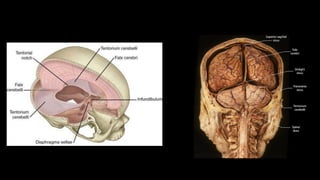
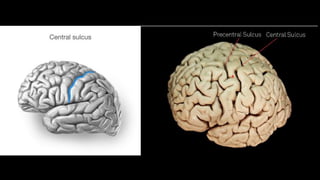
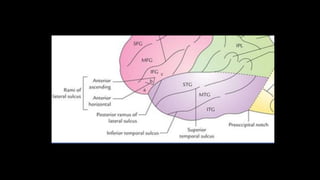
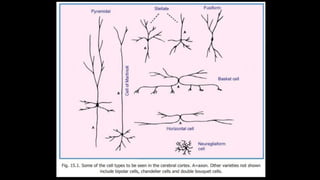
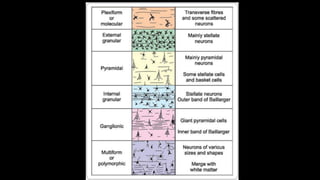
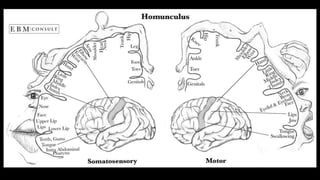
The cerebrum is the largest part of the human brain and consists of two hemispheres separated by the longitudinal cerebral fissure. Each hemisphere has an outer layer of grey matter called the cerebral cortex and an inner mass of white matter. The cortex is highly folded to fit within the skull, forming convolutions called gyri separated by sulci. The cortex can be divided into four lobes - frontal, parietal, temporal and occipital - based on sulci and gyri. Within each lobe are functional areas including motor, sensory, and association areas that control voluntary movement, process sensation, and integrate sensory information respectively.