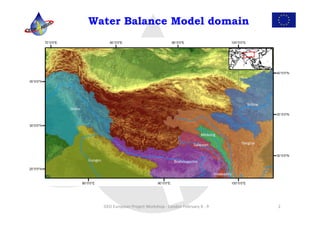
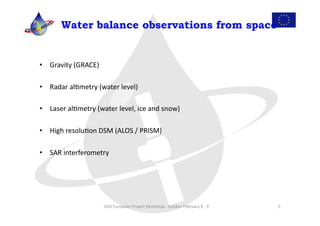
This document discusses water resources, agriculture, ecosystems, and biodiversity as they relate to climate change. It summarizes several European projects focused on using observations from space and on the ground to monitor water balances, adapt to climate change impacts, and ensure food and water security for populations that rely on water from glacial regions in Asia. Opportunities for collaboration between these projects are also discussed.