1. The document discusses cell division through the processes of mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis produces two identical daughter cells from one parent cell, while meiosis produces gametes with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell.
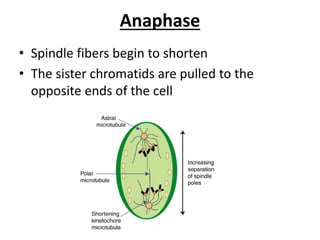
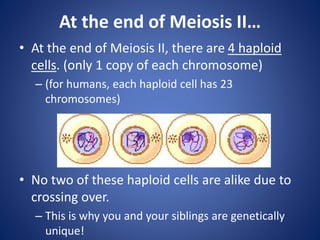
2. It provides animations and descriptions of the stages of interphase, mitosis, and meiosis. This includes DNA replication in S phase, separation of chromosomes in anaphase, and formation of four haploid daughter cells in meiosis II.
3. Meiosis introduces genetic variation through independent assortment of homologous chromosomes and crossing over, allowing offspring to receive unique combinations of chromosomes from each parent.