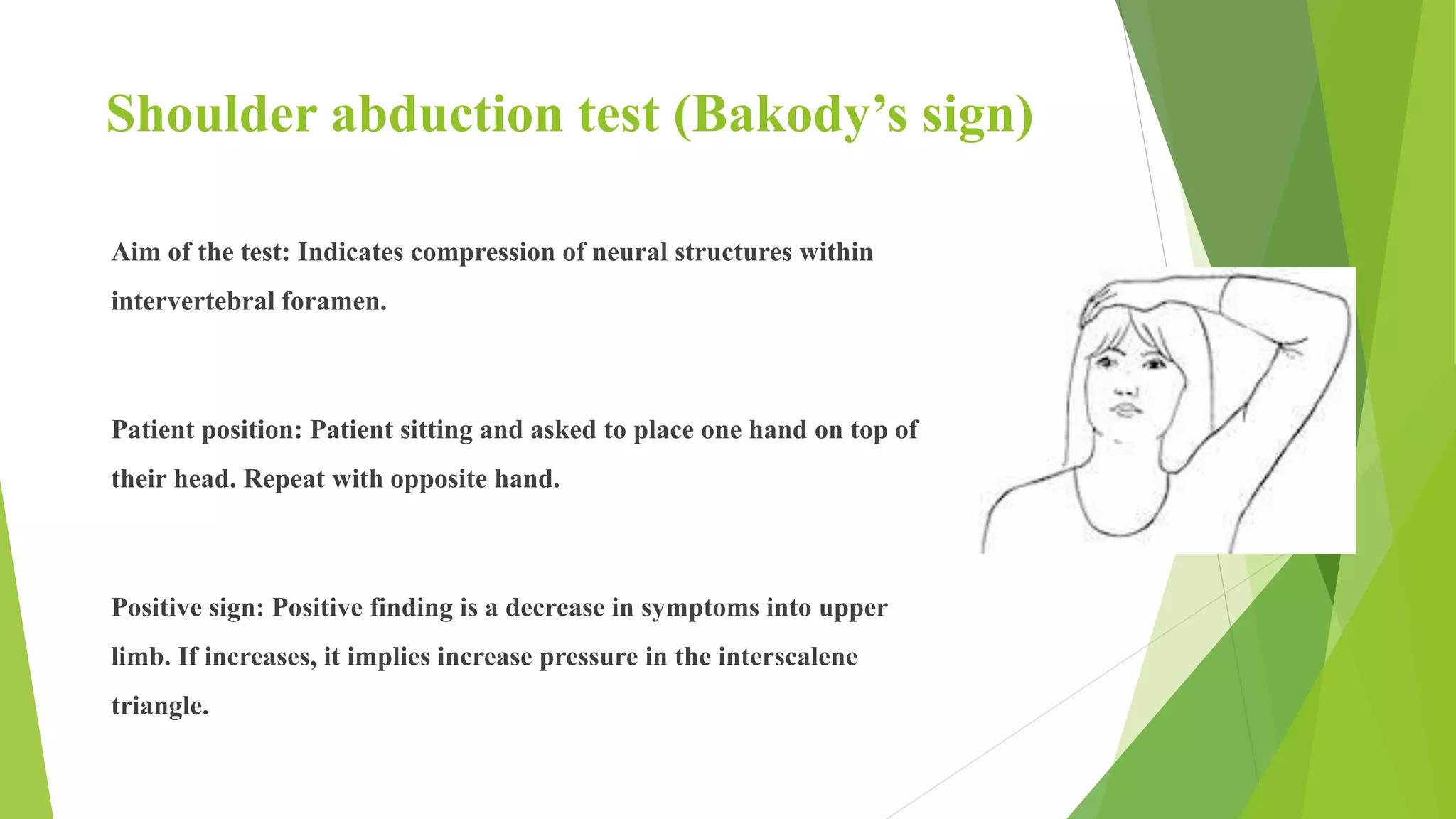
This document describes several orthopedic tests used to evaluate the cervical spine:
1) Cervical compression, distraction, and shoulder abduction tests evaluate nerve root dysfunction by reproducing symptoms. Positive findings include pain or paresthesia in specific dermatomal patterns.
2) Cervical flexion, rotation, and Soto Hall tests evaluate joint dysfunction by stressing cervical structures. Positive findings include decreased range of motion or reproduction of symptoms.
3) Deep neck flexor endurance and Jull's tests evaluate muscle endurance by having patients maintain chin retraction positions. Failure indicates weak deep neck flexors.
4) Resisted muscle and shoulder depression tests evaluate strains by inducing isometric contractions