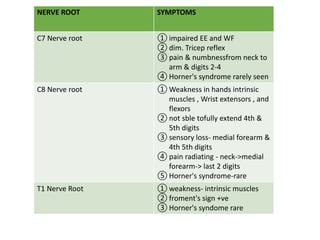
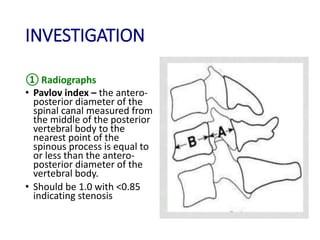
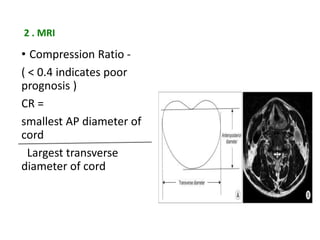
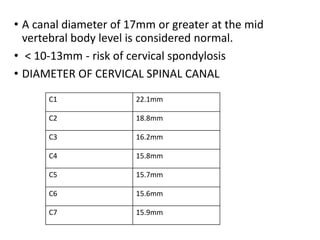
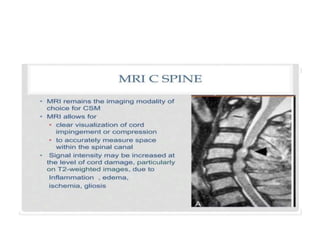
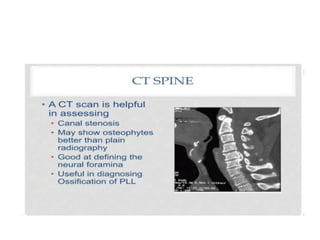
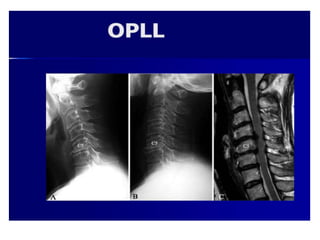
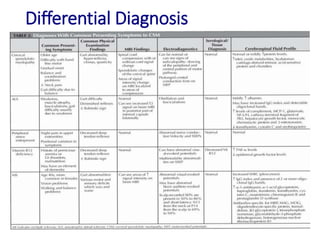
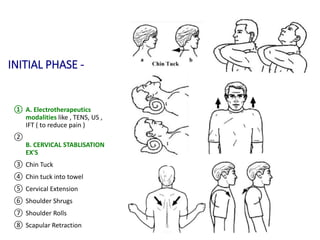
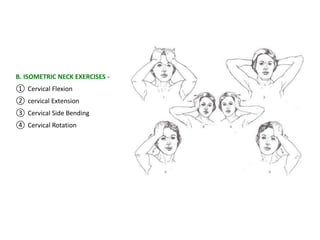
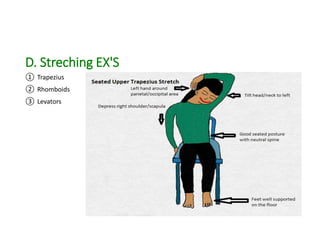
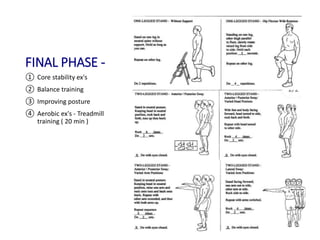
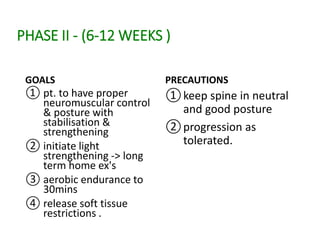
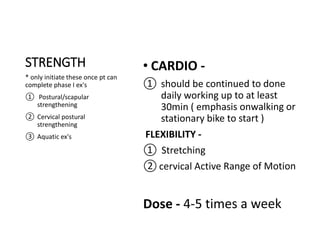
Cervical myelopathy is a neurological impairment caused by compression of the cervical spinal cord, most commonly due to degenerative changes like spondylosis. It presents with neck stiffness, leg weakness, gait abnormalities, and clumsy hands. Physiotherapy management includes electrotherapeutic modalities to reduce pain, cervical stabilization exercises, isometric neck exercises, stretching, and progressive resistance exercises. The goals are to relieve pain, improve function, prevent further neurological deficits, and improve existing deficits. Surgery or immobilization may also be considered depending on severity.